《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3(Supplement - Rules of crystal binding)

3-1 supplement:Rules of crystal binding Electronegative:used to characterize the ability of losing or getting electrons.In the periodical tables,the Electronegativity is increased from the left to right in the same period,and is reduced from the top to down Mulliken definition: Electronegativity=0.18 (ionization energy+electron affinity)
3-1 supplement:Rules of crystal binding Electronegative:used to characterize the ability of losing or getting electrons. In the periodical tables, the Electronegativity is increased from the left to right in the same period, and is reduced from the top to down Mulliken definition: Electronegativity=0.18(ionization energy+electron affinity)
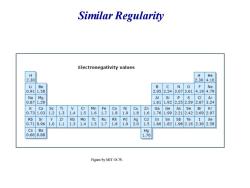
Similar Regularity Electronegativity values H H He 2.30 2.304.16 Be B C N 0 F Ne 0.91 1.58 2.052.543.073.61 4.194.79 Na Si P Ar 0.87 1.611.922.252.592.873.24 K Ca Sc Ti Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 0.73 1.03 1.2 1.3 1.4 .5 1.6 1.8 1.9 1.8 1.6 1.76 1.99 2.212.42 2.692.97 Rb Sr Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe 0.71 0.96 1.0 1.1 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 1.5 1.66 1.82 1.982.162.362.58 Cs Ba Ha 0.660.88 1.76 Figure by MIT OCW
Similar Regularity
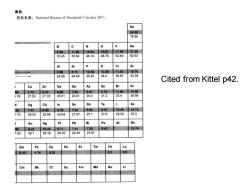
离能 资料来源:National Bureau of Standards Circular467). He 24.58 78.98 B c N 0 Ne 8.30 11.26 14.54 13.61 1742 21.56 33.45 35.64 44.14 48.76 52.40 62.63 Si CI Ar 5.98 8.15 10.55 10.38 1301 15.76 24.80 24.49 30.20 34.0 36.81 43.38 Cited from Kittel p42 Cu Zn Ga Ge AS Se Br Kr 3 7.72 9.39 6.00 7,88 9.81 9.75 11.84 14.00 5.78 27.93 27.35 26.51 23.81 30.0 312 33.4 38.56 Ag Cd In Sn Sb Xe 33 7.57 899 578 7.34 8.64 9.01 10.45 12.13 775 29.05 25.89 24.64 21.97 25.1 27.6 29.54 33.3 Au Hg Pb Po At Rn 96 922 10.43 6.11 7.41 729 8.43 10.74 7.52 29.7 29.18 26.53 22.44 23.97 Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb 6.16 6.74 6.82 82 5.0 Cm Bk Fm Md No
Cited from Kittel p42

General rules for crystal binding lowest electronegativity for alkali metal,liable to lose elctrons *IV-VI elements possess a higher electronegativity,and strong ability to obtain electrons,liable to form covalent bonds.IVelements are typical example.C (diamond)have biggest electronegativity, and have a strong covalent bond,while Pb is weakly electronegative and is a mental The value of electronegativity for elements at both end of the periodical tables have a big differnce,so,I -VII elements are lible to form ionic crystal,for example,NaCl,CsCl. With the reduction of the electronegativity difference,the ionic binding gradually is tranformed to covalent bingding
★ The value of electronegativity for elements at both end of the periodical tables have a big differnce, so , Ⅰ-Ⅶ elements are lible to form ionic crystal , for example, NaCl,CsCl. ★ With the reduction of the electronegativity difference,the ionic binding gradually is tranformed to covalent bingding. 。 General rules for crystal binding ★ lowest electronegativity for alkali metal, liable to lose elctrons ★ Ⅳ-Ⅵ elements possess a higher electronegativity, and strong ability to obtain electrons, liable to form covalent bonds. Ⅳelements are typical example. C(diamond) have biggest electronegativity, and have a strong covalent bond, while Pb is weakly electronegative and is a mental
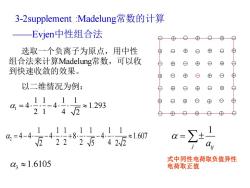
3-2 supplement:Madelung常数的计算 Evjen中性组合法 ⊕ O⊕ 选取一个负离子为原点,用中性 ⊕ ⊕ o ⊕ ⊕ 组合法来计算Madelung常数,可以收 ⊕ ⊕ ⑧ 到快速收敛的效果。 ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ 以二维情况为例: ⊕ 4=4)4161293 ⊕ 214√2 2=446-4+851-411 -4-+8 迈42225中422 ≈1.607 03≈1.6105 式中同性电荷取负值异性 电荷取正值
3-2supplement :Madelung常数的计算 ——Evjen中性组合法 选取一个负离子为原点,用中性 组合法来计算Madelung常数,可以收 到快速收敛的效果。 以二维情况为例: 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 1.293 2 1 4 2 = − 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 4 8 4 1.607 2 5 2 2 2 2 2 4 = − − + − 3 1.6105 1 j ij a = 式中同性电荷取负值异性 电荷取正值

