《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 4 Acid-base equilibria

G 归东理工大军 Analytical Chemistry >To master the requirements of the titration error; To know about the classical applications and calculation of all kinds of titrations. 20254/6
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 2 ➢To master the requirements of the titration error; ➢ To know about the classical applications and calculation of all kinds of titrations

山东理子大军 Analytical Chemistry 4.1 Acid-base equilibria 1.Acid-base theory The acidity or basicity of a solution is frequently an important factor in chemical reactions.Fundamental acid-base equilibria are important in understanding acid-base titration and the effect of acids on chemical species and reactions. According to Bronsted theory: >An acid is a substance that can give up protons; >A base is any compound or ion that can accept protons. 202514/
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 3 §4.1 Acid-base equilibria 1. Acid-base theory The acidity or basicity of a solution is frequently an important factor in chemical reactions. Fundamental acid-base equilibria are important in understanding acid-base titration and the effect of acids on chemical species and reactions. According to Bronsted theory: ➢An acid is a substance that can give up protons; ➢A base is any compound or ion that can accept protons

G 归东理2大军 Analytical Chemistry >A strong acid or base is completely dissociated in aqueous solution; >A weak acid is one that is only partially dissociated in water,all weak acids HA react with water by donating a proton to H2O: HA+H,O→HO++A The acid dissociation constant is K,=H*4】 HA] 20254/6
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 4 ➢A strong acid or base is completely dissociated in aqueous solution; ➢A weak acid is one that is only partially dissociated in water, all weak acids HA react with water by donating a proton to H2O: + − HA + H2 O H3 O + A The acid dissociation constant is [HA] [H ][A ] + − Ka =

归东理工大买 Analytical Chemistry For a strong acid,the K,is large and small for a weak acid. And the base dissociation constant is expressed as Kp. Note that the acid and the base constitute conjugate acid-base pair. And for any acid-base pair, Ka·Kb=Kw for polyprotic acids,such as H3A, Ka1K3=Ka2·K2=Ka3K1=K。 20254/6
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 5 For a strong acid, the Ka is large and small for a weak acid. And the base dissociation constant is expressed as Kb . Note that the acid and the base constitute conjugate acid-base pair. And for any acid-base pair, Ka Kb = Kw for polyprotic acids, such as H3A, Ka Kb Ka Kb Ka Kb = Kw = = 1 3 2 2 3 1
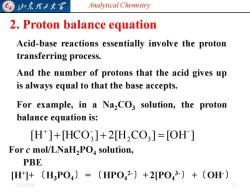
G 归东理2大军 Analytical Chemistry 2.Proton balance equation Acid-base reactions essentially involve the proton transferring process. And the number of protons that the acid gives up is always equal to that the base accepts. For example,in a NaCO3 solution,the proton balance equation is: [H]+HCO3]+2H2C03]=[OH] For c mol/LNaH2PO solution, PBE [H]+(H3PO4)=(HPO42-)+2P043-)+(OH) 20254/6
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 6 2. Proton balance equation Acid-base reactions essentially involve the proton transferring process. And the number of protons that the acid gives up is always equal to that the base accepts. For example, in a Na2CO3 solution, the proton balance equation is: [H ] [HCO ] 2[H CO ] [OH ] - 2 3 - + 3 + = + For c mol/LNaH2PO4 solution, PBE [H+ ]+ 〔H3PO4〕 = 〔HPO4 2-〕+ 2[PO4 3-〕 +〔OH-〕

归东理工大军 Analytical Chemistry 3.Calculation of pH (1)Solutions of strong acids and bases In an aqueous solution of strong acid (HA),the proton balance equation is [H]=[A]+[OH] Suppose the concentration of the acid is c mol/L, as we know the strong acids dissociate completely in aqueous solution,if c>10-6 mol/L,then, c=[H]=[A] 20254/6
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 7 3. Calculation of pH (1) Solutions of strong acids and bases In an aqueous solution of strong acid (HA), the proton balance equation is [H ] [A ] [OH ] - - = + + Suppose the concentration of the acid is c mol/L, as we know the strong acids dissociate completely in aqueous solution, if c>10-6 mol/L, then, [H ] [A ] + − c = =

G归东理工大军 Analytical Chemistry if c<10-6 mol/L, The autoprotolysis of water should not be neglected, [H]=c+ Kv [H] []=C++4K 2 For strong bases,similar equations can be derived for calculation of [OH-]. 20254/0
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 8 if c<10-6 mol/L, The autoprotolysis of water should not be neglected, [H ] [H ] + + = + Kw c 2 4 [H ] 2 Kw c + c + = + For strong bases, similar equations can be derived for calculation of [OH- ]

