《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.1 Elementary Crystallography 1.2 Crystal Structure ≡ Lattice + Basis 1.3 Lattice Translation Vectors 1.4 Non-Bravais Lattices 1.5 Wigner-Seitz Method

Chapter 1:Crystal Structure Objectives At the end of this Chapter,you should: 1.Be able to identify a unit cell in a symmetrical pattern. 2.Know that there are7 Possible unit cell shapes. 3.Be able to define cubic,tetragonal,orthorhombic hexagonal unit cell shapes. 4.Know how to index the crystal plane and the crystal direction. 5.Understand the difference between complex lattice and simple lattice 6.Understand the symmetry elements
Objectives At the end of this Chapter, you should: 1.Be able to identify a unit cell in a symmetrical pattern. 2. Know that there are7 Possible unit cell shapes. 3. Be able to define cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic & hexagonal unit cell shapes. 4. Know how to index the crystal plane and the crystal direction. 5.Understand the difference between complex lattice and simple lattice 6. Understand the symmetry elements Chapter 1: Crystal Structure

The (Common)Phases of Matter MATTER LIQUIDS GASES AND LIQUID SOLIDS CRYSTALS This doesn't include Plasmas,but these are the“common”phases! “Condensed Matter”includes both ofthese.We'll focus on Solids!
The (Common) Phases of Matter Matter GASES LIQUIDS and LIQUID CRYSTALS SOLIDS “Condensed Matter” includes both of these. We’ll focus on Solids! This doesn’t include Plasmas, but these are the “common” phases!!

1.1 Elementary Crystallography Solid Material Types Crystalline Polycrystalline Amorphous (Non-Crystalline) Single Crystal
1.1 Elementary Crystallography Solid Material Types Crystalline Polycrystalline Amorphous (Non-Crystalline) Single Crystal

Single Crystal A Single Crystal has an atomic structure that repeats periodically across its whole volume.Even at infinite length scales,each atom is related to every other equivalent atom in the structure by translational symmetry. Single Crystals Single Pyrite Amorphous Crystal Solid
A Single Crystal has an atomic structure that repeats periodically across its whole volume. Even at infinite length scales, each atom is related to every other equivalent atom in the structure by translational symmetry. Single Crystals Single Pyrite Crystal Amorphous Solid Single Crystal

Polycrystalline Solids A Polycrystalline Solid is made up of an aggregate of many small single crystals have a high degree of order over many atomic or molecular dimensions,vary in size orientation with respect to one another.These regions are called grains (or domains) are separated from one another by grain boundaries. Polycrystals with grains that are 10 nm in diameter are called nanocrystallites Grain Boundaries (Differently red Crystals)
Polycrystalline Solids A Polycrystalline Solid is made up of an aggregate of many small single crystals , have a high degree of order over many atomic or molecular dimensions, vary in size & orientation with respect to one another. These regions are called grains (or domains) & are separated from one another by grain boundaries. Polycrystals with grains that are < 10 nm in diameter are called nanocrystallites

Amorphous Solids Amorphous (Non-crystalline)Solids are composed of randomly orientated atoms,ions,or molecules that do not form defined patterns or lattice structures.Amorphous materials have order only within a few atomic or molecular dimensions.They do not have any long-range order,but they have varying degrees of short-range order.Examples of amorphous material include amorphous silicon,plastics, glasses
Amorphous Solids • Amorphous (Non-crystalline) Solids are composed of randomly orientated atoms, ions, or molecules that do not form defined patterns or lattice structures. Amorphous materials have order only within a few atomic or molecular dimensions. They do not have any long-range order, but they have varying degrees of short-range order. Examples of amorphous material include amorphous silicon, plastics, & glasses
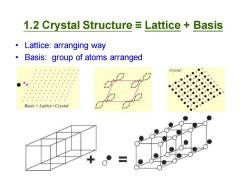
1.2 Crystal Structure Lattice Basis Lattice:arranging way Basis:group of atoms arranged Crystal ● ● ● ● ,● ● ●】 ●● ● ●● ●● Basis Lattice=Crystal
• Lattice: arranging way • Basis: group of atoms arranged 1.2 Crystal Structure ≡ Lattice + Basis

A Two-Dimensional Bravais Lattice with Different Choices for the Basis Bravais basis crystal lattice ●
A Two-Dimensional Bravais Lattice with Different Choices for the Basis

Crystal Structure Lattice Basis Basis The atoms do not necessarily lie at lattice points!!
9 Crystal Structure = Lattice + Basis Basis The atoms do not necessarily lie at lattice points!!
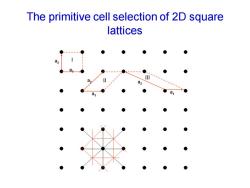
The primitive cell selection of 2D square lattices
The primitive cell selection of 2D square lattices
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.6 typical crystal structure.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.7 Lattice Sites in a Cubic Unit Cell 1.8 crystal plane and miller index.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学资源(参考资料)词汇汉英对照.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 能带理论.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 晶体结构.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 晶体的结合.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 晶格振动.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 晶体结构的测定.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)晶体能带结构理解电导特性.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 固体电子论基础.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)紧束缚近似理论研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)非谐效应——热膨胀研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程教学大纲 Solid State Physics.pdf
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第4章 晶圆制造与外延硅生长.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第2章 集成电路工艺介绍.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 化学气相沉积与电介质薄膜.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第5章 加热工艺.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第1章 半导体制程技术导论.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第2章 集成电路工艺介绍.ppt
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第3章 半导体基础原理、组件与制程.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Introduction.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure(Supplement - microstructure and crystal system).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.9 Elements of Symmetry 1.10 Space groups 1.11 7 crystal system and 14 Bravis Lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(supplement - Review & Overview of X-Rays).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice 2.6 X-Ray Diffraction Methods 2.7 Applications of XRD.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(2.1-2.5).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3(Supplement - Rules of crystal binding).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.1 General crystal binding 3.2 typical binding.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.1 Normal Modes of Vibration 4.2 Density of States 4.3 Harmonic approximation and normal mode coordinates 4.4 phonon.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.5 Heat capacity of the lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.1 general background and approximations 5.2 Bloch’s Theorem.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.6 Anharmonic Effects 4.7 Equation of states for Lattice 4.8 Experimental methods for the determinations of lattice vibration spectroscopy.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4(supplement - Thermal Expansion of Glass).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.5 The symmetry of bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.3 Nearly Free Electron 5.4 BZ and energy bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.4 Tight Binding Approximation(TBA).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.1 The quasi-classical description of Bloch electrons 6.2. Electron quasi-momentum 6.3 The accelerated velocity and effective mass.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6(supplement - a more concise description of quasi-momentum).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.4 The electron motion in a constant electric field 6.5 Band structure of conductor, insulator and semiconductor.ppt