NaCl结构Madelung常数的计算: 参考二维做法,一层一层计算,逐步扩大,收敛很快。 002 012 022 10 111 001 011 021 000 010 020 Na* OC
NaCl结构Madelung常数的计算: 参考二维做法,一层一层计算,逐步扩大,收敛很快。 000 010 020 001 011 002 021 111 012 022 101
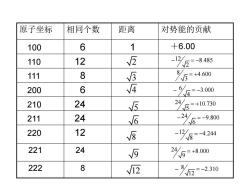
原子坐标 相同个数 距离 对势能的贡献 100 6 1 +6.00 110 12 2 -1%2-8485 111 8 万460 200 6 √4 -4=-300 210 24 5 2以5=+10730 211 24 6 ☐26-9800 220 12 V⑧ 84244 -12/ 221 24 √ 245=+80 222 8 √2 -82-2310
原子坐标 相同个数 距离 对势能的贡献 100 6 1 +6.00 110 12 111 8 200 6 210 24 211 24 220 12 221 24 222 8 2 12 8.485 2 − = − 3 8 4.600 3 = + 4 5 6 8 9 12 6 3.000 4 − = − 24 10.730 5 = + 24 9.800 6 − = − 12 4.244 8 − = − 24 8.000 9 = + 8 2.310 12 − = −
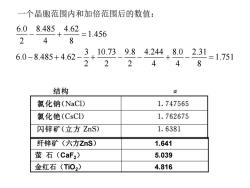
一个晶胞范围内和加倍范围后的数值: 6.08.485.4.62 =1.456 248 6.0-8.485+4.62- 3,10.739.84.244,8.02. 1=1.751 22 2 48 结构 a 氯化钠(NaCl) 1.747565 氯化铯(CsCI) 1.762675 闪锌矿(立方ZnS) 1.6381 纤锌矿(六方ZnS) 1.641 萤石(CaF2) 5.039 金红石(Ti02) 4.816
6.0 8.485 4.62 1.456 2 4 8 3 10.73 9.8 4.244 8.0 2.31 6.0 8.485 4.62 1.751 2 2 2 4 4 8 − + = − + − + − − + − = 一个晶胞范围内和加倍范围后的数值: 纤锌矿(六方ZnS) 1.641 萤 石(CaF2) 5.039 金红石(TiO2) 4.816
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(2.1-2.5).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice 2.6 X-Ray Diffraction Methods 2.7 Applications of XRD.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(supplement - Review & Overview of X-Rays).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.9 Elements of Symmetry 1.10 Space groups 1.11 7 crystal system and 14 Bravis Lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure(Supplement - microstructure and crystal system).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Introduction.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.1 Elementary Crystallography 1.2 Crystal Structure ≡ Lattice + Basis 1.3 Lattice Translation Vectors 1.4 Non-Bravais Lattices 1.5 Wigner-Seitz Method.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.6 typical crystal structure.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.7 Lattice Sites in a Cubic Unit Cell 1.8 crystal plane and miller index.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学资源(参考资料)词汇汉英对照.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 能带理论.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 晶体结构.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 晶体的结合.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 晶格振动.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 晶体结构的测定.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)晶体能带结构理解电导特性.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 固体电子论基础.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)紧束缚近似理论研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)非谐效应——热膨胀研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.1 General crystal binding 3.2 typical binding.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.1 Normal Modes of Vibration 4.2 Density of States 4.3 Harmonic approximation and normal mode coordinates 4.4 phonon.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.5 Heat capacity of the lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.1 general background and approximations 5.2 Bloch’s Theorem.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.6 Anharmonic Effects 4.7 Equation of states for Lattice 4.8 Experimental methods for the determinations of lattice vibration spectroscopy.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4(supplement - Thermal Expansion of Glass).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.5 The symmetry of bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.3 Nearly Free Electron 5.4 BZ and energy bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.4 Tight Binding Approximation(TBA).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.1 The quasi-classical description of Bloch electrons 6.2. Electron quasi-momentum 6.3 The accelerated velocity and effective mass.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6(supplement - a more concise description of quasi-momentum).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.4 The electron motion in a constant electric field 6.5 Band structure of conductor, insulator and semiconductor.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal(supplement - Sommerfield expansion).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal 7.1 Fermi statistics and the heat capacity of electron 7.2 Work function and contact potential.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.6 Density of states(DOS)and Fermi surface 5.7 the electrons in the crystal 5.8 the experimental results for DOS.ppt
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学大纲.doc
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,共五部分).ppt
- 《工程光学》课程教学大纲 Engineering Optics.doc
- 安徽大学:《工程光学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十三章,授课教师:李桂华).doc
- 《工程光学》课程实验指导书(共六个实验).doc
