《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(口译)Module 5 Consecutive interpreting
Module5 Consecutive interpreting (500 minutes) 教学内容 指导思想 交替传译 onsecutive interpreting describes a process by which a speake 交替传译 须知 delivers a statement that is followed immediately by an interprete 是口译中 (20分钟) rendering this message in another language. 非常重要 This type of interpreting is most often used in small-group settings 的·部 ngs,interviews,public forums andinvarious legal po 了2 such as trials,dep sitions,hearings,arbitrations,and meetings 交传的 between clients and attorneys. 作机制、 Once the speaker pauses or has conveyed a significant amount of 工作特点 information.the interpreter.who might take notes during the stream of 可以使初初 speech in order to facilitate the recollection of information,will 学老少击 弯路。 Consecutive interpretation is rendered as "short CI"or "long CI" In short CI,the interpreter relies on memory,each message segment being brief enough to memorize In long CL the interpreter takes notes of the me sage to aid renderins before the interpretation is effected,depending upon the subject,its complexity,and the purpose of the interpretation. Highly experienced consecutive interpreters will interpret phrase-by-phrase.a process that is quite similar to simultaneous interpreting interpreters totranslat audience questions back to the speaker On occasion,document sight translation is required of the interprete during consecutive interpretation work.Sight translation combines interpretation and translation:the interpreter must render the source-language document to the target-language as if it were written in the target language.Sigh tion occurs usually,but no exclusively,in judicial and medical work. Consecutively-interpreted speeches,or segments of them,tend to be short.Fifty years ago,the Cl interpreter would render speeches of 20 or 30 minutes:today.10 or 15 minutes is considered too long particularly since audiences usually prefer not to sit though 20 minutes of speech they cannot understand. Often,if not previously advised.the source-language speaker is unaware that he or she may speak more than a single sentence before the CI interpretation is rendered and might stop after each sentence to await its target-language rendering etimes,however.depending upon the setting or subject matte and upon the interpreter's capacity to memorize,the interpreter may ask the speaker to pause after each sentence or after each clause. Sentence-by-sentence interpreting requires less memorization and therefore lower likelihood for omissions,yet its disadvantage is in the
Module 5 Consecutive interpreting (500 minutes) 教学内容 指导思想 交替传译 须知 (20 分钟) Consecutive interpreting describes a process by which a speaker delivers a statement that is followed immediately by an interpreter rendering this message in another language. This type of interpreting is most often used in small-group settings, meetings, interviews, public forums, and in various legal proceedings, such as trials, depositions, hearings, arbitrations, and meetings between clients and attorneys. Once the speaker pauses or has conveyed a significant amount of information, the interpreter, who might take notes during the stream of speech in order to facilitate the recollection of information, will deliver the translation in the target language. Consecutive interpretation is rendered as "short CI" or "long CI". In short CI, the interpreter relies on memory, each message segment being brief enough to memorize. In long CI, the interpreter takes notes of the message to aid rendering long passages. These informal divisions are established with the client before the interpretation is effected, depending upon the subject, its complexity, and the purpose of the interpretation. Highly experienced consecutive interpreters will interpret phrase-by-phrase, a process that is quite similar to simultaneous interpreting. Consecutive interpreters may also be required to