《高等数学》课程教学大纲 C(下)

高等数学C(下)一、课程基本情况课程编号:1131000632课程总学时:4课程学分:必修课程分类:春开课学期:秀开课单位:理学学院数学适用专业:农学、园艺、园林、植保、动物医学、动物科学、化学、社会、农村发展、水产等所需先修课:高高等数学C(上)课程负责人:李国辉二、课程目标:1、课程总目标:高等数学C(下)课程适应专业为是农学、动物科学、动物医学、应用化学、人文等,在高等数学C(上)的基础上介绍空间解析几何、多元函数微分理论、多重积分、二阶微分方程、无穷级数知识的课程。通过本课程的学习,学生将了解多元函数微积分的基本概念,掌握多元函数微积分的运算方法为学生学习概率论与数理统计等后继课程和解决实际问题提供常用的数学方法。多元微积分部分内容不追求严格的论证和推导,只做简单介绍和基本训练。对与实际应用联系较多的基础知识、基本方法应重点加强,不追求过分复杂的计算和变换。2、课程分目标:课程分目标1:二阶微分方程(6学时)了解二阶线性微分方程解的结构,会求常系数齐次线性微分方程通解,了解非齐次线性微分方程的特解形式。课程分目标2:空间解析几何(6学时)掌握空间解析几何的基本概念,会计算向量的数量积和向量积。了解曲面方程、曲线方程的概念,了解二次曲面的图形。掌握空间直线和平面的一般方程。课程分目标3:多元函数微分学(10学时)了解二元函数的极限与连续的概念,理解偏导数、全微分等概念,掌握复合函数一阶偏导数的求法、会求复合函数的二阶偏导数。掌握极值存在的必要条件和充分条件,了解曲线的切线、曲面的切平面等几何问题的求法。了解函数1
1 高等数学 C(下) 一、 课程基本情况 课程编号:11310006 课程总学时: 32 课程学分: 4 课程分类: 必修 开课学期: 春 开课单位: 理学 学院 数学 系 适用专业: 农学、园艺、园林、植保、动物医学、动物科学、化学、社会、农村发展、水产等 所需先修课:高等数学 C(上) 课程负责人:李国辉 二、课程目标: 1、课程总目标: 高等数学 C(下)课程适应专业为是农学、动物科学、动物医学、应用化学、人文等,在高等数 学 C(上)的基础上介绍空间解析几何、多元函数微分理论、多重积分、二阶微分方程、无穷级数知 识的课程。 通过本课程的学习,学生将了解多元函数微积分的基本概念,掌握多元函数微积分的运算方法, 为学生学习概率论与数理统计等后继课程和解决实际问题提供常用的数学方法。多元微积分部分内容 不追求严格的论证和推导,只做简单介绍和基本训练。对与实际应用联系较多的基础知识、基本方法 应重点加强,不追求过分复杂的计算和变换。 2、课程分目标: 课程分目标 1: 二阶微分方程(6 学时) 了解二阶线性微分方程解的结构,会求常系数齐次线性微分方程通解,了解非齐次线性微分方程的特 解形式。 课程分目标 2: 空间解析几何(6 学时) 掌握空间解析几何的基本概念,会计算向量的数量积和向量积。了解曲面方程、曲线方程的概念,了 解二次曲面的图形。掌握空间直线和平面的一般方程。 课程分目标 3:多元函数微分学(10 学时) 了解二元函数的极限与连续的概念,理解偏导数、全微分等概念,掌握复合函数一阶偏导数的求法、 会求复合函数的二阶偏导数。 掌握极值存在的必要条件和充分条件,了解曲线的切线、曲面的切平面等几何问题的求法。了解函数
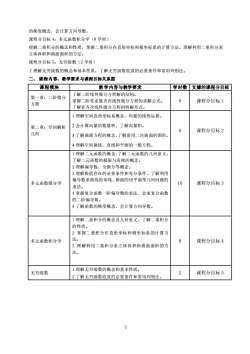
的梯度概念,会计算方向导数。课程分目标4:多元函数积分学(8学时)理解二重积分的概念和性质,掌握二重积分在直角坐标和极坐标系的计算方法。理解利用二重积分求立体体积和曲面面积的方法。课程分目标5:无穷级数(2学时)了理解无穷级数的概念和基本性质,了解无穷级数收敛的必要条件和常用判别法。二、课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图课程模块教学内容与教学要求学时数支撑的课程分目标了解二阶线性微分方程解的结构。第一章:二阶微分6课程分目标1掌握二阶常系数齐次线性微分方程的求解公式。方程了解非齐次线性微分方程的特解形式。1理解空间直角坐标系概念,向量的线性运算。2会计算向量的数量积,了解向量积。第二章:空间解析6课程分目标2几何3了解曲面方程的概念,了解常用二次曲面的图形。4理解空间曲线、直线和平面的一般方程。1理解二元函数的概念,了解二元函数的几何意义,了解二元函数的极限与连续的概念。2理解偏导数、全微分等概念。3理解极值存在的必要条件和充分条件,了解利用偏导数求曲线的切线、曲面的切平面等几何问题的10课程分目标3多元函数微分学求法。4掌握复合函数一阶偏导数的求法、会求复合函数的二阶偏导数。5了解函数的梯度概念,会计算方向导数。1理解二重积分的概念及几何意义,了解二重积分的性质。2掌握二重积分在直角坐标和极坐标系的计算方法。多元函数积分学d课程分目标43理解利用二重积分求立体体积和曲面面积的方法。1理解无穷级数的概念和基本性质。2无穷级数课程分目标52了解无穷级数收敛的必要条件和常用判别法。2
2 的梯度概念,会计算方向导数。 课程分目标 4:多元函数积分学(8 学时) 理解二重积分的概念和性质,掌握二重积分在直角坐标和极坐标系的计算方法。理解利用二重积分求 立体体积和曲面面积的方法。 课程分目标 5:无穷级数(2 学时) 了理解无穷级数的概念和基本性质,了解无穷级数收敛的必要条件和常用判别法。 二、 课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图 课程模块 教学内容与教学要求 学时数 支撑的课程分目标 第一章:二阶微分 方程 了解二阶线性微分方程解的结构。 掌握二阶常系数齐次线性微分方程的求解公式。 了解非齐次线性微分方程的特解形式。 6 课程分目标 1 第二章:空间解析 几何 1 理解空间直角坐标系概念,向量的线性运算。 2 会计算向量的数量积,了解向量积。 3 了解曲面方程的概念,了解常用二次曲面的图形。 4 理解空间曲线、直线和平面的一般方程。 6 课程分目标 2 多元函数微分学 1 理解二元函数的概念,了解二元函数的几何意义, 了解二元函数的极限与连续的概念。 2 理解偏导数、全微分等概念。 3 理解极值存在的必要条件和充分条件,了解利用 偏导数求曲线的切线、曲面的切平面等几何问题的 求法。 4 掌握复合函数一阶偏导数的求法、会求复合函数 的二阶偏导数。 5 了解函数的梯度概念,会计算方向导数。 10 课程分目标 3 多元函数积分学 1 理解二重积分的概念及几何意义,了解二重积分 的性质。 2 掌握二重积分在直角坐标和极坐标系的计算方 法。 3 理解利用二重积分求立体体积和曲面面积的方 法。 8 课程分目标 4 无穷级数 1 理解无穷级数的概念和基本性质。 2 了解无穷级数收敛的必要条件和常用判别法。 2 课程分目标 5
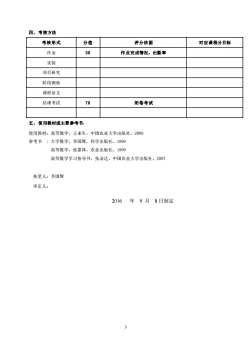
四、考核方法分值考核形式评分依据对应课程分目标作业30作业完成情况,出勤率实验项目研究阶段测验课程论文70结课考试闭卷考试五、使用教材或主要参考书使用教材:高等数学,王来生,中国农业大学出版社,2009参考书:大学数学,李国辉,科学出版社,1999高等数学,张嘉林,农业出版社,1999高等数学学习指导书,张录达,中国农业大学出版社,2007执笔人:李国辉审定人:年9月8日制定20163
3 四、考核方法 考核形式 分值 评分依据 对应课程分目标 作业 30 作业完成情况,出勤率 实验 项目研究 阶段测验 课程论文 结课考试 70 闭卷考试 五、使用教材或主要参考书: 使用教材:高等数学,王来生,中国农业大学出版社,2009 参考书 : 大学数学,李国辉,科学出版社,1999 高等数学,张嘉林,农业出版社,1999 高等数学学习指导书,张录达,中国农业大学出版社,2007 执笔人:李国辉 审定人: 2016 年 9 月 8 日制定

