《高等数学》课程教学大纲 C(上)

高等数学C上课程基本情况1、课程编号:1131000564课程总学时:4课程学分:必修课程分类:秋开课学期:秀开课单位:理学学院数学适用专业:农学、园艺、园林、植保、动物医学、动物科学、化学、社会、农村发展、水产等所需先修课:无课程负责人:二、课程目标:1、课程总目标:高等数学C(上)课程是农学、动物科学及人文发展各专业的必修基础课。通过本课程的学习,学生将系统地获得微积分的基础理论和基本知识、掌握微积分的运算方法,为学生学习后继课程和解决实际问题提供必要的数学基础知识及常用的数学方法。课程的主要内容包括极限理论、一元函数微分学、一元函数积分学、微分方程。要求必须深刻理解一元微积分的基本概念,熟练掌握导数和积分的计算方法,并能了解它们在几何与物理上的简单应用,微分方程则不追求严格的论证和推导。注重基本运算的训练,不追求过分复杂的计算和变换。教学中要逐步培养学生具有比较熟练的基本运算能力、自学能力、抽象概括问题的能力,综合运用所学知识去分析和解决问题。2、课程分目标:课程分目标1:函数的连续性了解极坐标概念,掌握基本初等函数性质,掌握数列的极限和函数的极限的定义,了解函数极限的性质。掌握无穷小与无穷大概念,熟练掌握极限的运算定理和两个重要极限,了解函数的连续性课程分目标2:导数与微分深刻理解导数的概念及其意义,熟练掌握初等函数的导数公式,掌握函数的求导法则,会求隐函数、参数方程所确定的函数的导数,了解微分和高阶导数的概念。1
1 高等数学 C 上 一、 课程基本情况 课程编号:11310005 课程总学时: 64 课程学分: 4 课程分类: 必修 开课学期: 秋 开课单位: 理学 学院 数学 系 适用专业: 农学、园艺、园林、植保、动物医学、动物科学、化学、社会、农村发展、水产等 所需先修课:无 课程负责人: 二、课程目标: 1、课程总目标: 高等数学 C(上)课程是农学、动物科学及人文发展各专业的必修基础课。通过本课程的学习, 学生将系统地获得微积分的基础理论和基本知识、掌握微积分的运算方法,为学生学习后继课程和解 决实际问题提供必要的数学基础知识及常用的数学方法。课程的主要内容包括极限理论、一元函数微 分学、一元函数积分学、微分方程。要求必须深刻理解一元微积分的基本概念,熟练掌握导数和积分 的计算方法,并能了解它们在几何与物理上的简单应用,微分方程则不追求严格的论证和推导。注重 基本运算的训练,不追求过分复杂的计算和变换。 教学中要逐步培养学生具有比较熟练的基本运算能力、自学能力、抽象概括问题的能力,综合运 用所学知识去分析和解决问题。 2、课程分目标: 课程分目标 1: 函数的连续性 了解极坐标概念,掌握基本初等函数性质,掌握数列的极限和函数的极限的定义,了解函数极限的性 质。掌握无穷小与无穷大概念,熟练掌握极限的运算定理和两个重要极限,了解函数的连续性。 课程分目标 2: 导数与微分 深刻理解导数的概念及其意义,熟练掌握初等函数的导数公式,掌握函数的求导法则,会求隐函数、 参数方程所确定的函数的导数,了解微分和高阶导数的概念
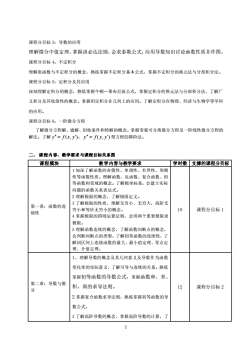
课程分目标3:导数的应用理解微分中值定理,掌握洛必达法则,会求泰勒公式,应用导数知识讨论函数性质并作图。课程分目标4:不定积分理解原函数与不定积分的概念,熟练掌握不定积分基本公式,掌握不定积分的换元法与分部积分法课程分目标5:定积分及其应用深刻理解定积分的概念,熟练掌握牛顿一莱布尼兹公式,掌握定积分的换元法与分部积分法,了解广义积分及其收敛性的概念。掌握用定积分在几何上的应用。了解定积分在物理、经济与生物学等学科的应用。课程分目标6:一阶微分方程了解微分方程解、通解、初始条件和特解的概念。掌握变量可分离微分方程及一阶线性微分方程的解法。了解y"=f(x,y),y"=f(y,y)型方程的降阶法。二、课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图课程模块教学内容与教学要求学时数支撑的课程分目标1加深了解函数的奇偶性、单调性、有界性、周期性等函数性质。理解函数、反函数、复合函数、初等函数和邻域的概念。了解极坐标系,会建立实际问题的函数关系表达式。2理解极限的概念,了解极限定义。3了解极限的性质,理解无穷小、无穷大,高阶无第一章:函数的连10课程分目标1穷小和等价无穷小的概念。续性4掌握极限的四则运算法则,会用两个重要极限求极限。5理解函数连续的概念,了解函数间断点的概念,会判断间断点的类型。了解初等函数的连续性,了解闭区间上连续函数的最大、最小值定理、零点定理、介值定理。1、理解导数的概念及其几何意义及导数作为函数变化率的实际意义,了解可导与连续的关系。熟练掌握初等函数的导数公式,掌握函数和、差、第二章:导数与微积、商的求导法则。12课程分目标2分2掌握复合函数求导法则,熟练掌握初等函数的导数公式。3了解高阶导数的概念,掌握高阶导数的计算,了2
2 课程分目标 3:导数的应用 理解微分中值定理,掌握洛必达法则,会求泰勒公式,应用导数知识讨论函数性质并作图。 课程分目标 4:不定积分 理解原函数与不定积分的概念,熟练掌握不定积分基本公式,掌握不定积分的换元法与分部积分法。 课程分目标 5:定积分及其应用 深刻理解定积分的概念,熟练掌握牛顿—莱布尼兹公式,掌握定积分的换元法与分部积分法,了解广 义积分及其收敛性的概念。掌握用定积分在几何上的应用。了解定积分在物理、经济与生物学等学科 的应用。 课程分目标 6:一阶微分方程 了解微分方程解、通解、初始条件和特解的概念。掌握变量可分离微分方程及一阶线性微分方程的 解法。了解 y = f (x, y), y = f ( y, y) 型方程的降阶法。 二、 课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图 课程模块 教学内容与教学要求 学时数 支撑的课程分目标 第一章:函数的连 续性 1 加深了解函数的奇偶性、单调性、有界性、周期 性等函数性质。理解函数、反函数、复合函数、初 等函数和邻域的概念。了解极坐标系,会建立实际 问题的函数关系表达式。 2 理解极限的概念,了解极限定义。 3 了解极限的性质,理解无穷小、无穷大,高阶无 穷小和等价无穷小的概念。 4 掌握极限的四则运算法则,会用两个重要极限求 极限。 5 理解函数连续的概念,了解函数间断点的概念, 会判断间断点的类型。了解初等函数的连续性,了 解闭区间上连续函数的最大、最小值定理、零点定 理、介值定理。 10 课程分目标 1 第二章:导数与微 分 1、理解导数的概念及其几何意义及导数作为函数 变化率的实际意义,了解可导与连续的关系。熟练 掌握初等函数的导数公式,掌握函数和、差、 积、商的求导法则。 2 掌握复合函数求导法则,熟练掌握初等函数的导 数公式。 3 了解高阶导数的概念,掌握高阶导数的计算,了 12 课程分目标 2
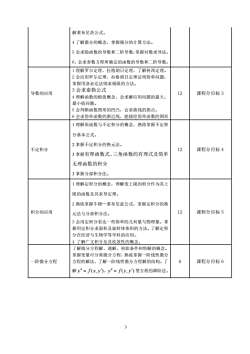
解莱布尼茨公式。4了解微分的概念,掌握微分的计算方法。5会求隐函数的导数和二阶导数,掌握对数求导法。6、会求参数方程所确定的函数的导数和二阶导数。1理解罗尔定理、拉格朗日定理,了解柯西定理。2会应用罗尔定理、拉格朗日定理证明简单问题,掌握用洛必达法则求极限的方法。3会求泰勒公式12课程分目标3导数的应用4理解函数的极值概念,会求解应用问题的最大、最小值问题。5会判断函数图形的凹凸,会求曲线的拐点。6会求简单函数的渐近线,能描绘简单函数的图形1理解原函数与不定积分的概念,熟练掌握不定积分基本公式。2掌握不定积分的换元法。12不定积分课程分目标43掌握有理函数式、三角函数的有理式及简单无理函数的积分3掌握分部积分法。1理解定积分的概念,理解变上限的积分作为其上限的函数及其求导定理。2熟练掌握牛顿一莱布尼兹公式,掌握定积分的换12课程分目标5积分的应用元法与分部积分法。3会用定积分表达一些简单的几何量与物理量。掌握用定积分求面积及旋转体体积的方法。了解定积分在经济与生物学等学科的应用。4了解广义积分及其收敛性的概念。了解微分方程解、通解、初始条件和特解的概念。掌握变量可分离微分方程,熟练掌握一阶线性微分6课程分目标6一阶微分方程方程的解法,了解一阶线性微分方程解的结构。了解y"=f(x,y),y"=f(y,y')型方程的降阶法。3
