《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 11 Communicating Customer Value

Chapter 11 Communicating Customer Value -Integrated Marketing Communications Strategy 教学目的:通过本章学习,掌握整合营销传播等基本概念,了解促销的含义与作用, 促销组合的基本内容以及各种促销方式的主要特点,掌握广告的各种类型和人员推 销的基本策略以及公共关系和营业推广的主要活动方式。要求能应用市场传播及促 销组合理论,分析企业促销实践中存在的问题,制定市场传播及促销组合的方案。 教学重点:促销组合的含义、促销组合策略的类型及其含义、影响因素:人员推销 的形式、策略;营业推广策略。 教学难点:促销组合策略的类型及其含义:营业推广的含义、特点、方式。 学时分配: 教学内容: 一、Integrated Marketing Communications The promotion mix is the marketer's bag of tools for communicating with custo ers and other stakeholders.All of these many tools must be carefully coordinated under the ncept of integrated marketing communications in order to deliver a clear and compelling message. (-)The Promotion Mix 1.Promotion mix-the specific blend of promotion tools that the company uses to persuasively communicate customer value and build customer relationships. 2.Advertising:any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and Promotion of Ideas. Goods,or Services by an Identified Sponsor. 3.Sales promotion-short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sale of a product or service 4.Personal selling-personal presentation by the firm's sales force for the purpose of making sales and building customer relationships. 5.Public relations-building good relations with the company's various publics by
1 Chapter 11 Communicating Customer Value -Integrated Marketing Communications Strategy 教学目的:通过本章学习,掌握整合营销传播等基本概念,了解促销的含义与作用, 促销组合的基本内容以及各种促销方式的主要特点,掌握广告的各种类型和人员推 销的基本策略以及公共关系和营业推广的主要活动方式。要求能应用市场传播及促 销组合理论,分析企业促销实践中存在的问题,制定市场传播及促销组合的方案。 教学重点:促销组合的含义、促销组合策略的类型及其含义、影响因素;人员推销 的形式、策略;营业推广策略。 教学难点:促销组合策略的类型及其含义;营业推广的含义、特点、方式。 学时分配: 教学内容: 一、 Integrated Marketing Communications (一) The Promotion Mix 1. Promotion mix—the specific blend of promotion tools that the company uses to persuasively communicate customer value and build customer relationships. 2. Advertising: any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and Promotion of Ideas, Goods, or Services by an Identified Sponsor. 3. Sales promotion—short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sale of a product or service. 4. Personal selling—personal presentation by the firm’s sales force for the purpose of making sales and building customer relationships. 5. Public relations—building good relations with the company’s various publics by The promotion mix is the marketer’s bag of tools for communicating with customers and other stakeholders. All of these many tools must be carefully coordinated under the concept of integrated marketing communications in order to deliver a clear and compelling message

obtaining favorable publicity,building up a good corporate image and handling or heading off unfavorable rumors,stories and events. 6. Direct marketing-direct connections with carefully targeted individual consumers to both obtain an immediate response and cultivate lasting customer relationships-the use of direct mail,the telephone.direct-response television. e-mail,the Intemet,and other tools to communicate directly with specific consumers. (二) Integrated Marketing Communications 1.Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC):Carefully Integrates and Coordinates its Many Communications Channels to Deliver a Clear,Consistent, and Compelling Message About the Organization and Its Products. (1)IMC calls for recognizing all touch points where the customer may encounter the company and its brands (2)IMC ties together all the company's messages and images. 2.The Communication Process mn8rae Key Factors in Good Communication (1)Sellers Need to Know What Audiences They Wish to Reach and Response Desired. (2)Sellers Must Develop Feedback Channels to Assess Audience's Response to Messages. (3)Sellers Must Send Messages Through Media that Reach Target Audiences
2 obtaining favorable publicity, building up a good corporate image and handling or heading off unfavorable rumors, stories and events. 6. Direct marketing—direct connections with carefully targeted individual consumers to both obtain an immediate response and cultivate lasting customer relationships—the use of direct mail, the telephone, direct-response television, e-mail, the Internet, and other tools to communicate directly with specific consumers. (二) Integrated Marketing Communications 1. Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC): Carefully Integrates and Coordinates its Many Communications Channels to Deliver a Clear, Consistent, and Compelling Message About the Organization and Its Products. (1) IMC calls for recognizing all touch points where the customer may encounter the company and its brands. (2) IMC ties together all the company’s messages and images. 2. The Communication Process Key Factors in Good Communication (1) Sellers Need to Know What Audiences They Wish to Reach and Response Desired. (2) Sellers Must Develop Feedback Channels to Assess Audience’s Response to Messages. (3) Sellers Must Send Messages Through Media that Reach Target Audiences