translate audience questions back to the speaker. On occasion, document sight translation is required of the interpreter during consecutive interpretation work. Sight translation combines interpretation and translation; the interpreter must render the source-language document to the target-language as if it were written in the target language. Sight translation occurs usually, but not exclusively, in judicial and medical work. Consecutively-interpreted speeches, or segments of them, tend to be short. Fifty years ago, the CI interpreter would render speeches of 20 or 30 minutes; today, 10 or 15 minutes is considered too long, particularly since audiences usually prefer not to sit through 20 minutes of speech they cannot understand. Often, if not previously advised, the source-language speaker is unaware that he or she may speak more than a single sentence before the CI interpretation is rendered and might stop after each sentence to await its target-language rendering. Sometimes, however, depending upon the setting or subject matter, and upon the interpreter's capacity to memorize, the interpreter may ask the speaker to pause after each sentence or after each clause. Sentence-by-sentence interpreting requires less memorization and therefore lower likelihood for omissions, yet its disadvantage is in the 交替传译 是口译中 非常重要 的一部 分,了解 交传的工 作机制、 工作特点 可以使初 学者少走 弯路

interpreter's not having heard the entire speech or its gist and the age is r both beca of lack o 0 text and because of interrupted delivery (for example,imagine joke told in bits and pieces.with breaks for translation in between). This method is often used in rendering speeches,depositions,recorded Full (ie.,unbroken)consecutive interpreting of whole thoughts allow for the full meaning of the source-language message to be understood before the interpreter renders it in the target language.This affords a truer,more accurate,and more accessible interpretation than does Are additional interpreters necessary for consecutive settings? Although consecutive settings do not require the attendance of more than one interpreter.in meetings where mistakes cannot be tolerated both parties may elect to have an interpreter each for quality assurance.These types on consecutive with linguists are very common for meetings of heads of state What are the downsides of consecutive interpreting? As the flow of conversation during meeting that are dependent on consecutive interpretations interrupted by the linguist rendering the content in another language,meetings that utilize consecutive interpretations tend toproceed slower. numbers 小数、分数、百分数 数字口译 (120分小数点前面是零,英语一般有三种读法 是口译难 钟) 小数点后面的数字 般都是一个一个单独读出来。 在一种语 比如3.14 言内对有 分数中的分子用基数词,分母用序数词:如果分子大于1,分母就 些学生而 得用复数:带分数的读法: 言传达都 百分数中的%,重音在第二个音节上 有闲难, 千分之37怎么读?百万分之8呢? 要在两利 per thousand,per million,out of sixty thousand 语言之间 “六成”怎么表达? 转换更需 练习1:分别用中文和英文读出下列数字,熟练准确。 要好好练 0.08,235.18,4,%,6,三又三分之 习。 1706.37.1/500000.7成 2:准确记录听到的数字,并口译。(汉、英) 基数 汉语数字是四位一段,英语数字是三位一段。 百 千 十万 百万 千万
interpreter's not having heard the entire speech or its gist, and the overall message is sometimes harder to render both because of lack of context and because of interrupted delivery (for example, imagine a joke told in bits and pieces, with breaks for translation in between). This method is often used in rendering speeches, depositions, recorded statements, court witness testimony, and medical and job interviews, but it is usually best to complete a whole idea before it is interpreted. What is the advantage of full consecutive interpreting? Full (i.e., unbroken) consecutive interpreting of whole thoughts allows for the full meaning of the source-language message to be understood before the interpreter renders it in the target language. This affords a truer, more accurate, and more accessible interpretation than does simultaneous interpretation. Are additional interpreters necessary for consecutive settings? Although consecutive settings do not