《高等数学》课程教学大纲 B(下)

高等数学B(下)一、课程基本情况课程编号:课程总学时:72课程学分:4.5课程分类:必修开课学期:春开课单位:理学院应用数学系适用专业:生物与食品相关专业所需先修课:无课程负责人:王新平、邹辉二、课程目标:1、课程总目标:通过本课程的学习,使学生获得多元函数微分学、多元函数积分学、级数和微分方程等方面的基本概念、基本理论和基本运算技能。使学生掌握高等数学的基本理论知识的同时,培养学生的抽象思维能力、逻辑推理能力、运算能力、分析问题和解决问题的能力,提高学生用数学方法分析和处理本专业领域中数量关系的能力,为学习后继课程和进一步获取数学知识奠定必要的数学基础。2、课程分目标:课程分目标1:微分方程了解微分方程的概念。掌握不同类型微分方程的解法。会用微分方程解一些简单的几何和物理问题。课程分目标2:多元函数微分法及其应用了解多元函数的概念和二元函数的极限与连续性的概念。了解和掌握偏导数和全微分的概念,以及它们的应用。课程分目标3:重积分理解二重积分、三重积分的概念,了解重积分的性质。掌握二重积分的计算方法和三重积分的计算方法。会用重积分求一些几何量与物理量。课程分目标4:无穷级数理解无穷级数收敛、发散以及和的概念,了解无穷级数基本性质及收敛的必要条件。了解函数项级数的收敛域及和函数的概念。掌握幂级数和傅里叶级数展开与和函数的相关内容。课程分目标5:空间解析几何与向量代数理解空间直角坐标系和向量的概念,掌握向量的运算。掌握平面,直线,常用二次曲面和空间曲线的方程及相关内容。二、课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图课程模块学时数支撑的课程分目标教学内容与教学要求14第七章:微分方程1.了解微分方程的概念。课程分目标11
1 高等数学 B(下) 一、 课程基本情况 课程编号: 课程总学时:72 课程学分:4.5 课程分类:必修 开课学期:春 开课单位:理学院应用数学系 适用专业:生物与食品相关专业 所需先修课:无 课程负责人:王新平、邹辉 二、课程目标: 1、课程总目标: 通过本课程的学习,使学生获得多元函数微分学、多元函数积分学、级数和微分方程等方面的基 本概念、基本理论和基本运算技能。使学生掌握高等数学的基本理论知识的同时,培养学生的抽象思 维能力、逻辑推理能力、运算能力、分析问题和解决问题的能力,提高学生用数学方法分析和处理本 专业领域中数量关系的能力,为学习后继课程和进一步获取数学知识奠定必要的数学基础。 2、课程分目标: 课程分目标 1:微分方程 了解微分方程的概念。掌握不同类型微分方程的解法。会用微分方程解一些简单的几何和物理问 题。 课程分目标 2:多元函数微分法及其应用 了解多元函数的概念和二元函数的极限与连续性的概念。了解和掌握偏导数和全微分的概念,以 及它们的应用。 课程分目标 3:重积分 理解二重积分、三重积分的概念,了解重积分的性质。掌握二重积分的计算方法和三重积分的计 算方法。会用重积分求一些几何量与物理量。 课程分目标 4:无穷级数 理解无穷级数收敛、发散以及和的概念,了解无穷级数基本性质及收敛的必要条件。了解函数项 级数的收敛域及和函数的概念。掌握幂级数和傅里叶级数展开与和函数的相关内容。 课程分目标 5:空间解析几何与向量代数 理解空间直角坐标系和向量的概念,掌握向量的运算。掌握平面,直线,常用二次曲面和空间曲 线的方程及相关内容。 二、 课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图 课程模块 教学内容与教学要求 学时数 支撑的课程分目标 第七章:微分方程 1.了解微分方程的概念。 14 课程分目标 1
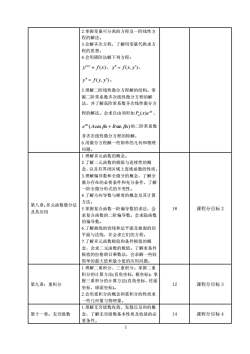
2.掌握变量可分离的方程及一阶线性方程的解法。3.会解齐次方程,了解用变量代换求方程的思想。4.会用降阶法解下列方程:y(n) = f(x), y"=f(x,y),y"= f(y,y')。5.理解二阶线性微分方程解的结构。掌握二阶常系数齐次线性微分方程的解法,并了解高阶常系数齐次线性微分方程的解法。会求自由项形如P,(x)ee(Acosx+BsinBx)的二阶常系数非齐次线性微分方程的特解。6.用微分方程解一些简单的几何和物理问题。1.理解多元函数的概念。2.了解二元函数的极限与连续性的概念,以及有界闭区域上连续函数的性质。3.理解偏导数和全微分的概念,了解全微分存在的必要条件和充分条件,了解一阶全微分形式的不变性。4.了解方向导数与梯度的概念及其计算方法。第八章:多元函数微分法18课程分目标25.掌握复合函数一阶偏导数的求法,会及其应用求复合函数的二阶偏导数。会求隐函数的偏导数。6.了解曲线的切线和法平面及曲面的切平面与法线,并会求它们的方程。7.了解多元函数极值和条件极值的概念,会求二元函数的极值。了解求条件极值的拉格朗日乘数法,会求解一些较简单的最大值和最小值的应用问题。1.理解二重积分、三重积分。掌握二重积分的计算方法(直角坐标,极坐标):掌握三重积分的计算方法(直角坐标、柱面12第九章:重积分课程分目标3坐标、球面坐标)。2.会用重积分的概念和重积分的性质求一些几何量与物理量。1.理解无穷级数收敛、发散以及和的概14第十一章:无穷级数念,了解无穷级数基本性质及收敛的必课程分目标4要条件。2
2 2.掌握变量可分离的方程及一阶线性方 程的解法。 3.会解齐次方程,了解用变量代换求方 程的思想。 4.会用降阶法解下列方程: ( ) ( ) y f x n = , y = f (x, y), y = f ( y, y) 。 5.理解二阶线性微分方程解的结构。掌 握二阶常系数齐次线性微分方程的解 法,并了解高阶常系数齐次线性微分方 程的解法。会求自由项形如 x n P x e ( ) 、 e (Acos x Bsin x) x + 的二阶常系数 非齐次线性微分方程的特解。 6.用微分方程解一些简单的几何和物理 问题。 第八章:多元函数微分法 及其应用 1.理解多元函数的概念。 2.了解二元函数的极限与连续性的概 念,以及有界闭区域上连续函数的性质。 3.理解偏导数和全微分的概念,了解全 微分存在的必要条件和充分条件,了解 一阶全微分形式的不变性。 4.了解方向导数与梯度的概念及其计算 方法。 5.掌握复合函数一阶偏导数的求法,会 求复合函数的二阶偏导数。会求隐函数 的偏导数。 6.了解曲线的切线和法平面及曲面的切 平面与法线,并会求它们的方程。 7.了解多元函数极值和条件极值的概 念,会求二元函数的极值。了解求条件 极值的拉格朗日乘数法,会求解一些较 简单的最大值和最小值的应用问题。 18 课程分目标 2 第九章:重积分 1.理解二重积分、三重积分。掌握二重 积分的计算方法(直角坐标,极坐标);掌 握三重积分的计算方法(直角坐标、柱面 坐标、球面坐标)。 2.会用重积分的概念和重积分的性质求 一些几何量与物理量。 12 课程分目标 3 第十一章:无穷级数 1.理解无穷级数收敛、发散以及和的概 念,了解无穷级数基本性质及收敛的必 要条件。 14 课程分目标 4
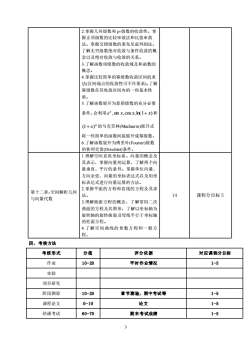