3 解莱布尼茨公式。 4 了解微分的概念,掌握微分的计算方法。 5 会求隐函数的导数和二阶导数,掌握对数求导法。 6、会求参数方程所确定的函数的导数和二阶导数。 导数的应用 1 理解罗尔定理、拉格朗日定理,了解柯西定理。 2 会应用罗尔定理、拉格朗日定理证明简单问题, 掌握用洛必达法则求极限的方法。 3 会求泰勒公式 4 理解函数的极值概念,会求解应用问题的最大、 最小值问题。 5 会判断函数图形的凹凸,会求曲线的拐点。 6 会求简单函数的渐近线,能描绘简单函数的图形 12 课程分目标 3 不定积分 1 理解原函数与不定积分的概念,熟练掌握不定积 分基本公式。 2 掌握不定积分的换元法。 3 掌握有理函数式、三角函数的有理式及简单 无理函数的积分 3 掌握分部积分法。 12 课程分目标 4 积分的应用 1 理解定积分的概念,理解变上限的积分作为其上 限的函数及其求导定理。 2 熟练掌握牛顿—莱布尼兹公式,掌握定积分的换 元法与分部积分法。 3 会用定积分表达一些简单的几何量与物理量。掌 握用定积分求面积及旋转体体积的方法。了解定积 分在经济与生物学等学科的应用。 4 了解广义积分及其收敛性的概念。 12 课程分目标 5 一阶微分方程 了解微分方程解、通解、初始条件和特解的概念。 掌握变量可分离微分方程,熟练掌握一阶线性微分 方程的解法,了解一阶线性微分方程解的结构。了 解 y = f (x, y),y = f ( y, y) 型方程的降阶法。 6 课程分目标 6
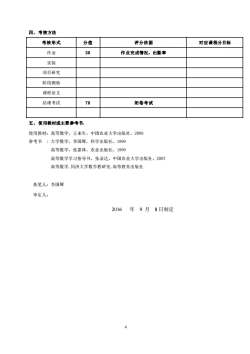
四、考核方法分值考核形式评分依据对应课程分目标作业30作业完成情况,出勤率实验项目研究阶段测验课程论文70结课考试闭卷考试五、使用教材或主要参考书:使用教材:高等数学,王来生,中国农业大学出版社,2009参考书:大学数学,李国辉,科学出版社,1999高等数学,张嘉林,农业出版社,1999高等数学学习指导书,张录达,中国农业大学出版社,2007高等数学,同济大学数学教研室,高等教育出版社执笔人:李国辉审定人:2016年9月8日制定4
4 四、考核方法 考核形式 分值 评分依据 对应课程分目标 作业 30 作业完成情况,出勤率 实验 项目研究 阶段测验 课程论文 结课考试 70 闭卷考试 五、使用教材或主要参考书: 使用教材:高等数学,王来生,中国农业大学出版社,2009 参考书 : 大学数学,李国辉,科学出版社,1999 高等数学,张嘉林,农业出版社,1999 高等数学学习指导书,张录达,中国农业大学出版社,2007 高等数学,同济大学数学教研室,高等教育出版社 执笔人:李国辉 审定人: 2016 年 9 月 8 日制定

(Attachment:formatoftheteachingsyllabus)English name of the course1. Basic informationCourse code:64Total teaching hours:,amongwhichhours for lectures,hoursforexperiments,hours foron-line teaching.Credits: 4Typeofthecourse:(compulsoryorelective):compulsoryTeachingterms: (spring,summerorautumn) : autumnOwner of the course: (Teaching group, department, college) : Department of applied mathematics.collegeofmathematicsMajors applicable:Agriculture, horticulture,garden architecture,plant protection,Veterinary Medicine,Animal Science, Chemistry,Society,Rural Area Development,AquaculturePrerequisites:NonePerson in charge ofthe course:2.Course Objectives(1)GeneralAimAdvanced Mathematics C(I) is a compulsorybase course for themajors of agriculture,animal science and human development. Through the study of this course, students will learnsystematically basic theory and fundamental knowledge of calculus, master the calculationmethods in calculus, and prepare necessary mathematical basic knowledge and commonmathematical methods for the subsequent courses and solving practical problems. The maincontent of the course include:limit theory, differentiation of functions of one variable,integration of functions of one variable, and differential equations. Require mandatorilyto understand deeply the basic concepts in calculus of functions of onevariable,to masterproficiently the calculation methods of derivative and integrals, and toknowtheir simpleapplications in geometry and physics, but not to argue or derive rigorously. Emphasize ontraining of basic calculations,but not on too complicated computation or transformations.In teaching, foster the students gradually the basic calculation ability, self-studyability,abstraction and summarization ability,and to apply comprehensively theknowledgelearned to analyze and solve problems.(2)BranchObjectivesTheFirst one:Continuityof functions5
5 (Attachment: format of the teaching syllabus) English name of the course 1. Basic information Course code: Total teaching hours: _64_, among which_ hours for lectures, _ hours for experiments, _hours for on-line teaching. Credits: 4 Type of the course: (compulsory or elective): compulsory Teaching terms: (spring, summer or autumn) : autumn Owner of the course: (Teaching group, department, college) : Department of applied mathematics, college of mathematics Majors applicable: Agriculture, horticulture, garden architecture, plant protection, Veterinary Medicine, Animal Science, Chemistry, Society, Rural Area Development, Aquaculture Prerequisites: None Person