《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal
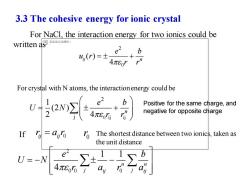
3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal For NaCl,the interaction energy for two ionics could be written a尽无法显示该国片, u(r)=± e+ b 4πEor For crystal with N atoms,the interactionenergy could be wy Positive for the same charge,and negative for opposite charge If 1 The shortest distance between two ionics,taken as the unit distance U=-N e 4πEo6j
3.3 The cohesive energy for ionic crystal For NaCl, the interaction energy for two ionics could be written as 2 0 ( ) 4 ij n e b u r r r = + 0 ij ij 2 j 1 (2 ) 2 4 n e b U N r r = + Positive for the same charge, and negative for opposite charge If ij ij 0 r a r = The shortest distance between two ionics, taken as the unit distance 0 r 2 0 0 0 1 1 4 n n j j ij ij e b U N r a r a = − − For crystal with N atoms, the interaction energy could be
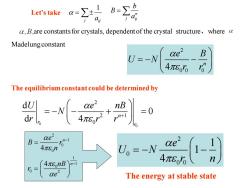
Let's take a,B,are constants for crystals,dependent of the crystal structure,where Madelung constant B U=-N Qe2 4π8% The equilibrium constant could be determined by B、 ae 4πn 4πEonB ae2 The energy at stable state
2 0 0 0 4 n e B U N r r = − − 2 0 0 0 1 1 4 e U N r n = − − 0 0 2 2 1 0 d 0 d 4 n r r U e nB N r r r + = − − + = 2 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 2 4 4 n n e B r n nB r e − − = = The energy at stable state 1 j ij a = n j ij b B a Let’s take = are constants for crystals, dependent of the crystal structure,where Madelung constant The equilibrium constant could be determined by

*For a given crystal,the Madelung constant could be calculated *ionic distance ro could be determined by the XRD *the value of n could be determined by the experimental investigation of elastic modulus K All of these results show that the experimental results are consistent with the theoretical values,which supports the fact that the interaction between positive and negative ionics should be responsible for the ionic bonding
★For a given crystal, the Madelung constant could be calculated ★ionic distance r0 could be determined by the XRD ★the value of n could be determined by the experimental investigation of elastic modulus K All of these results show that the experimental results are consistent with the theoretical values, which supports the fact that the interaction between positive and negative ionics should be responsible for the ionic bonding
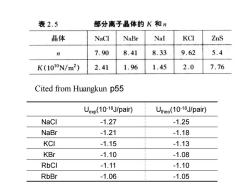
表2.5 部分离子晶体的K和n 晶体 NaCl NaBr Nal KCI ZnS n 7.90 8.41 8.33 9.62 5.4 K(1010N/m2) 2.41 1.96 1.45 2.0 7.76 Cited from Huangkun p55 Uexp(10-18J/pair)) Utheo(10-1J/pair) NaCl -1.27 -1.25 NaBr -1.21 -1.18 KCI -1.15 -1.13 KBr -1.10 -1.08 RbCI -1.11 -1.10 RbBr -1.06 -1.05
Uexp(10-18J/pair) Utheo(10-18J/pair) NaCl -1.27 -1.25 NaBr -1.21 -1.18 KCl -1.15 -1.13 KBr -1.10 -1.08 RbCl -1.11 -1.10 RbBr -1.06 -1.05 Cited from Huangkun p55
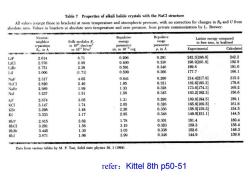
Table 7 Properties of alkali halide crystals with the NaCl structure All values(except those in brackets)at room temperature and atmospheric pressure,with no correction for changes in Ro and U from absolute zero.Values in brackets at absolute zero temperature and zero pressure,from private communication by L.Brewer. Nearest- Repulsive Repulsive Lattice energy compared neighbor Bulk modulus B. energy range to free ions,in kcal/mol in 1011 dyn/em? parameter parameter or 1010 N/m2 zA,in 10-"erg p.in A Experimental Calculated LiF 2.014 6.71 0.296 0.291 242.3[246.8] 242.2 LiC] 2.570 2.98 0.490 0.330 198.9[201.8] 192.9 LiBr 2.751 2.38 0.591 0.340 189.8 181.0 Lil 3.000 (1.71) 0.599 0.366 177.7 166.1 NaF 2.317 4.65 0.641 0.290 214.4[217.9 215.2 NaCl 2.820 2.40 1.05 0.321 182.6185.3] 178.6 NaBr 2.989 1.99 1.33 0.328 173.6174.3] 169.2 Nal 3.237 1.51 1.58 0.345 163.2162.3] 156.6 KF 2.674 3.05 1.31 0.298 189.8[194.5] 189.1 KCI 3.147 1.74 2.05 0.326 165.8169.5] 161.6 KBr 3.298 1.48 2.30 0.336 158.5[159.3] 154.5 KI 3.533 1.17 2.85 0.348 149.9151.1] 144.5 RbF 2.815 2.62 1.78 0.301 181.4 180.4 RbCl 3.291 1.56 3.19 0.323 159.3 155.4 RbBr 3.445 1.30 3.03 0.338 152.6 148.3 RbI 3.671 1.06 3.99 0.348 144.9 139.6 Data from various tables by M.P. Tosi, Solid state physics 16.1(1964) refer:Kittel 8th p50-51
refer:Kittel 8th p50-51

