《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4(supplement - Thermal Expansion of Glass)

4-1 supplement Thermal Expansion of Glass Thermal expansion determines if a glass will be shock resistant,able to withstand high thermal stresses Small thermal expansion coefficient leads to high thermal shock resistance Large thermal expansion leads to low thermal shock resistance Most materials expand as they are heated Refractory metals and ceramics-Expand less Polymers-Expand more Some materials expand very little SiO2 glass;b-spodumene,Li2O.Al2O3.4SiO2 Complex systems with more than one material must have matched or compensated thermal expansions
4-1 supplement : Thermal Expansion of Glass • Thermal expansion determines if a glass will be shock resistant, able to withstand high thermal stresses • Small thermal expansion coefficient leads to high thermal shock resistance • Large thermal expansion leads to low thermal shock resistance Most materials expand as they are heated Refractory metals and ceramics-Expand less Polymers-Expand more Some materials expand very little SiO2 glass; b-spodumene, Li2O.Al2O3 .4SiO2 Complex systems with more than one material must have matched or compensated thermal expansions

Thermal expansion on the atomic scale f1 更1 interatomic dstance r (equilibrium d stance)
Thermal expansion on the atomic scale

Materials change size when heating. Lfinal -Linitial =a(Tfinal-Tinitial Linitial CTE:coefficient of thermal expansion (units:1/K) Uov) Sides symmetry for harmonic approximation
• Materials change size when heating. Lfinal − Linitial Linitial = (Tfinal − Tinitial ) CTE: coefficient of thermal expansion (units: 1/K) Sides symmetry for harmonic approximation
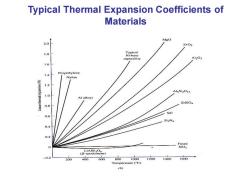
Typical Thermal Expansion Coefficients of Materials Mgo 20 1.8 Ni-base superalloy A12O3 1.6 1.4 Polyethylene Nylon (wotsuedxa eu 1.2 Al alloys ZrSiO 0.8 Sic 0.6 SiaNa 0.4 0.2 LiAlSi2O6 (B-spodumene) 0.2 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 Temperature (C) (b)
Typical Thermal Expansion Coefficients of Materials

Polycrystalline materials undergo phase transformations Thermal expansion changes at each phase transition 。 c-SiO,has numerous phase changes and numerous volume changes that must be accounted for during heat up of systems using SiO2 B-Quartz 1.5 B-Cristobalite B'-Tridymite 1.0 B-Tr a-Quartz 0.5 a-Tr @-Cristobalite 0 200 400 600 Temperature (C)
• Polycrystalline materials undergo phase transformations • Thermal expansion changes at each phase transition • c-SiO2 has numerous phase changes and numerous volume changes that must be accounted for during heat up of systems using SiO2
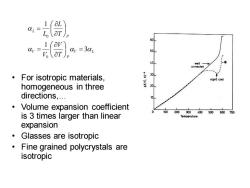
aL 1 =3z 50 40 well annealed For isotropic materials, 30 rapid cool homogeneous in three 20 directions,. Volume expansion coefficient 100 200300400500600700 is 3 times larger than linear Temperature expansion Glasses are isotropic Fine grained polycrystals are isotropic
• For isotropic materials, homogeneous in three directions,. • Volume expansion coefficient is 3 times larger than linear expansion • Glasses are isotropic • Fine grained polycrystals are isotropic V L P V P L T V V T L L 3 1 1 0 0 = = =

Thermal Expansion of Alkali Borate Glasses 27 oLi 口Ne OK 2 Rb NOISNYdX3 20 40 60 100 MOL%R,0 Addition of alkali modifier decreases thermal expansion coefficient in alkali borate glasses Modifier in low alkali borate glasses,cross links glass structure Creation of tetrahedral borons Adding bonds to boron,increasing connectivity of network Strengthening the network Rigidity of the glassy network increases Thermal expansion decreases with modifier
Thermal Expansion of Alkali Borate Glasses • Addition of alkali modifier decreases thermal expansion coefficient in alkali borate glasses • Modifier in low alkali borate glasses, cross links glass structure • Creation of tetrahedral borons • Adding bonds to boron, increasing connectivity of network • Strengthening the network • Rigidity of the glassy network increases • Thermal expansion decreases with modifier
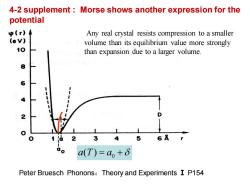
4-2 supplement Morse shows another expression for the potential p(r) Any real crystal resists compression to a smaller ev) volume than its equilibrium value more strongly 10 than expansion due to a larger volume. 12 ao a(T)=a+δ Peter Bruesch Phonons:Theory and Experiments I P154
4-2 supplement : Morse shows another expression for the potential Peter Bruesch Phonons:Theory and Experiments Ⅰ P154 Any real crystal resists compression to a smaller volume than its equilibrium value more strongly than expansion due to a larger volume. 0 a T a ( ) = +