(4)Sellers must be Good at Encoding Messages That Target Audience Can Decode. (三) Steps in Developing Effective Communication 1.Identifying the Target Audience The target audience will heavily affect the communicator's decisions on what will be said,how it will be said,when it will be said,where it will be said,and how will say it. 2.Determining the Communication Objectives Good marketing communication calls for"good deeds followed by good words" 3.Designing a Message-AIDAmodel:attention,interest,desire,action. (1)Message content 1)Rational appeals:show that the product will produce the desired benefits. 2)Emotional appeals:attempt to stir up either negative or positive emotions that can motivate purchase 3)Moral appeals:are directed to the audience's sense of what is"right"and "proper".They are often used to urge people to support social causes such as acleaner environment or aid tothe disadvantaged (2)Message structure 1)Whether to draw a conclusion or leave it to the audience 2)Whether to present the strongest arguments first or last. 3)Whether to present a one-sided argument or a two-sided argument (3)Message format 1)Print ad:headline,copy,illustration,color 2)Radio:words,soundsand voices. 3)TV:facial expressions,gestures,dress,posture and hairstyles 4.Choosing Media (1)Personal Communication Channels
3 (4) Sellers must be Good at Encoding Messages That Target Audience Can Decode. (三) Steps in Developing Effective Communication 1. Identifying the Target Audience The target audience will heavily affect the communicator’s decisions on what will be said, how it will be said, when it will be said, where it will be said, and how will say it. 2. Determining the Communication Objectives Good marketing communication calls for “good deeds followed by good words”. 3. Designing a Message-AIDA model: attention, interest, desire, action. (1) Message content 1) Rational appeals: show that the product will produce the desired benefits. 2) Emotional appeals: attempt to stir up either negative or positive emotions that can motivate purchase. 3) Moral appeals: are directed to the audience’s sense of what is “right” and “proper”. They are often used to urge people to support social causes such as a cleaner environment or aid to the disadvantaged. (2) Message structure 1) Whether to draw a conclusion or leave it to the audience. 2) Whether to present the strongest arguments first or last. 3) Whether to present a one-sided argument or a two-sided argument. (3) Message format 1) Print ad: headline, copy, illustration, color 2) Radio: words, sounds and voices. 3) TV: facial expressions, gestures, dress, posture and hairstyles. 4. Choosing Media (1) Personal Communication Channels Awareness Knowledge Liking Preference Conviction Purchase

1)Sales person 2)Word-or-mouth influence (2)Nonpersonal Communication Channels 1)Media Print media:newspapers,magazines,direct-mail >Broadcast:radio,TV Display:billboards,signs,posters >Online:e-mail,company Web sites,online social and sharing networks 2)Atmospheres-designed environments that create or reinforce the buyer's leamnings toward buying a product. 3)Events-staged occurrences that communicate messages to target audiences. 5.Selecting the Message Source 1)可信性:信息源拥有与信息相关的专业知识 2)可靠性:值得信赖的程度 3)可爱性:受喜爱的程度 6.Collecting Feedback Asking the audience members whether they remember the message,how many times they saw it,what points they recall,how they felt about the message and their past and present attitudes toward the product and company. (Setting the Total Promotion Budget and Mix 1.Setting the total promotion budget (1)Affordable:Based on What the Company Can Afford >Completely ignores the effects of promotion on sales. (2)Percentage of Sales:Based on a Certain Percentage of Current or Forecasted Sales Wrongly vies sales as the cause of promotion rather than as the result >Based on availability of funds rather than on opportunities. >Does not provide any basis for choosing a specific percentage,except what 4