require the attendance of more than one interpreter, in meetings where mistakes cannot be tolerated both parties may elect to have an interpreter each for quality assurance. These types on consecutive interpretations with two linguists are very common for meetings of heads of state. What are the downsides of consecutive interpreting? As the flow of conversation during meeting that are dependent on consecutive interpretations interrupted by the linguist rendering the content in another language, meetings that utilize consecutive interpretations tend to proceed slower. numbers ( 120 分 钟) 小数、分数、百分数 小数点前面是零,英语一般有三种读法 zero point; oh point; naught point 小数点后面的数字一般都是一个一个单独读出来, 比如 3.14 分数中的分子用基数词,分母用序数词;如果分子大于 1,分母就 得用复数;带分数的读法: 百分数中的%,重音在第二个音节上 千分之 37 怎么读?百万分之 8 呢? per thousand, per million, out of sixty thousand “六成”怎么表达? 练习 1:分别用中文和英文读出下列数字,熟练准确。 0.08,235.18,¼,⅔,½,三又三分之一 17%,37 ‰,1/500 000,7 成 练习 2:准确记录听到的数字,并口译。(汉、英) 基数 汉语数字是四位一段,英语数字是三位一段。 个 十 百 千 万 十万 百万 千万 数字口译 是口译难 点之一, 在一种语 言内对有 些学生而 言传达都 有困难, 要在两种 语言之间 转换更需 要好好练 习

亿 十亿 百亿 千亿 万亿 十万亿 百万亿 千万亿 one ten hundred thousand 10 thousand 100 thousand million 10 million 100 million billion 10 billion 100 billion 10 trillion 100 trillion 翻译较大基数的方法 上标下标法 英文的标注在数字下方,符合国际惯例:中文的标注在数字上方 练习3:熟练朗读较大基数 3.697.854,165, 405654117054 36763773366 43533455, 202784125 听数字,准确记录。(10汉10英) 翻译较大基数的方法: 2.缺位补 三亿零三百六十万三百零 303,60'0,302 one hundred billion thirty-six million seven thousand and forty-one 100.036.007.041 你将听到一组含零的数字,请准确记录并口译。(5汉5英) 3.公式对应法(练习5汉5英) 一万=ten thousand 十万=one hundred thousand -百万=one million ,千万=ten million 一亿 =one hundred million 十亿=one billion -百亿=ten billion 一千亿=one hundred billion 一万亿=one trillion 十万亿 翻译较大基数的方法 4.就近对应法 20万 0.2 million 850万 8.5 million 23.8 million 2380万 0.56 trillion
亿 十亿 百亿 千亿 万亿 十万亿 百万亿 千万亿 one ten hundred thousand 10 thousand 100 thousand million 10 million 100 million billion 10 billion 100 billion trillion 10 trillion 100 trillion 翻译较大基数的方法: 1. 上标下标法 英文的标注在数字下方,符合国际惯例;中文的标注在数字上方 练习 3: 熟练朗读较大基数 3,6’97,85’4,165, 405654117054, 36763773366, 43533455, 202784125 听数字,准确记录。(10 汉 10 英) 翻译较大基数的方法: 2. 缺位补零 三亿零三百六十万三百零二 3'03,60'0,302 one hundred billion thirty-six million seven thousand and forty-one 100,0'36, 00'7,041 你将听到一组含零的数字,请准确记录并口译。(5 汉 5 英) 3. 公式对应法 (练习 5 汉 5 英) 一万 = ten thousand 十万 = one hundred thousand 一百万 = one million 一千万 = ten million 一亿 = one hundred million 十亿 = one billion 一百亿 = ten billion 一千亿 = one hundred billion 一万亿 = one trillion 十万亿 = ten trillion 翻译较大基数的方法: 4. 就近对应法 20 万 0.2 million 850 万 8.5 million 23.8 million 2380 万 0.56 trillion
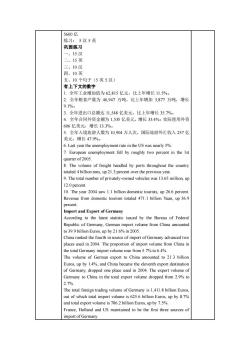
5600亿 5汉5英 一、15汉 二、15英 三、10汉 四、10英 、10个句子(6英5汉) 有上下文的数字 1.全年工业增加值为62,815亿元,比上年增长11.5%。 2.全年粮食产量为46,947万吨,比上年增加3,877万吨,增长 0105. 3.全年进出口总额达1,548亿美元,比上年增长35.7% 4.全年合同外资金额为1,535亿美元,增长33.4%:实际使用外资 606亿美元,增长13.3%。 5.全年入境旅游人数为10,904万人次,国际旅游外汇收入257亿 美元,增长47.9%。 6.Last year the unemployment rate in the US was nearly5%. 7.European unemployment fell by roughly two percent in the Ist quarter of 2005. 8.The volume of freight handled by ports throughout the country totaled 4 billion tons,up21.3 percent over the previous year. 9.The total number of privately-owned vehicles was 13.65 million,u 12 percent 10.The year 2004 saw 1.1 billion domestic tourists,up 266 percent Revenue from domestic tourism totaled 471.1 billion Yuan,up 36.9 percent Import and export of germany According to the e latest statistic issued by the Bureau of Federa Republic of Germany,German import volume from China amounted to 39.9 billion Euros.up by 21.6%in 2005. China ranked the fourth in source of import of Germany advanced two places used in 2004 The proportion of import volume from China ir the total Germ import volume rose from5.7%to6.4%. The volume of German export to China amounted to 21.3 billior Euros,up by 1.4%,and China became the eleventh export destination of Germany,dropped one place used in 2004.The export volume of Germany to China in the total export volume dropped from 29%to 270% The total foreign trading volume of Germany is 1,118 bilion Eu out of which total import volume is 625.6 billion Euros,up by 8.7% and total export volume is 786.2 billion Euros,up by 7.5%. France,Holland and US maintained to be the first three sources of import of Germany