in charge of the course: 2. Course Objectives (1)General Aim Advanced Mathematics C(I) is a compulsory base course for the majors of agriculture, animal science and human development. Through the study of this course, students will learn systematically basic theory and fundamental knowledge of calculus, master the calculation methods in calculus, and prepare necessary mathematical basic knowledge and common mathematical methods for the subsequent courses and solving practical problems. The main content of the course include: limit theory, differentiation of functions of one variable, integration of functions of one variable, and differential equations. Require mandatorily to understand deeply the basic concepts in calculus of functions of one variable, to master proficiently the calculation methods of derivative and integrals, and to know their simple applications in geometry and physics, but not to argue or derive rigorously. Emphasize on training of basic calculations, but not on too complicated computation or transformations. In teaching, foster the students gradually the basic calculation ability, self-study ability, abstraction and summarization ability, and to apply comprehensively the knowledge learned to analyze and solve problems. (2)Branch Objectives The First one:Continuity of functions

Knowthe concepts of polar coordinates, master the properties of basic elementaryfunctions,master the definitions oflimits of sequences andfunctions, andknowtheproperties of limitsof functions. Master the concepts of infinite and infinitesimal, master proficiently thecalculation theorems for limits and two important limits,knowthe continuity of functionsThe Second one: Derivatives and differntiationUnderstand deeplythe concepts and significanceof derivatives, master proficiently thederivativeformulaefor elementaryfunctions, masterthe differentiatingrules forfunctions,know how to find implicit functions and derivatives of functions determined by parametricequations,andknowtheconceptsof differentiation and higher order derivatives.The Third one: Applications of derivatives.Understand mean value theorem in differentiation, masterI'Hospital rule, know howto findTayler formula, and apply knowledge on derivatives to discuss properties of functions andgraphing.The Fourth one: Indefinite integrals.Understandthe concepts of primitivefunctions and indefinite integrals, masterproficientlythe basic formulae of indefinite integrals, master themethods of substitution andintegrationbyparts tocalculateindefiniteintegrals.TheFifthone:Definiteintegralsandapplications.Understand deeply the concepts of definite integrals, master proficiently Newton-Leibnitzformula, master the methods of substitution and integrationby parts fordefiniteintegrals,know the concepts of improper integral and its convergence. Master the applications ofdefinite integrals in geometry. Know the applications of definite integrals in physics,economic,biology,etc.TheSixthone:FirstorderdifferentialeuqationsKnow the concepts of solutions,general solutions,initial conditions and special6
6 Know the concepts of polar coordinates, master the properties of basic elementary functions, master the definitions of limits of sequences and functions, and know the properties of limits of functions. Master the concepts of infinite and infinitesimal, master proficiently the calculation theorems for limits and two important limits, know the continuity of functions. The Second one:Derivatives and differntiation Understand deeply the concepts and significance of derivatives, master proficiently the derivative formulae for elementary functions, master