(说明:教学大纲标题用小四号宋体加粗,各部分的标题用五号宋体加粗,正文用五号宋体不加粗,行距用单倍行距。提交大纲时请把括弧内的说明文字删除)(Attachment: format of the teaching syllabus)Advanced mathematicsC (I1)1.Basic informationCoursecode:11310006????Total teaching hours:_32_, among whichhoursforlectures,hoursforexperimentshours for on-line teaching.Credits: 4Typeofthecourse:(compulsoryorelective):compulsoryTeachingterms:(spring,summerorautumn):SpringOwner of the course:(Teaching group,department, college)College of Science,department ofmathematicsMajors applicable:Prerequisites: Advanced mathematics C (I)Person in charge ofthe course:GuohuiLi2.Course Objectives(1) GeneralAimAdvanced mathematics C (Il) is a course for the majors such as Agriculture, Animal Science,VeterinaryMedicine, Applied Chemistry, Human culture, and introduces the knowedge of analytic geometry inspace, differentiation of functions of several variables, multiple integrals, second order differentialequations and infiniteseries.Throughthestudyofthiscourse,studentswillknowthebasicconceptsofcalculusoffunctionsof severalvariables,and master the calculation methods of derivatives and integrals of functions of severalvariables.Italsoprovidesthecommonmathematical methodsforstudentsto studysubsequent coursessuchasprobabilitytheoryand statistics,andtosolvepractical problems.Forsomepartsof materials incalculus of functions of several variables,we don'tpursue rigorous argument and derivation,but justintroduce them briefly and do basic training. Emphasize on the basic knowledge and basic methodsrelatedtopracticalapplication,butdon'tpursuetoocomplicatedcomputationandtransfomations.(2) BranchObjectivesTheFirst one:Secondorder differential equations (6 class hours)Know the structure of second orderlineardifferential equations,knowhow to find generalsolutions of homogeneous linear differential equations with constant coefficients, know the4
4 (说明:教学大纲标题用小四号宋体加粗,各部分的标题用五号宋体加粗,正文用五号宋体不加粗, 行距用单倍行距。提交大纲时请把括弧内的说明文字删除) (Attachment: format of the teaching syllabus) Advanced mathematics C (II) 1. Basic information Course code: 11310006???? Total teaching hours: _32_, among which_ hours for lectures, _ hours for experiments, _hours for on-line teaching. Credits: 4 Type of the course: (compulsory or elective): compulsory Teaching terms: (spring, summer or autumn) : Spring Owner of the course: (Teaching group, department, college) College of Science, department of mathematics Majors applicable: Prerequisites: Advanced mathematics C (I) Person in charge of the course: Guohui Li 2. Course Objectives (1)General Aim Advanced mathematics C (II) is a course for the majors such as Agriculture, Animal Science, Veterinary Medicine, Applied Chemistry, Human culture, and introduces the knowledge of analytic geometry in space, differentiation of functions of several variables, multiple integrals, second order differential equations and infinite series. Through the study of this course, students will know the basic concepts of calculus of functions of several variables, and master the calculation methods of derivatives and integrals of functions of several variables. It also provides the common mathematical methods for students to study subsequent courses such as probability theory and statistics, and to solve practical problems. For some parts of materials in calculus of functions of several variables, we don’t pursue rigorous argument and derivation, but just introduce them briefly and do basic training. Emphasize on the basic knowledge and basic methods related to practical application, but don’t pursue too complicated computation and transformations. (2)Branch Objectives The First one:Second order differential equations (6 class hours) Know the structure of second order linear differential equations, know how to find general solutions of homogeneous linear differential equations with constant coefficients, know the