5600 亿 练习: 5 汉 5 英 巩固练习 一、15 汉 二、15 英 三、10 汉 四、10 英 五、10 个句子(5 英 5 汉) 有上下文的数字 1. 全年工业增加值为 62,815 亿元,比上年增长 11.5%。 2. 全年粮食产量为 46,947 万吨,比上年增加 3,877 万吨,增长 9.1%。 3. 全年进出口总额达 11,548 亿美元,比上年增长 35.7%。 4. 全年合同外资金额为 1,535 亿美元,增长 33.4%;实际使用外资 606 亿美元,增长 13.3%。 5. 全年入境旅游人数为 10,904 万人次,国际旅游外汇收入 257 亿 美元,增长 47.9%。 6. Last year the unemployment rate in the US was nearly 5%. 7. European unemployment fell by roughly two percent in the 1st quarter of 2005. 8. The volume of freight handled by ports throughout the country totaled 4 billion tons, up 21.3 percent over the previous year. 9. The total number of privately-owned vehicles was 13.65 million, up 12.0 percent. 10. The year 2004 saw 1.1 billion domestic tourists, up 26.6 percent. Revenue from domestic tourism totaled 471.1 billion Yuan, up 36.9 percent. Import and Export of Germany According to the latest statistic issued by the Bureau of Federal Republic of Germany, German import volume from China amounted to 39.9 billion Euros, up by 21.6% in 2005. China ranked the fourth in source of import of Germany advanced two places used in 2004. The proportion of import volume from China in the total Germany import volume rose from 5.7% to 6.4%. The volume of German export to China amounted to 21.3 billion Euros, up by 1.4%, and China became the eleventh export destination of Germany, dropped one place used in 2004. The export volume of Germany to China in the total export volume dropped from 2.9% to 2.7%. The total foreign trading volume of Germany is 1,411.8 billion Euros, out of which total import volume is 625.6 billion Euros, up by 8.7% and total export volume is 786.2 billion Euros, up by 7.5%. France, Holland and US maintained to be the first three sources of import of Germany

Britain,Italy,Belgium,Swiss,Spain and Russia were the fifth to tenth orderly after China Fra Holland,Belgium,Austria,Spain,Swis and Poland were the first ten export destination of Germany. The World Population by 2050 New research shows that Earth will have more than 9000 millio people by 2050.The world population is currently estimated a6.4 and million.The will take place in developing countries in Africa and western Asia. India is expected to surpass China as the world's most populatec nation.By the mid of the century,the report says,India will have ove one and half thousand million citizens.an increase of fifty percent China has 13 thousand people.The research says th population should increase about ten percent by 2050 Most industrial nations will see a drop in their populations.The only big exception is expected to be the United States.The report says the United States will remain the third biggest nation. The population of the US is now.It isexpected to rea .The report says this will be because of immigration and low death rates among babies. The study is based on information from governments and the United Nations.Research Carl Haub wrote the report.He examined infant death rates,life expectancy,birth rates and the age structure of nations The family,for the first tim rates of AIDS 湖北省的经济情况 今年全省国内生产总值达5395.91亿元,按可比价格计算,比上年 增长93%。全省预算收入25957亿元,全年财政支出为538.34 亿元,比上年增长4.29%。其中农业和教有支出分别增长14%和 19% 年全省进出口总额为51.11亿美元,比上年增长292%,其中出 口总额26.56亿美元:进口总额24.55亿美元。 外商直接投资平稳增长,全年新批外商投资企业532家,实际利 用外商投资超过25亿美元,其中外商直接投资15.57亿美元,增 长11.1% 到今年年底,金融机构各项存款余额达5986.36亿元,比年初增加 96521亿元。各项贷款余额4999.55亿元,比年初增加68591亿 元。 中国出国留学情况 自从1978年改革开放以来,出国留学的相关工作迅速发展,现在 经成为向外宜传中国政苹开议的口,也有利行中国与其他国 去年,出国留学的学生和学者的总数为117,300人,其中3002人 受国家公费资助出国,5114人有单位出资出国,另外109,200人
