《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.6 typical crystal structure

1.6 typical crystal structure Body Centered Cubic Packing Space Group Im3m a=4r/(32 Atom Site x M 2a 0 0 0 *r=metallic radius Representative Examples Fe(a=2.8664A Cr(a=2.8846A) Mo(a=3.1469A W(a=3.1650A) Cubic or Hexagonal Close Packing Coordination Number =12 Ta(a=3.3026A) Packing Efficiency 74% Ba(a=5.019A) Body Centered Cubic Packing Coordination Number 8 Packing Efficiency 68%
1.6 typical crystal structure

1).bcc lattice (Li,Na,K,Rb,Cs.etc) One possible choice of primitive vectors lattice a constant a(+方-动 属-++头 A conventional unit cell, 属(-+头 (nonprimitive) Note:A bcc lattice is a simple lattice. But we can also treat it as a cubic lattice with a 2-point basis! (to take advantage of the cubic symmetry
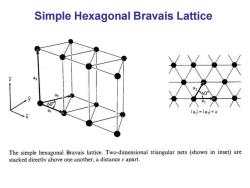
Simple Hexagonal Bravais Lattice 60 lal=la=a The simple hexagonal Bravais lattice.Two-dimensional triangular nets (shown in inset)are stacked directly above one another,a distance c apart
Simple Hexagonal Bravais Lattice

Conventional Primitive Unit Cells Points of Primitive Cell Hexagonal Bravais Lattice w Primitive Cell Conventional Cell Fractional coordinates of lattice points in conventional cell: 100,010,110,101,011 111,000,001 b
Conventional & Primitive Unit Cells Hexagonal Bravais Lattice Primitive Cell = Conventional Cell Fractional coordinates of lattice points in conventional cell: 100, 010, 110, 101, 011 111, 000, 001 Points of Primitive Cell a b c

Hexagonal Close Packed (HCP)Structure: (A Simple Hexagonal Bravais Lattice with a 2 Atom Basis) Figure 22 The hexagonal close-packed struc- ture.The atom positions in this structure do The HCP lattice is not a Bravais not constitute a space lattice.The space lattice is simple hexagonal with a basis of two identi- lattice,because the orientation of cal atoms associated with each lattice point. the environment of a point varies The lattice parameters a and c are indicated, where a is in the basal plane and c is the mag- from layer to layer along the c-axis. nitude of the axis ag of Fig.14
Hexagonal Close Packed (HCP) Structure: (A Simple Hexagonal Bravais Lattice with a 2 Atom Basis) The HCP lattice is not a Bravais lattice, because the orientation of the environment of a point varies from layer to layer along the c-axis

Hexagonal Close Packed (HCP)Lattice Hexagonal Close Packed and related structures Crystal cla Crystal cla Crystal clu He 1.633 1.861 1.594 Be 1.581 d 1.886 d 1.592 Mg 1.623 Co 1.622 Lu 1.586 1.586 Y 1.570
Hexagonal Close Packed (HCP) Lattice

3).hcp structure (=simple hexagonal lattice a 2-point basis.) e.g.Be,Mg.etc.complex lattices 2 overlapping "simple hexagonal lattices" d(dxa,)ae nt basis For ideal hcp structure Figure 22 The hexagonal close-packed struc Figure 23 The primitive cell has a,=ag ture.The atom positions in this structure do with an included angle of 120.The e axis (or not constitute a space lattice.The space lattice snormal to the plane of a and The /8 is simple hexagonal with a basts of two identi- ideal hep structure hase=1.633 The two C cal atoms associated with each lattice point. atoms of one basis are shown as solid cireles. One atom of the basis is at the origin:the a N =1.633 The lattice parameters a and c are indicated where a is in the basal plane and c is the mag. other atom is at which means at the posi nitude of the axis a of Fig 14. tion r ia+a:+las. >Primitive vectors:a,a2,c [c=2av(2/3)for hcp] >The 2 atoms of the basis are located at d,=0 and atd2=(2/3)a1+(13)a2+(1/2)c
a a a a c 2 1 2 3 2 3 ( ) = 1.633 3 8 = = a c For ideal hcp structure

Hexagonal Close Packed (HCP)Lattice Bravais Lattice: a=b Hexagonal Lattice Angle between a b=120 He,Be,Mg,Hf,Re c=1.633a, (Group IⅡelements) basis: ABABAB Type of Stacking (0,0,0)(2/3a,1/3a,1/2c)
Crystal Structure 8 Bravais Lattice : Hexagonal Lattice He, Be, Mg, Hf, Re (Group II elements) ABABAB Type of Stacking a = b Angle between a & b = 120° c = 1.633a, basis: (0,0,0) (2/3a ,1/3a,1/2c) Hexagonal Close Packed (HCP) Lattice

Close Packed Array of Spheres The gray spheres represent a 2D Close Packed Array. In 3D the next layer of spheres could sit on the depressions marked in red (B)or those marked in blue (C). AB Stacking AC Stacking
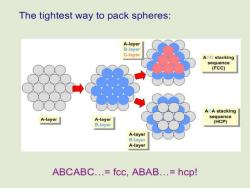
The tightest way to pack spheres: A-layer B-layer C-layer ABC stacking sequence (FCC) ABA stacking A-layer A-layer sequence (HCP) B-layer A-layer B-layer A-layer ABCABC.=fcc,ABAB.=hcp!
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.7 Lattice Sites in a Cubic Unit Cell 1.8 crystal plane and miller index.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学资源(参考资料)词汇汉英对照.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 能带理论.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 晶体结构.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 晶体的结合.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 晶格振动.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 晶体结构的测定.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)晶体能带结构理解电导特性.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 固体电子论基础.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)紧束缚近似理论研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)非谐效应——热膨胀研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程教学大纲 Solid State Physics.pdf
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第4章 晶圆制造与外延硅生长.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第2章 集成电路工艺介绍.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 化学气相沉积与电介质薄膜.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第5章 加热工艺.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第1章 半导体制程技术导论.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第2章 集成电路工艺介绍.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第3章 半导体基础原理、组件与制程.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第6章 光刻工艺.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.1 Elementary Crystallography 1.2 Crystal Structure ≡ Lattice + Basis 1.3 Lattice Translation Vectors 1.4 Non-Bravais Lattices 1.5 Wigner-Seitz Method.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Introduction.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure(Supplement - microstructure and crystal system).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.9 Elements of Symmetry 1.10 Space groups 1.11 7 crystal system and 14 Bravis Lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(supplement - Review & Overview of X-Rays).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice 2.6 X-Ray Diffraction Methods 2.7 Applications of XRD.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(2.1-2.5).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3(Supplement - Rules of crystal binding).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.1 General crystal binding 3.2 typical binding.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.1 Normal Modes of Vibration 4.2 Density of States 4.3 Harmonic approximation and normal mode coordinates 4.4 phonon.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.5 Heat capacity of the lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.1 general background and approximations 5.2 Bloch’s Theorem.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.6 Anharmonic Effects 4.7 Equation of states for Lattice 4.8 Experimental methods for the determinations of lattice vibration spectroscopy.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4(supplement - Thermal Expansion of Glass).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.5 The symmetry of bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.3 Nearly Free Electron 5.4 BZ and energy bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.4 Tight Binding Approximation(TBA).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.1 The quasi-classical description of Bloch electrons 6.2. Electron quasi-momentum 6.3 The accelerated velocity and effective mass.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6(supplement - a more concise description of quasi-momentum).ppt