the differentiating rules for functions, know how to find implicit functions and derivatives of functions determined by parametric equations, and know the concepts of differentiation and higher order derivatives. The Third one:Applications of derivatives. Understand mean value theorem in differentiation, master l’Hospital rule, know how to find Tayler formula, and apply knowledge on derivatives to discuss properties of functions and graphing. The Fourth one:Indefinite integrals. Understand the concepts of primitive functions and indefinite integrals, master proficiently the basic formulae of indefinite integrals, master the methods of substitution and integration by parts to calculate indefinite integrals. The Fifth one:Definite integrals and applications. Understand deeply the concepts of definite integrals, master proficiently Newton-Leibnitz formula, master the methods of substitution and integration by parts for definite integrals, know the concepts of improper integral and its convergence. Master the applications of definite integrals in geometry. Know the applications of definite integrals in physics, economic, biology, etc. The Sixth one:First order differential euqations Know the concepts of solutions, general solutions, initial conditions and special
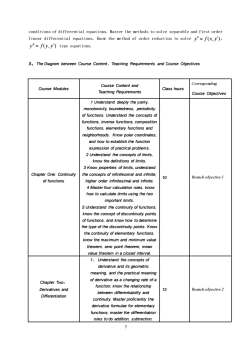
conditions of differential equations. Master the methods to solve separable and first orderlinear differential equations.Know the method of order reduction to solve y"=f(x,y'),y"= f(y,y') type equations.3、TheDiagrambetween Course Content、TeachingRequirements andCourse ObjectivesCorrespondingCourse Content andCourse ModulesClasshoursTeaching RequirementsCourse Objectives1Understanddeeplytheparity,monotonicity,boundedness,periodicityoffunctions.Understand the concepts offunctions,inversefunctions,compositionfunctions, elementary functions andneighborhoods.Know polarcoordinates,and how to establish the functionexpressionofpracticalproblems.2 Understand the concepts of limits,knowthedefinitions of limits.3Knowpropertiesoflimits,understandChapter One:Continuitytheconceptsofinfinitesimalandinfinite,Branchobjective!10offunctionshigher order infinitesimal and infinite.4Masterfour calculation rules,knowhowtocalculatelimitsusingthetwoimportant limits5Understand the continuityof functions,knowtheconceptofdiscontinuitypointsoffunctions,andknowhowtodeteminethetypeofthediscontinuitypoints.Knowthe continuity ofelementary functions,knowthemaximum andminimumvaluetheorem, zero point theorem, meanvaluetheorem inaclosedinterval1、Understand theconcepts ofderivative and its geometricmeaning,andthepractical meaningof derivative as a changing rate of aChapterTwo:function;knowtherelationshipDerivatives and12Branchobjective2between differentiabilityandDifferentiationcontinuity.Masterproficiently thederivativeformulaeforelementaryfunctions;masterthe differentiationrules todoaddition,subtraction,7
7 conditions of differential equations. Master the methods to solve separable and first order linear differential equations. Know the method of order reduction to solve y = f (x, y), y = f ( y, y) type equations. 3、The Diagram between Course Content、Teaching Requirements and Course Objectives Course Modules Course Content and Teaching Requirements Class hours Corresponding Course Objectives Chapter One: Continuity of functions 1 Understand deeply the parity, monotonicity, boundedness, periodicity of functions. Understand the concepts of functions, inverse functions, composition functions, elementary functions and neighborhoods. Know polar coordinates, and how to establish the function expression of practical problems. 