form of special solutions to nonhomogeneousIinear differential equations.The Second one:Analytic geometry in Space (6 class hours)Masterthebasic conceptsin analytic geometry in space;knowhowtocalculate scalarproductandvectorproduct of vectors.Knowthe concepts of surface and curve equations;knowthegraphsofquadratic surfaces.Masterthe general equations oflines and planes in space.TheThird one:Differentiationof functionsofseveralvariables(1oclasshours)Know theconcepts of limit and continuityof functions of severalvariables,understand theconceptsofpartialderivativesandtotaldifferential,masterthecomputationmethodforfirstorderpartial derivativesof compositionfunctions,knowhowtofind secondorderpartial derivatives of compositionfunctionsMasterthe sufficientand necessary conditionsfortheexistence of extremevalues,knowhowto solvethegeometricproblemssuchasfindingthetangent linesto curvesandtangentplanestosurfaces.Knowtheconcepts of gradientoffunctions,and howtofind directional derivatives.TheForth one:Integration of functionsofseveralvariables(8classhours)Understand the concepts and properties of double integrals, master the calculation methods of doubleintegrals in rectangular coordinates and polarcoordinates.Understand themethodtofind thevolume ofbodies and thearea of surfaces byusing doubleintegralsTheFifth one:Infinite series (2class hours)Understand theconcepts infinite series,understandthe necessary conditions of convergenceofinfiniteseries,and common criteriontodeterminethe convergence.3、TheDiagram between CourseContent、TeachingRequirements andCourseObjectivesCorrespondingCourseContentandCourse ModulesClasshoursCourse ObjectivesTeaching Requirements5
5 form of special solutions to nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. The Second one: Analytic geometry in Space (6 class hours) Master the basic concepts in analytic geometry in space; know how to calculate scalar product and vector product of vectors. Know the concepts of surface and curve equations; know the graphs of quadratic surfaces. Master the general equations of lines and planes in space. The Third one:Differentiation of functions of several variables (10 class hours) Know the concepts of limit and continuity of functions of several variables, understand the concepts of partial derivatives and total differential, master the computation method for first order partial derivatives of composition functions, know how to find second order partial derivatives of composition functions. Master the sufficient and necessary conditions for the existence of extreme values, know how to solve the geometric problems such as finding the tangent lines to curves and tangent planes to surfaces. Know the concepts of gradient of functions, and how to find directional derivatives. The Forth one:Integration of functions of several variables (8 class hours) Understand the concepts and properties of double integrals, master the calculation methods of double integrals in rectangular coordinates and polar coordinates. Understand the method to find the volume of bodies and the area of surfaces by using double integrals. The Fifth one:Infinite series (2 class hours) Understand the concepts infinite series, understand the necessary conditions of convergence of infinite series, and common criterion to determine the convergence. 3、The Diagram between Course Content、Teaching Requirements and Course Objectives Course Modules Course Content and Teaching Requirements Class hours Corresponding Course Objectives
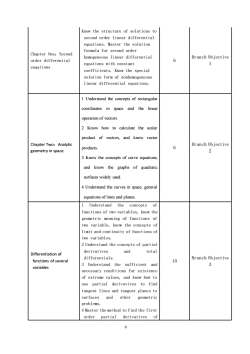
Know the structure of solutions tosecond order linear differentialequations. Master the solutionformula for second orderChapter One: Secondhomogeneous linear differentialBranch Objective6orderdifferential1equations with constanteugationscoefficients. Know the specialsolution form of nonhomogeneouslinear differential equations.1Understand the concepts of rectangularcoordinates in space and the linearoperationof vectors2Know how to calculate the scalarproduct of vectors, and know vectorBranch ObjectiveChapterTwo:Analytic6products.2geometryinspace3Knowtheconceptsof curveequations,and know the graphs of quadraticsurfaces widely used4 Understand the curves in space, generalequations of lines and planesUnderstandtheconceptsoffunctionsof twovariables,knowthegeometric meaning of functions oftwo variable, know the concepts oflimit and continuity of functions oftwo variables.2 Understand the concepts of partialandtotalderivativesDifferentiation ofBranch Objectivedifferentials.10functions of several33Understandd thesufficientandvariablesnecessary conditions for existenceof extremevalues,andknowhowtouse partial derivatives to findtangent lines and tangent planes tosurfacesandothergeometricproblems.4Master themethod tofind thefirstoorderpartialderivatives6