Britain, Italy, Belgium, Swiss, Spain and Russia were the fifth to tenth source of import of Germany orderly after China. France, US, Britain, Italy, Holland, Belgium, Austria, Spain, Swiss and Poland were the first ten export destination of Germany. The World Population by 2050 New research shows that Earth will have more than 9,000 million people by 2050. The world population is currently estimated at 6.4 thousand million. The research says most growth will take place in developing countries in Africa and western Asia. India is expected to surpass China as the world’s most populated nation. By the mid of the century, the report says, India will have over one and half thousand million citizens, an increase of fifty percent. China currently has 1.3 thousand million people. The research says the population should increase about ten percent by 2050. Most industrial nations will see a drop in their populations. The only big exception is expected to be the United States. The report says the United States will remain the third biggest nation. The population of the US is close to 300 million now. It is expected to reach 420 million. The report says this will be because of immigration and low death rates among babies. The study is based on information from governments and the United Nations. Research Carl Haub wrote the report. He examined infant death rates, life expectancy, birth rates and the age structure of nations. The study also considered family planning use and, for the first time, rates of AIDS. 湖北省的经济情况 今年全省国内生产总值达 5395.91 亿元,按可比价格计算,比上年 增长 9.3%。全省预算收入 259.57 亿元,全年财政支出为 538.34 亿元,比上年增长 4.29%。其中农业和教育支出分别增长 14%和 7.9%。 全年全省进出口总额为 51.11 亿美元,比上年增长 29.2%,其中出 口总额 26.56 亿美元;进口总额 24.55 亿美元。 外商直接投资平稳增长,全年新批外商投资企业 532 家,实际利 用外商投资超过 25 亿美元,其中外商直接投资 15.57 亿美元,增 长 11.1%。 到今年年底,金融机构各项存款余额达 5986.36 亿元,比年初增加 965.21 亿元。各项贷款余额 4999.55 亿元,比年初增加 685.91 亿 元。 中国出国留学情况 自从 1978 年改革开放以来,出国留学的相关工作迅速发展,现在 已经成为向外宣传中国改革开放的窗口,也有利于中国与其他国 家之间的文化交流。 去年,出国留学的学生和学者的总数为 117,300 人,其中 3002 人 受国家公费资助出国,5114 人有单位出资出国,另外 109,200 人
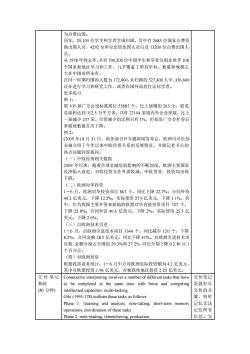
为自费出国 同年,20,100位学生和学者学成归国,其中有2683位国家公费资 助出国人员,4292位单位出资出国人员以及1520位自费出国入 员。 从1978年到去年,共右700200位中国学生和学者分别在世界108 个国家和地风学习和工作,几平覆盖了所有学科。数量和规模之 大在中国前所未有 在同 时期 国的人数为172,800。未归国的527,400人中,356,60 还在进行学习和研究工作,或者在国外高校任访问学者。 更多练习 列1。 第105届广交会设标准展位55885个,比上届增加265个,展览 总面积达到125万平方米,共有2104家境内外企业参展,比上 届减少237家。 尽管减少的比例只有1%,但却是广交会扩容后 参展商数量首次下降。 伤2: (2009年)8月31日,商务部召开专题新闻发布会,欧洲司司长孙 永福介绍了今年以来中欧经贸关系的发展情况,并就记者关心的 热点问题回答提问 (一)中欧经贸相关数据 2009年以来,随着全球金融危机影响的不断加深,欧洲主要国家 经济陷入衰退,对欧经贸合作外需锐减,中欧贸易、投资均出现 下降。 )欧洲对华投资 1一6月,欧洲对华投资项目867个,同比下降227%:合同外资 40.2亿美元,下降122%:实际使用27.9亿美元,下降11%。其 中,作为我国主要外资来源地的欧盟对华直接投资项目747个, 下降22.8%:合同外资40.6亿美元,下降2%:实际使用25.5亿 美元,下降2.6%。 (三)自欧洲技术引进 1-6月,自欧洲引进技术项目1344个,同比减少120个,下降 8.2%:合同金额28.5亿美元,同比下降41%。自欧洲引进技术项 目数、金额分别占全国的29.3%和27.2%,同比分别下降02和11.1 个百分占。 (四) 对欧洲投资 根据我部业务统计,1一6月中方对欧洲实际投资额为42亿美元 其中对欧盟投资1.96亿美元,对独联体地区投资225亿美元。 交传笔i记Consecutive interpreting involves a number of different tasks that have 交传笔记 to be completed at the same time with finite and competin 是做好 (80分钟) intellectual capacities:multi-tasking. Gile(1995:178)outlines these tasks as follows: 短 Phase 1:listening and analysis,note-taking short-term memory 记忆无法 operations,coordination of these tasks 记住所有 信息。交
为自费出国。 同年,20,100 位学生和学者学成归国,其中有 2683 位国家公费资 助出国人员,4292 位单位出资出国人员以及 13200 位自费出国人 员。 从 1978 年到去年,共有 700,200 位中国学生和学者分别在世界 108 个国家和地区学习和工作,几乎覆盖了所有学科。数量和规模之 大在中国前所未有。 在同一时期归国的人数为 172,800。未归国的 527,400 人中,356,600 还在进行学习和研究工作,或者在国外高校任访问学者。 更多练习 例 1: 第 105 届广交会设标准展位 55885 个,比上届增加 265 个,展览 总面积达到 112.5 万平方米。共有 22104 家境内外企业参展,比上 一届减少 237 家。尽管减少的比例只有 1%,但却是广交会扩容后 参展商数量首次下降。 例 2: (2009 年) 8 月 31 日,商务部召开专题新闻发布会,欧洲司司长孙 永福介绍了今年以来中欧经贸关系的发展情况,并就记者关心的 热点问题回答提问。 (一)中欧经贸相关数据 2009 年以来,随着全球金融危机影响的不断加深,欧洲主要国家 经济陷入衰退,对欧经贸合作外需锐减,中欧贸易、投资均出现 下降。 (二)欧洲对华投资 1-6 月,欧洲对华投资项目 867 个,同比下降 22.7%;合同外资 40.2 亿美元,下降 12.2%;实际使用 27.9 亿美元,下降 1.1%。其 中,作为我国主要外资来源地的欧盟对华直接投资项目 747 个, 下降 22.8%;合同外资 40.6 亿美元,下降 2%;实际使用 25.5 亿 美元,下降 2.6%。 (三)自欧洲技术引进 1-6 月,自欧洲引进技术项目 1344 个,同比减少 120 个,下降 8.2%;合同金额 28.5 亿美元,同比下降 41%。自欧洲引进技术项 目数、金额分别占全国的 29.3%和 27.2%,同比分别下降 0.2 和 11.1 个百分点。 (四)对欧洲投资 根据我部业务统计,1-6 月中方对欧洲实际投资额为 4.2 亿美元, 其中对欧盟投资 1.96 亿美元,对独联体地区投资 2.25 亿美元。 交传笔记 基础 (80 分钟) Consecutive interpreting involves a number of different tasks that have to be completed at the same time with finite and competing intellectual capacities: multi-tasking. Gile (1995:178) outlines these tasks as follows: Phase 1: listening and analysis, note-taking, short-term memory operations, coordination of these tasks Phase 2: note-reading, remembering, production 交传笔记 是做好长 交传的关 键,短时 记忆无法 记住所有 信息。交