2 Understand the concepts of limits, know the definitions of limits. 3 Know properties of limits, understand the concepts of infinitesimal and infinite, higher order infinitesimal and infinite. 4 Master four calculation rules, know how to calculate limits using the two important limits. 5 Understand the continuity of functions, know the concept of discontinuity points of functions, and know how to determine the type of the discontinuity points. Know the continuity of elementary functions, know the maximum and minimum value theorem, zero point theorem, mean value theorem in a closed interval. 10 Branch objective 1 Chapter Two: Derivatives and Differentiation 1、 Understand the concepts of derivative and its geometric meaning, and the practical meaning of derivative as a changing rate of a function; know the relationship between differentiability and continuity. Master proficiently the derivative formulae for elementary functions; master the differentiation rules to do addition, subtraction, 12 Branch objective 2
multiplicationanddivision.2、Masterthedifferentiationruleforcomposition functions;masterproficientlythederivativeformulaeforelementaryfunctions3Knowtheconceptsofhigherorderderivatives,master the computation ofhigherorder derivatives,knowLeibnitzformula.4Know the concepts of differentiation;masterthecomputation methods ofdifferentiation.5Knowhowtoderivativesof inversefunctions and second order derivatives,masterthe methodof differentiatinglogarithms.6Knowhowtofindthederivativesandsecond order derivatives of the functionsdetermined by parametric equations.1understandRoll theorem andLagrange theorem, know Cauchytheorem2KnowhowtoapplyRoll theoremandLagrange theorem toprovesimplequestions, masterthe method of usingI'Hospital rulesto find limits.3KnowhowtofindTaylor'sfomula4UnderstandtheconceptofextremeApplications ofBranchobjective312valuesoffunctions;knowhowtosolvederivativesthemaximumandminimumvalueprobleminpracticalproblems.5Knowhowtodeterminetheconvexityandconcavityoffunctiongraphs,andknowhowtofindtheinflectionpointsofcurves.6 Know how to find the asymptotes ofsimplefunctions,andknowhowtographsimple functions1Understandthe conceptsof primitivefunctions and indefinite integrals,andmasterproficientlythebasicfomulaefor12Branchobjective4Indefintieintegralsindefiniteintegrals2Masterthesubstitutionmethodforindefinite integrals3Masterthe integralofrational8
8 multiplication and division. 2、 Master the differentiation rule for composition functions; master proficiently the derivative formulae for elementary functions. 3 Know the concepts of higher order derivatives, master the computation of higher order derivatives, know Leibnitz formula. 4 Know the concepts of differentiation; master the computation methods of differentiation. 5 Know how to derivatives of inverse functions and second order derivatives, master the method of differentiating logarithms. 6 Know how to find the derivatives and second order derivatives of the functions determined by parametric equations. Applications of derivatives 1 understand Roll theorem and Lagrange theorem, know Cauchy theorem 2 Know how to apply Roll theorem and Lagrange theorem to prove simple questions, master the method of using l’Hospital rulesto find limits. 3 Know how to find Taylor’s formula. 4 Understand the concept of extreme values of functions; know how to solve the maximum and minimum value problem in practical problems. 5 Know how to determine the convexity and concavity of function graphs, and know how to find the inflection points of curves. 6 Know how to find the asymptotes of simple functions, and know how to graph simple functions. 12 Branch objective 3 Indefintie integrals 1 Understand the concepts of primitive functions and indefinite integrals, and master proficiently the basic formulae for indefinite integrals. 2 Master the substitution method for indefinite integrals. 3 Master the integral of rational 12 Branch objective 4