The relation between elastic modulus K and repulsive efficient n a'U sc: y=1 K=Vo Vo=yNi NaCl:Y=2 x=器=r器】 1 U K= 9YNr dr2 B= 4π8n d2U Nae2 (n-1) 4πe0 K= ae2 (n-1) n=1+ 72E2K 72π8oYT0 ae2
The relation between elastic modulus K and repulsive efficient n 0 2 0 2 ( )V U K V V = 3 V Nr 0 0 = sc: =1 NaCl: =2 0 2 2 0 1 d 9 d r U K Nr r = ( ) ( ) 2 1 0 0 2 2 2 3 0 0 2 4 0 0 4 d 1 d 4 1 72 e n B r n U N e n r r e K n r − = = − = − 4 0 0 2 72 1 r n K e = + 2 2 2 2 2 U U r K V V V r V = =
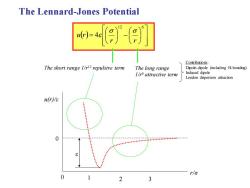
The Lennard-Jones Potential j Contributions: The short range 1/r12 repulsive term The long range Dipole-dipole (including H-bonding) 1/attractive term Induced dipole London dispersion attraction u(r)/e : 0 : r/a 0 3
The Lennard-Jones Potential ( ) − = 12 6 4 r r u r The long range 1/r6 attractive term The short range 1/r12 repulsive term u(r)/ε r/σ 0 0 1 2 3 Contributions: Dipole-dipole (including H-bonding) Induced dipole London dispersion attraction ε

Interaction potential for atoms pair - a=480°,b=48o2,or:o 93 a 4b When there are N atoms or molecules in the crystal,the interaction energy should be: a The shortest distance between two atoms is ro,if= U(r)=2Nε
Interaction potential for atoms pair 6 12 ( ) a b u r r r = − + 12 6 u r( ) 4 r r = − 6 12 a b = = 4 , 4 , 1 2 6 , 4 b a a b = = or: When there are N atoms or molecules in the crystal, the interaction energy should be: 12 6 0 j j 4 2 N U r r = − j The shortest distance between two atoms is r0 , if 0 r a r j j = 12 6 12 6 0 0 U r N ( ) 2 A A r r = − &

where are dependent of the crystal structures lattice summerary for three cubic Bravis lattices scc bec fee 8.40 12.25 14.45 6.20 9.11 12.13 Using equilibrium condition, aU(r) =0 6=0 2A2 ☐1.09g Or Ao The majority of molecular crystals possess fec structure.we can introduce the corresponding data into the above expression,and we can find that o represent the radius for atomic core repulsion At equilibrium state,the energy should be: U(6) 40= N =-8.66 reflects the binding energy For fcc structure,the energy of an atom on average U6)=-N82Ag
0 U r N ( ) = − 2 6 12 A 2A At equilibrium state, the energy should be: 0 0 ( ) 8.6 U r u N = = − For fcc structure, the energy of an atom on average ε reflects the binding energy

