《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(2.1-2.5)

Ch2:Wave Diffraction the Reciprocal Lattice Objectives At the end of this Chapter,you should: 1. Understand the concept of the reciprocal lattice. 2.Know how to use the Bragg's law. 3.Know the relationship between Bragg's law and the Laue equation. 4. Know the drawing method and the concept of Brilluoin Zone. 5. Be able to calculate the structure factor of the typical crystal structures
At the end of this Chapter, you should: 1. Understand the concept of the reciprocal lattice. 2. Know how to use the Bragg’s law. 3. Know the relationship between Bragg’s law and the Laue equation. 4. Know the drawing method and the concept of Brilluoin Zone. 5. Be able to calculate the structure factor of the typical crystal structures Ch2:Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice Objectives

2.1 The reciprocal lattice (direct)lattice reciprocal lattice primitive vectors a1,a2,a3 primitive vectors b1,b2,b3 Def. 1 6 -2 a b2=2n(a) b1∝a2×a3 because of orthogonality, then useb1·a1=2π 63-2 1 to determine the constant. Def. 2 b1·a1=2n,b1·a2=b1·a3=0, b2·a2=2n,b2·a3=b2·a1=0, b3·a3=2n,b3·a1=b3·a2=0
2.1

Reciprocal Lattice for Aluminium
Reciprocal Lattice for Aluminium
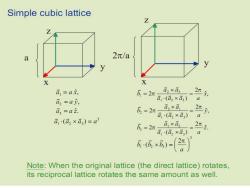
Simple cubic lattice Z a 2π/a y X a1=a元, 万=2π a2×a3 2元, a a,=ay, a1(a2×a) a3=a2 万=2π a3×a 2, a·(a2×a) a1(a2×a)=a3 万3=2π a1×a 2r. a1(a2×a3) 万(6×五)= Note:When the original lattice (the direct lattice)rotates, its reciprocal lattice rotates the same amount as well

FCC lattice BCC lattice Z An/a a X 6+》 6=2π ā×ā,-4机(+-2) a(a2×a)a2 a×a= 4π1 a+到 ,=2 a1(a2×a) 。2++) 日9 6=2π- axa a(a2×a3)=a3/4 低-)》

The reciprocal of a reciprocal lattice is the direct lattice: 6=2π a×a a(a2×a) C= 6,=2r a3×a, 低×动 a(a2×a) A×(BxC)=B(AC)-C(AB) i3=2 a×a a(a2×a) b:xb-m(asxa)x (axa)-aa 2π a1 21 2.2=i1(i2×i3)-2=(2π)2(a1b1)=(2π)3 Direct lattice Reciprocal lattice , C1= 2xQY a-a cubic(a) 22 cubic(2π/a) fcc(a) bcc(4m/a) C2=a2,C3=a3, bcc(a) fcc(4元la) hexagonal (a,c) hexagonal(4π/N3a,2π/c) Take the reciprocal lattice as and rotated by 30 degrees direct one,start construct the reciprocal one:
The reciprocal of a reciprocal lattice is the direct lattice: 2 3 1 * 2 c b b ( ) = 2 2 3 3 1 1 2 1 2 2 (2 ) b b a a a a a ( ) ( ) = = A B C B A C C A B = − ( ) ( ) ( ) * 2 3 = = = b b b a b 1 2 3 1 1 ( ) (2 ) ( ) (2 ) 2 1 1 1 * 2 (2 ) c a a = = c a c a 2 2 3 3 = = , , Take the reciprocal lattice as direct one, start construct the reciprocal one:

Two simple properties: R=n,a+n,a2+n,a3(n,h,n3∈Z)∈direct attice G=k+(k,k2,kZ)Ereciprocal lattice →G.R=2π(nk+n,k2+nk3)=2r×int eger. .exp(iG.R)is always equal to 1 Conversely,assume G.R=2rxinteger for all R, G.a =2nh, G.d=2nk, G.d=2nl, (h,k,l∈Z) then G=hd+k五,+瓜,(∈G)