functions,rationalformoftrigonometricfunctionsandsimpleirrationalfunctions3Masterthemethodof integrationbyparts.1 Understand the conceptsofdefiniteintegrals,understand the integrals withvarying upperbound as afunction oftheupper bound and the differentiationtheorem.2Master proficiently Newton-Leibnitzfomula,andmasterthemethodsofsubstitution and integration by parts fordefinite integrals12Branch objective 5Applications of integrals3Knowhowtoexpresssomesimplegeometric andphysicalquantitiesusingdefinite integrals.Masterthemethod tofind area anvolume of body of revolutionusing definite integrals.Know theapplications of definite integrals ineconomics and biology4Knowtheconceptsof improperintegraland its convergence.Know the concepts of solutions,initialgeneral solutions,conditions and special conditions ofdifferential equations. Master themethodstosolveseparableFirst order differential6Branch objective 6differentialequationssandmasterequations.proficiently the methods to solve andfirst order linear differentialequations. Know the method of orderreductionn to solve y"= f(x,y'),y"=f(y,y')type equations4、Methods of AssessmentScoreScoring MethodCorresponding CourseEvaluation ContentObjectives30SchoolworkHomework,attendanceExperimentProject ResearchPeriodic Examination9
9 functions, rational form of trigonometric functions and simple irrational functions. 3 Master the method of integration by parts. Applications of integrals 1 Understand the concepts of definite integrals, understand the integrals with varying upper bound as a function of the upper bound and the differentiation theorem. 2 Master proficiently Newton-Leibnitz formula, and master the methods of substitution and integration by parts for definite integrals. 3 Know how to express some simple geometric and physical quantities using definite integrals. Master the method to find area an volume of body of revolution using definite integrals. Know the applications of definite integrals in economics and biology. 4 Know the concepts of improper integral and its convergence. 12 Branch objective 5 First order differential equations. Know the concepts of solutions, general solutions, initial conditions and special conditions of differential equations. Master the methods to solve separable differential equations and master proficiently the methods to solve and first order linear differential equations. Know the method of order reduction to solve y = f (x, y) , y = f ( y, y) type equations. 6 Branch objective 6 4、Methods of Assessment Evaluation Content Score Scoring Method Corresponding Course Objectives Schoolwork 30 Homework, attendance Experiment Project Research Periodic Examination

Course Paper70Final ExaminationExam,notextbooks ornotespermitted(If you have any other evaluationcontent,please fill in the bottom of the form)5.Teaching materialsorreferences:AdvancedmathematicsWritten by: Laisheng WangAuthorizedby:Chinaagricultureuniversitypress,2009References:Collegemathematics,GuohuiLi,Sciencepress,1999Advancedmathematics,JialinZhang,Agriculturepress,1999Advanced mathematics Reference book, Luda Zhang, China agricul ture university press, 2009Advancedmathematics,TongjiUniversitymathdepartment,ChinaHigherEducationPressComposed on(date)(note:the title of the course syllabus should be in Times new Rome, size 12, in bold; The title of therest part should be in Times new Rome, size ll, in bold; the font of the rest words is Times newRome, size 1l, single space. All the instruction words in brackets, including this note, should bedeletedinsubmission.)10