2.掌握几何级数和p-级数的收敛性。掌握正项级数的比较审敛法和比值审敛法。掌握交错级数的莱布尼兹判别法。了解无穷级数绝对收敛与条件收敛的概念以及绝对收敛与收敛的关系。3.了解函数项级数的收敛域及和函数的概念。4.掌握比较简单的幂级数收敛区间的求法(区间端点的收敛性可不作要求)。了解幂级数在其收敛区间内的一些基本性质。5.了解函数展开为泰勒级数的充分必要条件。会利用e*sinxcosx,ln(1+x)和(1+x)"的马克劳林(Maclaurin)展开式将一些简单的函数间接展开成幂级数。6.了解函数展开为傅里叶(Fourier)级数的狄利克雷(Dirichlet)条件。1.理解空间直角坐标系。向量的概念及其表示,掌握向量的运算,了解两个向量垂直、平行的条件。掌握单位向量、方向余弦、向量的坐标表达式以及用坐标表达式进行向量运算的方法。2.掌握平面的方程和直线的方程及其求第十二章:空间解析几何14法。课程分目标5与向量代数3.理解曲面方程的概念,了解常用二次曲面的方程及其图形,了解以坐标轴为旋转轴的旋转曲面及母线平行于坐标轴的柱面方程。4.了解空间曲线的参数方程和一般方程。四、考核方法考核形式分值评分依据对应课程分目标作业10-20平时作业情况1-5实验项目研究1-5阶段测验章节测验,期中考试等1020论文课程论文0-101-5结课考试60-70期末考试成绩1-53
3 2.掌握几何级数和 p-级数的收敛性。掌 握正项级数的比较审敛法和比值审敛 法。掌握交错级数的莱布尼兹判别法。 了解无穷级数绝对收敛与条件收敛的概 念以及绝对收敛与收敛的关系。 3.了解函数项级数的收敛域及和函数的 概念。 4.掌握比较简单的幂级数收敛区间的求 法(区间端点的收敛性可不作要求)。了解 幂级数在其收敛区间内的一些基本性 质。 5.了解函数展开为泰勒级数的充分必要 条件。会利用 e ,sin x,cos x,ln(1 x) x + 和 (1+ x) 的马克劳林(Maclaurin)展开式 将一些简单的函数间接展开成幂级数。 6.了解函数展开为傅里叶(Fourier)级数 的狄利克雷(Dirichlet)条件。 第十二章:空间解析几何 与向量代数 1.理解空间直角坐标系。向量的概念及 其表示,掌握向量的运算,了解两个向 量垂直、平行的条件。掌握单位向量、 方向余弦、向量的坐标表达式以及用坐 标表达式进行向量运算的方法。 2.掌握平面的方程和直线的方程及其求 法。 3.理解曲面方程的概念,了解常用二次 曲面的方程及其图形,了解以坐标轴为 旋转轴的旋转曲面及母线平行于坐标轴 的柱面方程。 4.了解空间曲线的参数方程和一般方 程。 14 课程分目标 5 四、考核方法 考核形式 分值 评分依据 对应课程分目标 作业 10-20 平时作业情况 1-5 实验 项目研究 阶段测验 10-20 章节测验,期中考试等 1-5 课程论文 0-10 论文 1-5 结课考试 60-70 期末考试成绩 1-5

五、使用教材或主要参考书:(列出教材及参数名称、主编人、出版社、出版时间及版次)教材:《高等数学(下)》,同济大学应用数学系主编,高等教育出版社,2014年7月第7版。执笔人:王新平邹辉审定人:2016年9月19日制定4
4 五、使用教材或主要参考书:(列出教材及参数名称、主编人、出版社、出版时间及版次) 教材:《高等数学(下)》,同济大学应用数学系主编,高等教育出版社,2014 年 7 月第 7 版。 执笔人:王新平 邹辉 审定人: 2016 年 9 月 19 日制定

Advanced Mathematics()1. Basic informationCourse code:Totalteachinghours:72,amongwhich hoursforlectures,ohoursforexperiments,Qhoursforon-line teaching.Credits:4.5Typeofthecourse:compulsoryTeaching terms: springOwnerofthecourse:DepartmentofAppliedMathematics,CollegeofScienceMajors applicable:Biological scienceandFoodscience,etcPrerequisites: nonePerson in charge of the course: Xinping Wang, HuiZou2.Course Objectives(1)GeneralAimThe course consists of four parts: multivariable differential calculus,multivariable integral calculus,series and differential equations. Besides teaching students the fundamental theory of mathematics, thecourse also aims at giving the students the ability of abstract thinking, logical reasoning, computinganalyzing and solving. improving the ability of analyze and process quantitative relationships appearedin their own majors with mathematical methods, building a solid foundation for the students for thestudies of subsequentcourses andfuture process in mathematicalknowledge acquisition.(2)BranchObjectivesTheFirst one:Understand the concept ofdifferential equations.Be ableto solvedifferent types ofdifferential equations.Be able to solve some simple geometry and physics problems by using diferentialequations.The Second one:Understand the concept of multivariate functions and the concepts of limits and continuitiesfor binary functions.Understand the concepts of partial derivatives and total differential, and master theapplicationof them.The Third one:Understand the concepts of double and triple integrals.Know the properties of multipleintegrals.Masterthe computation of doubleintegrals and triple integrals.Beabletocalculate somegeometricor physical quantities by multiple integrals.The Fouth one: Understand the concepts of convergence, divergence and sum for infinite series, know thebasic properties for infinite series and necessary