automatization 传笔记要 求迅速准 确记录说 it does not come from an intellectual understanding of how to 话人的主 complete a task but from repeated practice of the completion of the 要信息, task.until it is completed correctly without thinking 以须右 There is no"right"way to do things,but some are better than others. 定的技巧 Note-taking:What to Not 才能完成 Ideas 这样的任 Links 务。 Who is sneaking Verb tense modal verbs Proper name,numbers ates,lists Terms to be transoded The last sentence ofa speech Note-taking:How to note recognizing and splitting ideas (identifying ideas) And thank you for joining us as we host President Hu and the Chinese delegation,and as we pay tribute to the bonds between two great nations and two proud peoples. links Eg Ther are to many distinguished guests tomentional of you onigh But I do want to acknowledge a few who have championed relations between our nations:First of all,President Jimmy Carter and his wonderful wife Rosalynn Carter are here.(Applause.)As well as President Bill Clinton and my outstanding Secretary of State,Hillary Clinton.(Applause.) Why use symbols? are quicker and easier to write than words. are easier to read on the page than words. represent concepts not words,helping us avoid source languag concepts that come up again and agair Frequently occuring verbs speak.say,announce.declare.etc want wish desire hope for think,consider,hold the view,be minded tobe of the convictior propose,suggest,put forward,move to.nominate concepts that come up again and again Frequently occuring nouns support,backing.endorsement,etc
automatization note-taking is a mechanical activity. internalization it does not come from an intellectual understanding of how to complete a task but from repeated practice of the completion of the task, until it is completed correctly without thinking. There is no "right" way to do things, but some are better than others. Note-taking: What to Note Ideas Links Who is speaking Verb tense & modal verbs Proper name, numbers, dates, lists Terms to be transcoded The last sentence of a speech Note-taking: How to note recognizing and splitting ideas (identifying ideas) E.g.: And thank you for joining us as we host President Hu and the Chinese delegation, and as we pay tribute to the bonds between two great nations and two proud peoples. links E.g. There are too many distinguished guests to mention all of you tonight. But I do want to acknowledge a few who have championed relations between our nations: First of all, President Jimmy Carter and his wonderful wife Rosalynn Carter are here. (Applause.) As well as President Bill Clinton and my outstanding Secretary of State, Hillary Clinton. (Applause.) Why use symbols? are quicker and easier to write than words. are easier to read on the page than words. represent concepts not words, helping us avoid source language interference when we interpret. What to note with symbols? concepts that come up again and again Frequently occuring verbs speak, say, announce, declare, etc. want, wish, desire, hope for, think, consider, hold the view, be minded to, be of the conviction propose, suggest, put forward, move to, nominate concepts that come up again and again Frequently occuring nouns support, backing, endorsement, etc. 传笔记要 求迅速准 确记录说 话人的主 要信息, 必须有一 定的技巧 才能完成 这样的任 务