4 1) Sales person 2) Word-or-mouth influence (2) Nonpersonal Communication Channels 1) Media ➢ Print media: newspapers, magazines, direct-mail ➢ Broadcast: radio, TV ➢ Display: billboards, signs, posters ➢ Online: e-mail, company Web sites, online social and sharing networks 2) Atmospheres—designed environments that create or reinforce the buyer’s learnings toward buying a product. 3) Events—staged occurrences that communicate messages to target audiences. 5. Selecting the Message Source 1) 可信性:信息源拥有与信息相关的专业知识 2) 可靠性:值得信赖的程度 3) 可爱性:受喜爱的程度 6. Collecting Feedback Asking the audience members whether they remember the message, how many times they saw it, what points they recall, how they felt about the message and their past and present attitudes toward the product and company. (四) Setting the Total Promotion Budget and Mix 1. Setting the total promotion budget (1) Affordable: Based on What the Company Can Afford ➢ Completely ignores the effects of promotion on sales. (2) Percentage of Sales: Based on a Certain Percentage of Current or Forecasted Sales ➢ Wrongly vies sales as the cause of promotion rather than as the result. ➢ Based on availability of funds rather than on opportunities. ➢ Does not provide any basis for choosing a specific percentage, except what

has been done in the past or what competitors are doing. (3)Competitive-Parity:Based on the Competitor's Promotion Budget >There is no evidence that budgets based on competitive parity prevent promotion wars. (4)Objective-and-Task:Based on Determining Objectives&Tasks,Then Estimating Costs It is hard to figure out which specific tasks will achieve stated objectives. 2.Shaping the overall promotion mix (1)The nature ofeach promotion tool 1)Advertising Can reach masses of geographically dispersed buyers at low cost per exposure and enables the seller to repeat a message many times. Large-scale advertising says something positive about the seller's size popularity and success. Consumers tend to view advertised products as more legitimate. √Expressive Impersonal 女Very costly 2)Personal selling Most effective tool at certain stages of the buying process particularly in building up buyers'preferences,convictions and actions. Allows all kinds of customer relationships to spring up,ranging from matter-of-fact selling relationships to personal friendships. The buyer usually feels a greater need to listen and respond 女High cost 3)Sales promotion Attract attention Offer strong incentives to purchase ◇Short lived 5
5 has been done in the past or what competitors are doing. (3) Competitive-Parity: Based on the Competitor’s Promotion Budget ➢ There is no evidence that budgets based on competitive parity prevent promotion wars. (4) Objective-and-Task: Based on Determining Objectives & Tasks, Then Estimating Costs ➢ It is hard to figure out which specific tasks will achieve stated objectives. 2. Shaping the overall promotion mix (1) The nature of each promotion tool 1) Advertising ✓ Can reach masses of geographically dispersed buyers at low cost per exposure and enables the seller to repeat a message many times. ✓ Large-scale advertising says something positive about the seller’s size, popularity and success. ✓ Consumers tend to view advertised products as more legitimate. ✓ Expressive Impersonal Very costly 2) Personal selling ✓ Most effective tool at certain stages of the buying process, particularly in building up buyers’ preferences, convictions and actions. ✓ Allows all kinds of customer relationships to spring up, ranging from matter-of-fact selling relationships to personal friendships. ✓ The buyer usually feels a greater need to listen and respond High cost 3) Sales promotion ✓ Attract attention ✓ Offer strong incentives to purchase Short lived

4)Public relations √Believable Reach many prospects who avoid salespeople and advertisements 5)Direct marketing Less public √Immediate √Customized √interactive (2)Promotion mix strategies 1)Push strategy-calls for using the sales force and trade promotion to push the product through channels.The producer promotes the product to channel members who in turn promote it to final consumers. 2)Pull strategy-calls for spending a lot on advertising and consumer promotion to induce final consumers to buy the product,creating a demand vacuum that"pulls"the product through the channel. 二、Advertising (一)Settingadvertising Objectives Specific Communication Task Accomplished with a Specific Target Audience During a Specific Period of Time. The overall advertising goal is to help build customer relationships by communicating customer value. 1.Informative Advertising-Inform Consumers or Build Primary Demand.i.e CD Players 2.Persuasive Advertising-Build Selective Demand.ie Sony CD Players 3.Comparison Advertising-Compares One Brand to Another.ie.Avis vs.Hertz 4.Reminder Advertising-Keeps Consumers Thinking About a Product.ie. Coca-Cola Informative advertising