conditions for convergence. Know the convergence domainand sumfunctions forfunction series.Grasp sum functionsand expansionsofpower series andFourierseries.The Fifth oneUnderstand rectangular coordinates systems in space and concepts of vectors, master theoperations of vectors. Master the equations and reluctant content of planes, lines, the frequently usedquadratic surfaces and spatial curves.3、TheDiagram between Course Content、Teaching Requirements and Course ObjectivesCorrespondingCourse Content andCourse ModulesClass hoursTeaching RequirementsCourse Objectives5
5 Advanced Mathematics(II) 1. Basic information Course code: Total teaching hours: 72 , among which_0_ hours for lectures, _0_ hours for experiments, _0_hours for on-line teaching. Credits:4.5 Type of the course: compulsory Teaching terms: spring Owner of the course: Department of Applied Mathematics, College of Science Majors applicable: Biological science and Food science, etc. Prerequisites: none Person in charge of the course: Xinping Wang, Hui Zou 2. Course Objectives (1)General Aim The course consists of four parts: multivariable differential calculus, multivariable integral calculus, series and differential equations. Besides teaching students the fundamental theory of mathematics, the course also aims at giving the students the ability of abstract thinking, logical reasoning, computing, analyzing and solving, improving the ability of analyze and process quantitative relationships appeared in their own majors with mathematical methods, building a solid foundation for the students for the studies of subsequent courses and future process in mathematical knowledge acquisition. (2)Branch Objectives The First one:Understand the concept of differential equations. Be able to solve different types of differential equations. Be able to solve some simple geometry and physics problems by using differential equations. The Second one:Understand the concept of multivariate functions and the concepts of limits and continuities for binary functions. Understand the concepts of partial derivatives and total differential, and master the application of them. The Third one:Understand the concepts of double and triple integrals. Know the properties of multiple integrals. Master the computation of double integrals and triple integrals. Be able to calculate some geometric or physical quantities by multiple integrals. The Fouth one:Understand the concepts of convergence, divergence and sum for infinite series, know the basic properties for infinite series and necessary conditions for convergence. Know the convergence domain and sum functions for function series. Grasp sum functions and expansions of power series and Fourier series. The Fifth one:Understand rectangular coordinates systems in space and concepts of vectors, master the operations of vectors. Master the equations and reluctant content of planes, lines, the frequently used quadratic surfaces and spatial curves. 3、The Diagram between Course Content、Teaching Requirements and Course Objectives Course Modules Course Content and Teaching Requirements Class hours Corresponding Course Objectives
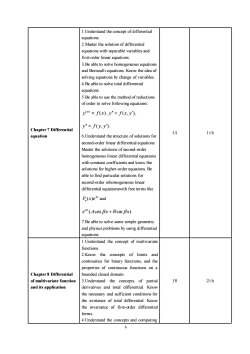