10 Course Paper Final Examination 70 Exam, no textbooks or notes permitted (If you have any other evaluation content,please fill in the bottom of the form) 5. Teaching materials or references: Advanced mathematics Written by: Laisheng Wang Authorized by: China agriculture university press, 2009 References: College mathematics, Guohui Li, Science press, 1999 Advanced mathematics, Jialin Zhang, Agriculture press, 1999 Advanced mathematics Reference book, Luda Zhang, China agriculture university press, 2009 Advanced mathematics, Tongji University math department, China Higher Education Press Composed on (date) (note: the title of the course syllabus should be in Times new Rome, size 12, in bold; The title of the rest part should be in Times new Rome, size 11, in bold; the font of the rest words is Times new Rome, size 11, single space. All the instruction words in brackets, including this note, should be deleted in submission.)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 B(下).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 C(下).docx
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第一节 向量的内积.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第三节 相似矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第二节 方阵的特征值与特征向量.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第五节 二次型及其标准型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第四节 对称矩阵的相似矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第六节 用配方法化二次型成标准型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第七节 正定二次型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-4 线性方程组的解的结构.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-1 向量组及其线性组合.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-3 向量组的秩.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-5 向量空间.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-2 向量组的线性相关性.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-2 初等矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-4 线性方程组的解.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-1 矩阵的初等变换.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-3 矩阵的秩.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-2 矩阵的运算.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-1 矩阵.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 B(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 A(下).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 A(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十一章 无穷级数.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十章 曲线积分与曲面积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十二章 微分方程.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第九章 重积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 定积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第八章 多元函数微分法及其应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 定积分的应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 导数与微分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 不定积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第七章 空间解析几何与向量代数.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 函数与极限.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-0 简介.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-习题课.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-09 第九节 连续函数的运算与初等函数的连续性.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-10 第十节 闭区间上连续函数的性质.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-07 第七节 无穷小的比较.ppt