ceresutnd-efectramifications repercusion oblem,difficully,hindrance block country politics,policy money (1)Organic symbols oally 02e o (2)symbols return.come back.reverse.regress lead to.consequence of.therefore ↑orx rise,increase,grow,climb,ete. Jorw fall,decline,slide,slip,drop,shrink 40r台 exchange,relations stronger and stronger,progress in step LL weaker and weaker,drop at the same time (3)Mathematical marks 表示"多,t加,正,阳":many,lotsof agreat deal of,a good many of. plus,add,inaddition,positive; +or+2 表示"多"的比较级:more +++Or+3 表示“多”的最高级:ms 表示"少,减,负,阴:litte,few,lack,in short of/be in shortage of. subtract,minus:negative:few.little
consequence, result, end-effect, ramifications, repercussions problem, difficulty, hindrance, hurdle, stumbling block country politics, policy money industry (1) Organic symbols □al □ally □ze □tn □o □ □· □/□ □ □ (2) symbols ← return, come back, reverse, regress → lead to, consequence of, therefore ↑ or ↗ rise, increase, grow, climb, etc. ↓ or ↘ fall, decline, slide, slip, drop, shrink or exchange, relations ↑↑ stronger and stronger, progress in step ↓↓ weaker and weaker, drop at the same time (3) Mathematical marks + 表示"多,加,正,阳": many, lots of, a great deal of, a good many of; plus, add, in addition; positive; ++ or +2 表示"多"的比较级:more +++ Or +3 表示"多"的最高级:most - 表示"少,减,负,阴": little, few, lack , in short of/ be in shortage of; subtract, minus; negative; few, little -

比较级,更少的:less 最高级,最少的,最小的,the least 不准确,可能:probably,possibly,.about, 表示"多于"t概念:bigger/arger/greater/more than/etter than,ctc 表示"高”概念:superior to,surpass,cc 表示"少于"概念:les/smaller,ctc. 表示"低"概念:inferior to,ete 表示"同等"概念:means,.that is to say,in other words,the same as be equal to,etc. 表示"对手"概念:a match,rival,competitor,.counterpart,etc. 表示"不同"概念:be different from,etc. 表示"无敌"概念:matchless,peerless,ctc 表示“大于或等于”、“不少于”:more thanorqto,no less than ≤ 表示“小于或等于”、“不多于”:less than or equal to,.no more than 大约:about//around,approximately,orso,ctc) 不少于,不小于,不劣于:not smaller than,no less than,no worse than,not inferior to 不大于,不多于,不好于:not larger than,no more than,no better than not superior to 无穷,无止境的,无限的:endless,.boundless,limitless “由于”、“因为”、“幸亏”:because,due to,thanks to,as,owing to “所以”、“因此”、“结果是”:so,therefore,asaresult,consequently 表示“在.基础上”:based on 或者“影响”、“效果”、“压力”“负担”:influence,effect,.impact ,burden,od 表示“属于”(belong to) 不属于
比较级,更少的;less - 最高级,最少的,最小的,the least ± 不准确,可能;probably, possibly, about, > 表示"多于"概念:bigger/larger/greater/more than/better than, etc. 表示"高" 概念:superior to,surpass, etc. < 表示"少于"概念:less/smaller,etc. 表示"低"概念:inferior to,etc. = 表示"同等"概念:means,that is to say, in other words,the same as, be equal to, etc. 表示"对手"概念:a match, rival, competitor, counterpart, etc. ≠ 表示"不同"概念:be different from, etc. 表示"无敌"概念:matchless, peerless, etc. ≥ 表示“大于或等于”、“不少于”: more than or equal to, no less than ≤ 表示“小于或等于”、“不多于”: less than or equal to, no more than ≈ 大约:about/around,approximately, or so,etc.) ≮ 不少于,不小于,不劣于:not smaller than, no less than, no worse than, not inferior to ≯ 不大于,不多于,不好于:not larger than, no more than, no better than, not superior to ∞ 无穷,无止境的,无限的:endless, boundless, limitless ∵ “由于”、“因为”、“幸亏”:because, due to, thanks to, as, owing to ∴ “所以”、“因此”、“结果是”:so, therefore, as a result, consequently ⊥ 表示“在.基础上”:based on 或者“影响”、“效果”、“压力”“负担”:influence, effect, impact, pressure, stress, burden, load Є 表示“属于”(belong to) 不属于

数学符号表示总值:total,totally,entire,entirely,.on the whole all ir all,to sum up,ect. 总和,合计:total,total amount,total value,.add up to,amount to 政治,政治的,政策:politics,.political,.polity 政治领导人,政客:politician 表示"否定","消除"等概念:cross out,eliminate,etc 表示"在之间:among.within,.ctc (4)other marks 表示"错误"、"失误"和"坏"的概念:mistakes,.not good, wrong/incorrect,something bad,notorious,negative,etc. 不好,反对,不同意:disagree,opp0s 正确,好,同意:correct,.good,okay,gree,approval 好的状态:famous/well-known,.etc 的 医院,医疗:hospital,medical (像酒杯协议,合同,合约:agrcetment,trealy,contract 0 转换,改变:transform,transition,.change 与.相比而言,表示转折:compared with,bu 表示“结束”:cnd 渔业:fishery n 替换成为:be replaced as 统治,政府,政府的:govern,government,governmental ya 政府领导人,政府官员:government officials 结尾,结束:emd,finish,windup,close,be over 代表,恢复,代替,象征:represent,resume,on bchalf of replace symbolize 4·