1.Understandtheconceptofdifferentialequations.2.Master the solution of differentialequations with separable variables andfirst-order linear equations.3.Be able to solve homogeneous equationsand Bernoulli equations. Know the idea ofsolving equations by change of variables4.Be able to solve total differentialequations.5.Be able to use the methodof reductionsof order to solve following equations:y(n) = f(x), y"= f(x,y),y"= f(y,y')Chapter7Differential141thequation6.Understand the structure of solutions forsecond-order linear differential equationsMasterthe solutionsof second-orderhomogeneous lineardifferential equationswith constant coefficients and know thesolutions for higher-order equations. Beable to find particular solutions forsecond-order inhomogeneous lineardifferential equationswith freeterms likeP,(x)e* and*(Acosβx+Bsinβx)7.Be able to solve some simple geometryand physics problems by using differentialequations.1.Understand the concept of multivariatefunctions.2.Know the concepts of limits andcontinuities for binary functions, and therproperties of continuous functions on aChapter 8 Differentialbounded closed domain182thofmultivariate function3.Understand the concepts of partialderivatives and total differential.Knowandits applicationthe necessary and sufficient conditions forthe existence of total differential.Knowthe invariance of first-order differentialforms.4.Understandtheconcepts and computing6
6 Chapter 7 Differential equation 1.Understand the concept of differential equations. 2.Master the solution of differential equations with separable variables and first-order linear equations. 3.Be able to solve homogeneous equations and Bernoulli equations. Know the idea of solving equations by change of variables. 4.Be able to solve total differential equations. 5.Be able to use the method of reductions of order to solve following equations: ( ) ( ) y f x n = , y = f (x, y), y = f ( y, y) . 6.Understand the structure of solutions for second-order linear differential equations. Master the solutions of second-order homogeneous linear differential equations with constant coefficients and know the solutions for higher-order equations. Be able to find particular solutions for second-order inhomogeneous linear differential equationswith free terms like ( ) x P x e n and ( cos sin ) x e A x B x + . 7.Be able to solve some simple geometry and physics problems by using differential equations. 14 1th Chapter 8 Differential of multivariate function and its application 1.Understand the concept of multivariate functions. 2.Know the concepts of limits and continuities for binary functions, and the properties of continuous functions on a bounded closed domain. 3.Understand the concepts of partial derivatives and total differential. Know the necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of total differential. Know the invariance of first-order differential forms. 4.Understand the concepts and computing 18 2th
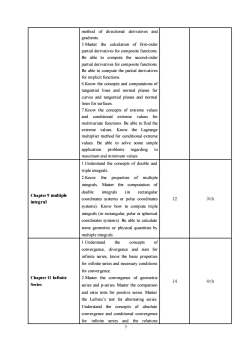