Morse potential 4r)=D[1-e-了 D deionization, 2>0 Expand it: u(a+6)=4(a)+ dr + Defined as 0 0,at equilibrium point Harmonic term anharmonic term A+后8+ ,1 h,64+. 24 64+
0 2 ( ) ( ) 1 r a u r D e− − = − D deionization, >0 Expand it: 0 0 0 2 3 2 3 0 0 2 3 2 3 4 0 0 0 d 1 d 1 d ( ) ( ) d 2 d 3! d 1 1 1 2 6 24 a a a u u u u a u a r r r g h + = + + + = + + + 0 4 4 4 1 d 4! d a u r + + Defined as 0 0, at equilibrium point Harmonic term Morse potential anharmonic term
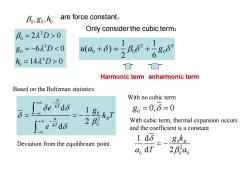
B,80,h are force constant, Only consider the cubic term: B。=222D>0 1 80=-6λ3D0 0 □ Harmonic term anharmonic term Based on the Boltzman statistics With no cubic term u +0 δekrdδ 80=0,6=0 δ= +00 2 With cubic term,thermal expansion occurs and the coefficient is a constant 1dδ Deviation from the equilibrium point goke a,dT 2ao
are force constant, 0 0 0 , , g h 2 0 3 0 4 0 2 0 6 0 14 0 D g D h D = = − = Only consider the cubic term: 2 3 0 0 0 1 1 ( ) 2 6 u a g + + Harmonic term anharmonic term Based on the Boltzman statistics 0 2 0 d 1 2 d u kT u B kT e g k T e + − − + − − = = − Deviation from the equilibrium point 0 g = = 0, 0 With no cubic term 0 2 0 0 0 1 d d 2 B g k a T a = − With cubic term, thermal expansion occurs and the coefficient is a constant
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.6 Anharmonic Effects 4.7 Equation of states for Lattice 4.8 Experimental methods for the determinations of lattice vibration spectroscopy.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.1 general background and approximations 5.2 Bloch’s Theorem.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.5 Heat capacity of the lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.1 Normal Modes of Vibration 4.2 Density of States 4.3 Harmonic approximation and normal mode coordinates 4.4 phonon.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.1 General crystal binding 3.2 typical binding.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3(Supplement - Rules of crystal binding).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(2.1-2.5).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice 2.6 X-Ray Diffraction Methods 2.7 Applications of XRD.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(supplement - Review & Overview of X-Rays).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.9 Elements of Symmetry 1.10 Space groups 1.11 7 crystal system and 14 Bravis Lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure(Supplement - microstructure and crystal system).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Introduction.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.1 Elementary Crystallography 1.2 Crystal Structure ≡ Lattice + Basis 1.3 Lattice Translation Vectors 1.4 Non-Bravais Lattices 1.5 Wigner-Seitz Method.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.6 typical crystal structure.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.7 Lattice Sites in a Cubic Unit Cell 1.8 crystal plane and miller index.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学资源(参考资料)词汇汉英对照.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 能带理论.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 晶体结构.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 晶体的结合.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.5 The symmetry of bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.3 Nearly Free Electron 5.4 BZ and energy bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.4 Tight Binding Approximation(TBA).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.1 The quasi-classical description of Bloch electrons 6.2. Electron quasi-momentum 6.3 The accelerated velocity and effective mass.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6(supplement - a more concise description of quasi-momentum).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.4 The electron motion in a constant electric field 6.5 Band structure of conductor, insulator and semiconductor.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal(supplement - Sommerfield expansion).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal 7.1 Fermi statistics and the heat capacity of electron 7.2 Work function and contact potential.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.6 Density of states(DOS)and Fermi surface 5.7 the electrons in the crystal 5.8 the experimental results for DOS.ppt
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学大纲.doc
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,共五部分).ppt
- 《工程光学》课程教学大纲 Engineering Optics.doc
- 安徽大学:《工程光学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十三章,授课教师:李桂华).doc
- 《工程光学》课程实验指导书(共六个实验).doc
- 《量子力学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 4 态和力学量的表象 The representation for the states and dynamical variable.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 1 绪论 Quantum mechanism(量子力学的诞生).pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 2 波函数和薛定谔方程 The wave function and Schrödinger Equation.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 3 量子力学中的力学量 The Dynamical variable in Quantum Mechanism.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 6 散射 Scattering.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 5 微扰理论近似方法 Approximation(本征值问题的似解).pdf