At equilibrium state,the elastic modulus for fcc structure K- 4cAg =758 √2yo3A Solid binding energy for inert gas elements uexp (eV/atom) uthe(eV/atom) Ne -0.02 -0.027(-0.019) Ar -0.08 -0.089(-0.080) Kr -0.11 -0.120(-0.113) Xe -0.17 -0.172 Referred from huangkun p70
uexp (eV/atom) uthe (eV/atom) Ne -0.02 -0.027 (-0.019) Ar -0.08 -0.089 (-0.080) Kr -0.11 -0.120 (-0.113) Xe -0.17 -0.172 Referred from huangkun p70 Solid binding energy for inert gas elements 3 3 4 75 K = 5 2 3 2 6 12 A 2 A At equilibrium state, the elastic modulus for fcc structure
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(2.1-2.5).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice 2.6 X-Ray Diffraction Methods 2.7 Applications of XRD.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Wave Diffraction & the Reciprocal Lattice(supplement - Review & Overview of X-Rays).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.9 Elements of Symmetry 1.10 Space groups 1.11 7 crystal system and 14 Bravis Lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure(Supplement - microstructure and crystal system).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Introduction.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.1 Elementary Crystallography 1.2 Crystal Structure ≡ Lattice + Basis 1.3 Lattice Translation Vectors 1.4 Non-Bravais Lattices 1.5 Wigner-Seitz Method.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.6 typical crystal structure.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Crystal Structure 1.7 Lattice Sites in a Cubic Unit Cell 1.8 crystal plane and miller index.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学资源(参考资料)词汇汉英对照.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 能带理论.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第一章 晶体结构.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第三章 晶体的结合.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第四章 晶格振动.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第二章 晶体结构的测定.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)晶体能带结构理解电导特性.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 固体电子论基础.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)紧束缚近似理论研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程授课教案(讲义)非谐效应——热膨胀研究性教学教案设计.doc
- 《固体物理学》课程教学大纲 Solid State Physics.pdf
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3(Supplement - Rules of crystal binding).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Interatomic Bonding 3.1 General crystal binding 3.2 typical binding.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.1 Normal Modes of Vibration 4.2 Density of States 4.3 Harmonic approximation and normal mode coordinates 4.4 phonon.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.5 Heat capacity of the lattice.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.1 general background and approximations 5.2 Bloch’s Theorem.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4.6 Anharmonic Effects 4.7 Equation of states for Lattice 4.8 Experimental methods for the determinations of lattice vibration spectroscopy.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 lattice dynamics and lattice capacity 4(supplement - Thermal Expansion of Glass).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.5 The symmetry of bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.3 Nearly Free Electron 5.4 BZ and energy bands.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.4 Tight Binding Approximation(TBA).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.1 The quasi-classical description of Bloch electrons 6.2. Electron quasi-momentum 6.3 The accelerated velocity and effective mass.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6(supplement - a more concise description of quasi-momentum).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Electron motion in the crystal 6.4 The electron motion in a constant electric field 6.5 Band structure of conductor, insulator and semiconductor.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal(supplement - Sommerfield expansion).ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 The electronic theory of metal 7.1 Fermi statistics and the heat capacity of electron 7.2 Work function and contact potential.ppt
- 《固体物理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 band theory 5.6 Density of states(DOS)and Fermi surface 5.7 the electrons in the crystal 5.8 the experimental results for DOS.ppt
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学大纲.doc
- 《近代物理实验》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,共五部分).ppt
- 《工程光学》课程教学大纲 Engineering Optics.doc
- 安徽大学:《工程光学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十三章,授课教师:李桂华).doc