method of directional derivatives andgradients.5.Master the calculation of first-orderpartial derivatives for composite functions.Be able to compute the second-ordertpartial derivatives for composite functionsBe able to compute the partial derivativesfor implicit functions.6.Knowtheconcepts and computations oftangential lines and normal planes forcurves and tangential planes and normallines for surfaces7.Know the concepts of extreme valuesandconditionalextremevaluesformultivariate functions. Be able to find theextremevalues.Know theLagrangemultiplier method for conditional extremevalues. Be able to solve some simpleproblemsregardingtoapplicationmaximumandminimumvalues1.Understand the concepts of double andtriple integrals.2.Knowthepropertiesofmultipleintegrals.Master the computation ofdouble(inrectangularintegralsChapter9 multiple123thcoordinates systems or polar coordinatesintegralsystems).Know how to compute tripleintegrals (in rectangular, polar or sphericalcoordinates systems).Be able to calculatesome geometric or physical quantities bymultiple integralstheof1.Understandconceptssumforconvergence,divergence andinfinite series, know the basic propertiesfor infinite series and necessary conditionsfor convergenceChapter11 Infinite2.Master the convergence of geometric144thSeriesseries and p-series. Master the comparisonand ratio tests for positive series. Masterthe Leibniz's test for alternating series.Understand theconceptsof absoluteconvergence and conditional convergenceforinfiniteandtherelationsseries7
7 method of directional derivatives and gradients. 5.Master the calculation of first-order partial derivatives for composite functions. Be able to compute the second-order partial derivatives for composite functions. Be able to compute the partial derivatives for implicit functions. 6.Know the concepts and computations of tangential lines and normal planes for curves and tangential planes and normal lines for surfaces. 7.Know the concepts of extreme values and conditional extreme values for multivariate functions. Be able to find the extreme values. Know the Lagrange multiplier method for conditional extreme values. Be able to solve some simple application problems regarding to maximum and minimum values Chapter 9 multiple integral 1.Understand the concepts of double and triple integrals. 2.Know the properties of multiple integrals. Master the computation of double integrals (in rectangular coordinates systems or polar coordinates systems). Know how to compute triple integrals (in rectangular, polar or spherical coordinates systems). Be able to calculate some geometric or physical quantities by multiple integrals. 12 3th Chapter 11 Infinite Series 1.Understand the concepts of convergence, divergence and sum for infinite series, know the basic properties for infinite series and necessary conditions for convergence. 2.Master the convergence of geometric series and p-series. Master the comparison and ratio tests for positive series. Master the Leibniz’s test for alternating series. Understand the concepts of absolute convergence and conditional convergence for infinite series and the relations 14 4th
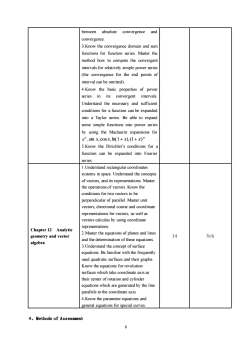