归东理工大买 Analytical Chemistry (2)Solutions of weak acids and bases The pH of a weak acid can be calculated from the dissociation constant,K Similarly,the pH of a weak base can be calculated from its K value. For a strong bases,similar equations can be derived for calculation of [OH-]. For a weak acid,HA,we can write its proton balance equation: [H]=[A]+[OH] 20254/6
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 9 (2) Solutions of weak acids and bases The pH of a weak acid can be calculated from the dissociation constant, Ka . Similarly, the pH of a weak base can be calculated from its Kb value. For a strong bases, similar equations can be derived for calculation of [OH- ]. For a weak acid, HA, we can write its proton balance equation: [H ] [A ] [OH ] - - = + +

G 归东理工大军 Analytical Chemistry [H]= Ko[HA],K H'] H'] We obtain [H']=K[HA]+K If K is not extremely small,that is cK。≥20Kw The Kw can be neglected,so [H]K[HA]=K(c-[H]) H门=-K,+VK+4Kc 2 20254/0
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 10 We obtain = Ka + Kw + [H ] [HA] a Kw cK 20[H ] [H ] [HA] [H ] + + + = + Ka Kw If Ka is not extremely small, that is The Kw can be neglected, so [H ] [HA] ( [H ]) + + Ka = Ka c − 2 4 [H ] 2 K K K c − a + a + a = +

山东理大 Analytical Chemistry Ifc/Ka≥400,the concentration of Ha can be considered c,the analytical concentration of the weak acid,then [H']=K.c This is the simplified equation. Similarly,the simplified equation of a weak base concentration is [OH ]=Kc 20254/6
Analytical Chemistry 2025/4/6 11 If c/Ka ≥400, the concentration of HA can be considered c, the analytical concentration of the weak acid, then K c = a + [H ] This is the simplified equation. Similarly, the simplified equation of a weak base concentration is K c = b − [OH ]
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文)Chapter 2 Errors and data treatment in quantitative analysis.pdf
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)重量分析2/2.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)重量分析1/2.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)酸碱滴定法(acid-base titration).ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)络合滴定2/2.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)络合滴定1/2.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)滴定分析法概述.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)沉淀滴定法.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)氧化还原滴定法 Oxidation-Reduction Titration.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)分析化学中的误差.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 热力学第一定律.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)酸碱滴定法(acid-base titration).ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)电化学_电解质溶液.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)热力学第一定律及其应用.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)总结.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第八章 表面现象分散系统.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 多相平衡 Phase Equilibrium.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 化学势.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 电化学.ppt
- 《物理化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第九章 化学动力学基本原理.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 6 Oxidation-reduction titration.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)绪论 Analytical chemistry(化学分析部分).ppt
- 《分析化学》课程各章 思考题(含答案)第七章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程各章 思考题(含答案)第九章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程各章 思考题(含答案)第八章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程各章 思考题(含答案)第十章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(各章知识点)第六章 配位滴定法、第七章 氧化还原滴定法、第八章 沉淀滴定法.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(各章知识点)第一章 概论、第三章 误差及数据处理、第五章 酸碱滴定法.doc
- 《高分子化学实验》课程实验指导(讲义)实验五 聚丙烯腈的部分水解反应.doc
- 《高分子化学实验》课程实验指导(讲义)实验四 三聚氰胺甲醛树脂的合成及层压板的制备.doc
- 《高分子化学实验》课程实验指导(讲义)实验五 本体聚合MMA及其透光率测定.doc
- 《高分子化学实验》课程实验指导(讲义)实验二 丙烯酰胺溶液聚合及其干燥加工.doc
- 《高分子化学实验》课程实验指导(讲义)实验四 醋酸乙烯酯的乳液聚合及固含量测定.doc
- 《生物仪器分析》课程教学课件(讲稿)气相色谱液相色谱导论(气相色谱法、高效液相色谱法).ppt
- 高等教育出版社:《现代仪器分析》教材书籍PDF电子版(扫描版,第三版,主编:刘约权).pdf
- 《生物仪器分析》课程教学课件(讲稿)第一章 绪论(山东理工大学:徐征豹).pdf
- 《生物仪器分析》课程教学课件(讲稿)第七章 分子发光分析法.pdf
- 《生物仪器分析》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 原子发射光谱法.pdf
- 《生物仪器分析》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二章 光分析法导论——以物质的光学性质为基础而建立的分析方法.pdf
- 《生物仪器分析》课程教学课件(讲稿)第五章 紫外-可见吸收光谱分析(UV-VIS).pdf