6 Chapter One:Second order differential euqations Know the structure of solutions to second order linear differential equations. Master the solution formula for second order homogeneous linear differential equations with constant coefficients. Know the special solution form of nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. 6 Branch Objective 1 Chapter Two:Analytic geometry in space 1 Understand the concepts of rectangular coordinates in space and the linear operation of vectors. 2 Know how to calculate the scalar product of vectors, and know vector products. 3 Know the concepts of curve equations, and know the graphs of quadratic surfaces widely used. 4 Understand the curves in space, general equations of lines and planes. 6 Branch Objective 2 Differentiation of functions of several variables 1 Understand the concepts of functions of two variables, know the geometric meaning of functions of two variable, know the concepts of limit and continuity of functions of two variables. 2 Understand the concepts of partial derivatives and total differentials. 3 Understand the sufficient and necessary conditions for existence of extreme values, and know how to use partial derivatives to find tangent lines and tangent planes to surfaces and other geometric problems. 4 Master the method to find the first order partial derivatives of 10 Branch Objective 3
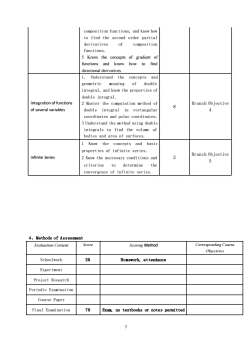
compositionfunctions,andknowhowto find the second order partialofderivativescompositionfunctions.5Know theof gradient ofconceptsfindfunctionsandknowhowtodirectional derivatives.1.Understandtheconceptsandofdoublegeometricmeaningintegral, and know the properties ofdouble integral.IntegrationoffunctionsBranch Objective2 Master the computation method of84ofseveralvariablesdouble integral in rectangularcoordinates and polar coordinates.3 Understand the method using doubleintegrals to find the volume ofbodies and area of surfaces.YKnowtheconceptsandbasicproperties of infinite series.Branch Objective2Infinite Series2 Know the necessary conditions and5criteriontodeterminetheconvergence of infinite series.4、Methods of AssessmentScoreCorresponding CourseScoring MethodEvaluation ContentObjectives30SchoolworkHomework, attendanceExperimentProject ResearchPeriodic ExaminationCourse Paper70Final ExaminationExam, no textbooks or notes permitted7
7 composition functions, and know how to find the second order partial derivatives of composition functions. 5 Know the concepts of gradient of functions and know how to find directional derivatives. Integration of functions of several variables 1. Understand the concepts and geometric meaning of double integral, and know the properties of double integral. 2 Master the computation method of double integral in rectangular coordinates and polar coordinates. 3 Understand the method using double integrals to find the volume of bodies and area of surfaces. 8 Branch Objective 4 Infinite Series 1 Know the concepts and basic properties of infinite series. 2 Know the necessary conditions and criterion to determine the convergence of infinite series. 2 Branch Objective 5 4、Methods of Assessment Evaluation Content Score Scoring Method Corresponding Course Objectives Schoolwork 30 Homework, attendance Experiment Project Research Periodic Examination Course Paper Final Examination 70 Exam, no textbooks or notes permitted