andabsolutebetweenconvergenceconvergence.3.Knowtheconvergencedomain and sumfunctions for function series. Master themethod how to compute the convergentintervals for relatively simple power series(the convergence for the end points ofintervalcanbeomitted)4.Know the basic propertiesof powerseries in its convergent intervals.Understand the necessary and sufficientconditions for a function can be expandedinto a Taylor series. Be able to expandsome simple functions into power seriesby using the Maclaurin expansions fore",sin x,cosx, In(1+ x),(1+ x)"5.Know the Dirichlet's conditions for afunction can be expanded into Fourierseries1.Understand rectangular coordinatessystems in space. Understand the conceptsofvectors,anditsrepresentations.Masterthe operations of vectors.Know theconditions for two vectors to beperpendicular of parallel. Master unitvectors, directional cosine and coordinaterepresentations for vectors, as well asvectors calculus by using coordinaterepresentations.Chapter122Analytic2.Master the equations of planes and lines145thgeometry and vectorand thedeterminationofthese equationsalgebra3.Understandtheconceptofsurfaceequations.Be familiar with the frequentlyused quadratic surfaces and their graphs.Knowthe equations for revolutionsurfaces whichtake coordinateaxis astheir center of rotation and cylinderequations which are generated by the lineparallels to the coordinate axis.4.Knowtheparameterequationsandgeneral equations for special curves4、Methodsof Assessment8
8 between absolute convergence and convergence. 3.Know the convergence domain and sum functions for function series. Master the method how to compute the convergent intervals for relatively simple power series (the convergence for the end points of interval can be omitted). 4.Know the basic properties of power series in its convergent intervals. Understand the necessary and sufficient conditions for a function can be expanded into a Taylor series. Be able to expand some simple functions into power series by using the Maclaurin expansions for e ,sin x,cos x,ln(1 x),(1 x) x + + . 5.Know the Dirichlet’s conditions for a function can be expanded into Fourier series. Chapter 12 Analytic geometry and vector algebra 1.Understand rectangular coordinates systems in space. Understand the concepts of vectors, and its representations. Master the operations of vectors. Know the conditions for two vectors to be perpendicular of parallel. Master unit vectors, directional cosine and coordinate representations for vectors, as well as vectors calculus by using coordinate representations. 2.Master the equations of planes and lines and the determination of these equations. 3.Understand the concept of surface equations. Be familiar with the frequently used quadratic surfaces and their graphs. Know the equations for revolution surfaces which take coordinate axis as their center of rotation and cylinder equations which are generated by the line parallels to the coordinate axis. 4.Know the parameter equations and general equations for special curves. 14 5th 4、Methods of Assessment
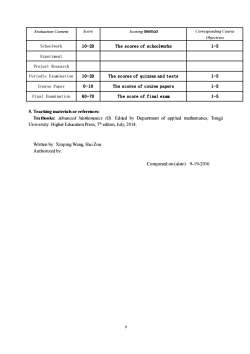
ScoreEvaluation ContentScoringMethodCorresponding CourseObjectives1-510-20SchoolworkThe scores of schoolworksExperimentProject Research1-510-20PeriodicExaminationThe scores of quizzes and tests1-50-10Course PaperThe scores of course papers60-701-5Final ExaminationThe score of final exam5.Teaching materials or references:Textbooks:AdvancedMathematics(l).Edited by Department of applied mathematics, TongjiUniversity.HigherEducationPress,7tediton,July,2014Written by:Xinping Wang,HuiZouAuthorizedby:9-19-2016Composed on(date)9