6 4) Public relations ✓ Believable ✓ Reach many prospects who avoid salespeople and advertisements 5) Direct marketing ✓ Less public ✓ Immediate ✓ Customized ✓ interactive (2) Promotion mix strategies 1) Push strategy—calls for using the sales force and trade promotion to push the product through channels. The producer promotes the product to channel members who in turn promote it to final consumers. 2) Pull strategy—calls for spending a lot on advertising and consumer promotion to induce final consumers to buy the product, creating a demand vacuum that “pulls” the product through the channel. 二、 Advertising (一) Setting advertising Objectives ⚫ Specific Communication Task Accomplished with a Specific Target Audience During a Specific Period of Time. ⚫ The overall advertising goal is to help build customer relationships by communicating customer value. 1. Informative Advertising-Inform Consumers or Build Primary Demand. i.e CD Players 2. Persuasive Advertising-Build Selective Demand. i.e Sony CD Players 3. Comparison Advertising-Compares One Brand to Another. i.e. Avis vs. Hertz 4. Reminder Advertising-Keeps Consumers Thinking About a Product. i.e. Coca-Cola Informative advertising

Communicating customer value suggesting new uses fora product Building a brand and company image Informing the market of a price change Telling the market about a new product Describing available services and support Explaining how the product works Correcting false impressions Persuasive advertising Building brand preference Persuading customers to purchase now Encouraging switching to your brand Persuading customers to receive a sales call Changing customer's perception of product value Comparative advertising Compares brand with one or more others Reminder advertising Maintaining customer relationships Reminding consumers where to buy the product Reminding consumers that the product may Keeping the brand in customer's mind be needed in the near future during off-seasons ()Settingtheadvertisingbudget 1.Methods (1)Affordable Approach (2)Percent ofsales (3)Competitive parity (4)Objective and task 2.Factors to be considered when setting the advertising budget: (1)Stage in the product life cycle (2)Market share, (3)Competition and clutter, (4)Product differentiation. (Developingadvertisingstrategy
7 (二) Setting the advertising budget 1. Methods (1) Affordable Approach (2) Percent of sales (3) Competitive parity (4) Objective and task 2. Factors to be considered when setting the advertising budget: (1) Stage in the product life cycle, (2) Market share, (3) Competition and clutter, (4) Product differentiation. (三) Developing advertising strategy Communicating customer value suggesting new uses for a product Building a brand and company image Informing the market of a price change Telling the market about a new product Describing available services and support Explaining how the product works Correcting false impressions Persuasive advertising Building brand preference Persuading customers to purchase now Encouraging switching to your brand Persuading customers to receive a sales call Changing customer’s perception of product value Convincing customers to tell others about the brand Comparative advertising Compares brand with one or more others Reminder advertising Maintaining customer relationships Reminding consumers where to buy the product Reminding consumers that the product may be needed in the near future Keeping the brand in customer’s mind during off-seasons

1.Creating the advertising message (1)Message Strategy 1)Develop a Message Focus on Customer Benefits 2)Creative Concept "Big Idea"Visualization or Phrase Combination of Both 3)Advertising AppealsMeaningful,Believable,Distinctive (2)Message execution 1)Slice of life 2)Lifestyle 3)Fantasy 4)Mood or image 5)Musical 6)Personality symbol 7)Technical expertise 8)Scientific evidence 9)Testimonial evidence or endorsement 2.Selecting advertising media (1)Deciding on reach,frequency and impact 1)Reach-the percentage of people in the target market who are exposed to the ad campaign during a given period of time. 2)Frequency-how many times the average person in the target market is exposed to the message 3)Media impact-qualitative value of a message exposure through a given medium. (2)Choosing among major media types 1)Major Media Types:Media Habits of Target Consumers,Nature of the Product,Types of Message,Cost Medium Advantages limitations Good mass-marketing coverage.High absolute costs,high clutter