If f(r)has lattice translation symmetry,that is,f(r)=f(r+R)for any lattice vector R [eg.f(r)can be the charge distribution in lattice], then it can be expanded as,f() all G where G is the reciprocal lattice vector. Pf Fourier expanson, f()=∑ef) f+=∑eef=f. R=h6+k6,+6 Yh,k,1 Therefore,e-1 for元 Fourier decomposition and reciprocal lattice vectors The expansion above is very general,it applies to all types of periodic lattice (e.g.bec,fec,tetragonal,orthorombic.) in all dimensions(1,2,and 3) All you need to do is to find out the reciprocal lattice vectors G

Two basic 1.(h,k,l)planes LG+b+ properties: 2.The distance between adjacent(h,k,1)planes, (useful later) d= 2 G See Prob.1 CA=04-0C= a1_a3 hh3 9 CB=OB-OC=92_a3 h hs Gh Ghthehy CA= a h+ha+Abn爱爱 h =2π-2π=0 图1-18晶面与倒易点阵位矢关系示意图 Ghibh,CB=0
1 3 1 3 2 3 2 3 a a CA OA OC h h a a CB OB OC h h = − = − = − = − 1 2 3 1 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 3 ( ) ( ) 2 2 0 G CA h h h a a h b h b h b h h = + + − =−= G CB h h h 1 2 3 = 0
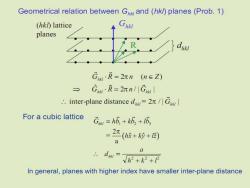
Geometrical relation between Ghk and(hkl)planes (Prob.1) (hkl)lattice planes G=2元n(n∈Z) → GR=2元n/小Gw .inter-plane distance dG For a cubic lattice G=h6+k5+, 2r(+k+) := a V2+k2+12 In general,planes with higher index have smaller inter-plane distance
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice 2.6 X-Ray Diffraction Methods 2.7 Applications of XRD.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(supplement - Review & Overview of X-Rays).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.9 Elements of Symmetry 1.10 Space groups 1.11 7 crystal system and 14 Bravis Lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure(Supplement - microstructure and crystal system).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Introduction.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.1 Elementary Crystallography 1.2 Crystal Structure ≡ Lattice + Basis 1.3 Lattice Translation Vectors 1.4 Non-Bravais Lattices 1.5 Wigner-Seitz Method.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.6 typical crystal structure.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.7 Lattice Sites in a Cubic Unit Cell 1.8 crystal plane and miller index.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学资源(参考资料)词汇汉英对照.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 能带理论.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 晶体结构.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 晶体的结合.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 晶格振动.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 晶体结构的测定.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)晶体能带结构理解电导特性.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 固体电子论基础.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)紧束缚近似理论研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)非谐效应——热膨胀研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程教学大纲 Solid State Physics.pdf
- 《半导体工艺原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第4章 晶圆制造与外延硅生长.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3(Supplement - Rules of crystal binding).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.1 General crystal binding 3.2 typical binding.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.1 Normal Modes of Vibration 4.2 Density of States 4.3 Harmonic approximation and normal mode coordinates 4.4 phonon.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.5 Heat capacity of the lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.1 general background and approximations 5.2 Bloch’s Theorem.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.6 Anharmonic Effects 4.7 Equation of states for Lattice 4.8 Experimental methods for the determinations of lattice vibration spectroscopy.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4(supplement - Thermal Expansion of Glass).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.5 The symmetry of bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.3 Nearly Free Electron 5.4 BZ and energy bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.4 Tight Binding Approximation(TBA).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.1 The quasi-classical description of Bloch electrons 6.2. Electron quasi-momentum 6.3 The accelerated velocity and effective mass.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6(supplement - a more concise description of quasi-momentum).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.4 The electron motion in a constant electric field 6.5 Band structure of conductor, insulator and semiconductor.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal(supplement - Sommerfield expansion).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal 7.1 Fermi statistics and the heat capacity of electron 7.2 Work function and contact potential.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.6 Density of states(DOS)and Fermi surface 5.7 the electrons in the crystal 5.8 the experimental results for DOS.ppt
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学大纲.doc
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,共五部分).ppt
- 《工程光学》课程教学大纲 Engineering Optics.doc