E 数学符号表示总值:total, totally, entire, entirely, on the whole, all in all, to sum up, ect. Σ 总和,合计:total, total amount, total value, add up to, amount to π 政治,政治的,政策:politics, political, polity π° 政治领导人,政客:politician / 表示"否定","消除"等概念:cross out, eliminate, etc. ( ) 表示"在.之间":among, within, etc. (4) other marks × 表 示 " 错 误 " 、 " 失 误 " 和 " 坏 " 的概念: mistakes, not good, wrong/incorrect,something bad,notorious,negative, etc. 不好,反对,不同意:disagree, oppose √ 正确,好,同意: correct, good, okay, agree, approval 好的状态:famous/well-known,etc ⊕ 医院,医疗:hospital, medical ∪ (像酒杯) 协议,合同,合约:agreetment, treaty, contract ∩ 转换,改变:transform, transition, change ∥ 与.相比而言,表示转折:compared with, but 表示“结束”: end ∝ 渔业:fishery ∽ 替换成为:be replaced as γ 统治,政府,政府的:govern, government, governmental γ° 政府领导人,政府官员:government officials # 结尾,结束:end, finish, conclude, wind up, close, be over △ 代表,恢复,代替,象征:represent, resume, on behalf of, replace, symbolize △°
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(口译)Module 6 Simultaneous interpreting.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(口译)Module 4 Escort & liaison interpreting.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(汉译英)第2讲 形合与意合.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(汉译英)第1讲 汉译英概论.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(汉译英)第6讲 长句的翻译.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(汉译英)第4讲 词性转换.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(汉译英)第3讲 句子衔接和布局.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(汉译英)第5讲 信息结构与翻译.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 2 Diction.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Units 3 and 4 Amplification and Omission.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 1Introduction.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 6 Restructuring.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 5 Conversion.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 7 Passive Voice.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 8 Affirmative vs negative.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Units 11 and 12 Nominal Clauses and Adverbial Clauses.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 9 Splitting.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 10 Conversion of Attributive Clauses.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(英译汉)Unit 13 Translation of Long Sentences.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程教学资源(汉英)钱钟书与杨绛.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(口译)Module 3 memory training.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(口译)Module 1 Introduction to interpreting course & lead-in.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程授课教案(口译)Module 2 Sight translation.doc
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 11 and 12 Nominal clauses and adverbial clauses.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 9 Splitting.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 13 Long sentences.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 10 Attributive clauses.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 6 Restructuring.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 5 Conversion.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 8 Affirmative vs negative.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 7 Passive Voice.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 1 Translation Criteria.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 3 Amplification.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 4 Omission.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(英译汉)Unit 2 Diction.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(汉译英)第5讲 信息结构与翻译.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(汉译英)第7讲 公示语和翻译中的文化.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(汉译英)第6讲 长句的翻译.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(汉译英)第4讲 词性转换.ppt
- 《大学英语翻译》课程PPT教学课件(汉译英)第2讲 翻译中的形合与意合.ppt