9 Evaluation Content Score Scoring Method Corresponding Course Objectives Schoolwork 10-20 The scores of schoolworks 1-5 Experiment Project Research Periodic Examination 10-20 The scores of quizzes and tests 1-5 Course Paper 0-10 The scores of course papers 1-5 Final Examination 60-70 The score of final exam 1-5 5. Teaching materials or references: Textbooks: Advanced Mathematics (II). Edited by Department of applied mathematics, Tongji University. Higher Education Press, 7th editon, July, 2014. Written by: Xinping Wang, Hui Zou Authorized by: Composed on (date) 9-19-2016
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 C(下).docx
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第一节 向量的内积.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第三节 相似矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第二节 方阵的特征值与特征向量.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第五节 二次型及其标准型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第四节 对称矩阵的相似矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第六节 用配方法化二次型成标准型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 相似矩阵及二次型 第七节 正定二次型.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-4 线性方程组的解的结构.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-1 向量组及其线性组合.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-3 向量组的秩.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-5 向量空间.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 向量组的线性相关性 4-2 向量组的线性相关性.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-2 初等矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-4 线性方程组的解.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-1 矩阵的初等变换.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组 3-3 矩阵的秩.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-2 矩阵的运算.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-1 矩阵.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 矩阵及其运算 2-4 矩阵分块法.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 C(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 B(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 A(下).docx
- 《高等数学》课程教学大纲 A(上).docx
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十一章 无穷级数.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十章 曲线积分与曲面积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十二章 微分方程.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第九章 重积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 定积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第八章 多元函数微分法及其应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 定积分的应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 导数与微分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 不定积分.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第七章 空间解析几何与向量代数.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 函数与极限.pdf
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-0 简介.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-习题课.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-09 第九节 连续函数的运算与初等函数的连续性.ppt
- 《高等数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 函数与极限 1-10 第十节 闭区间上连续函数的性质.ppt