(Ifyouhave any otherevaluationcontent,pleasefill in thebottomof theform)5. Teaching materials or references:AdvancedmathematicsWritten by: Laisheng WangAuthorizedby:Chinaagricultureuniversitypress,2009References:Collegemathematics,GuohuiLi,Sciencepress,1999Advancedmathematics,JialinZhang,Agriculturepress,1999Advanced mathematics Reference book, Luda Zhang, China agriculture university press, 2009Advanced mathematics, Tongji University math department, China Higher Education PressComposedon(date)(note:the title of the course syllabus should be in Times new Rome, size 12, in bold; The title of therest part should be in Times new Rome, size ll, in bold; the font of the rest words is Times newRome, size 1l, single space. All the instruction words in brackets, including this note, should bedeletedin submission.)0
8 (If you have any other evaluation content,please fill in the bottom of the form) 5. Teaching materials or references: Advanced mathematics Written by: Laisheng Wang Authorized by: China agriculture university press, 2009 References: College mathematics, Guohui Li, Science press, 1999 Advanced mathematics, Jialin Zhang, Agriculture press, 1999 Advanced mathematics Reference book, Luda Zhang, China agriculture university press, 2009 Advanced mathematics, Tongji University math department, China Higher Education Press Composed on (date) (note: the title of the course syllabus should be in Times new Rome, size 12, in bold; The title of the rest part should be in Times new Rome, size 11, in bold; the font of the rest words is Times new Rome, size 11, single space. All the instruction words in brackets, including this note, should be deleted in submission.)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第一节 向量的内积.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第三节 相似矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第二节 方阵的特征值与特征向量.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第五节 二次型及其标准型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第四节 对称矩阵的相似矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第六节 用配方法化二次型成标准型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第七节 正定二次型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-4 线性方程组的解的结构.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-1 向量组及其线性组合.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-3 向量组的秩.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-5 向量空间.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-2 向量组的线性相关性.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-2 初等矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-4 线性方程组的解.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-1 矩阵的初等变换.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-3 矩阵的秩.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-2 矩阵的运算.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-1 矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-4 矩阵分块法.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-3 逆矩阵.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 B(下).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 C(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 B(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 A(下).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 A(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十一章 无穷级数.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十章 曲线积分与曲面积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十二章 微分方程.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第九章 重积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 定积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第八章 多元函数微分法及其应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 定积分的应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 导数与微分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 不定积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第七章 空间解析几何与向量代数.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 函数与极限.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-0 简介.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-习题课.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-09 第九节 连续函数的运算与初等函数的连续性.ppt