8 1. Creating the advertising message (1) Message Strategy 1) Develop a Message Focus on Customer Benefits 2) Creative Concept “Big Idea” Visualization or Phrase Combination of Both 3) Advertising Appeals—Meaningful, Believable, Distinctive (2) Message execution 1) Slice of life 2) Lifestyle 3) Fantasy 4) Mood or image 5) Musical 6) Personality symbol 7) Technical expertise 8) Scientific evidence 9) Testimonial evidence or endorsement 2. Selecting advertising media (1) Deciding on reach, frequency and impact 1) Reach—the percentage of people in the target market who are exposed to the ad campaign during a given period of time. 2) Frequency—how many times the average person in the target market is exposed to the message 3) Media impact—qualitative value of a message exposure through a given medium. (2) Choosing among major media types 1) Major Media Types: Media Habits of Target Consumers, Nature of the Product, Types of Message, Cost Medium Advantages limitations TV Good mass-marketing coverage, High absolute costs, high clutter
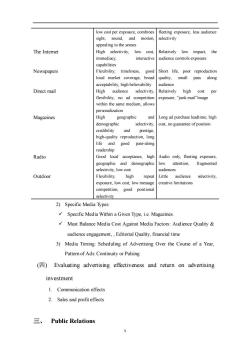
low cost per exposure,combines fleeting exposure,less audience sight,sound,and motion, selectivity appealing to the senses The Internet High selectivity.low cost Relatively low impact.the interactive audience contro exposure Newspapers Flexibility,timeliness, g00 Short life,poor reproduction local market coverage,broad quality.small pass along acceptability.high believability audience Direct mail High audience selectivity. Relatively high cost per flexibility,no ad exposure,"junk mail"image within the same medium,allow personalization Magazines High geographic and Long ad purchase leadtime;high demographic selectivity cost,no guarantee of position high-qualityreproduction. life and good pass-along readership Radio Good local acceptance.high Audio only.fleeting exposure. graphic and demographic attention, fragmented electivity,lowcos udiences Outdoor Flexibility, high repea Little audience selectivity, exposure.low cost.low message creative limitations competition,good positional selectivity 2)Specific Media Types: Specific Media Within a Given Type,ie.Magazines Must Balance Media Cost Against Media Factors:Audience Quality audience engagement,Editorial Quality,financial time 3)Media Timing:Scheduling of Advertising Over the Course of a Year. Pattem of Ads:Continuity or Pulsing (Evaluating advertising effectiveness and return on advertising investment 1.Communication effects 2.Sales and profit effects 三、Public Relations
9 low cost per exposure, combines sight, sound, and motion, appealing to the senses fleeting exposure, less audience selectivity The Internet High selectivity, low cost, immediacy, interactive capabilities Relatively low impact, the audience controls exposure Newspapers Flexibility, timeliness, good local market coverage, broad acceptability, high believability Short life, poor reproduction quality, small pass along audience Direct mail High audience selectivity, flexibility, no ad competition within the same medium, allows personalization Relatively high cost per exposure, “junk mail”image Magazines High geographic and demographic selectivity, credibility and prestige, high-quality reproduction, long life and good pass-along readership Long ad purchase leadtime; high cost, no guarantee of position Radio Good local acceptance, high geographic and demographic selectivity, low cost Audio only, fleeting exposure, low attention, fragmented audiences Outdoor Flexibility, high repeat exposure, low cost, low message competition, good positional selectivity Little audience selectivity, creative limitations 2) Specific Media Types: ✓ Specific Media Within a Given Type, i.e. Magazines. ✓ Must Balance Media Cost Against Media Factors: Audience Quality & audience engagement, , Editorial Quality, financial time 3) Media Timing: Scheduling of Advertising Over the Course of a Year, Pattern of Ads: Continuity or Pulsing (四) Evaluating advertising effectiveness and return on advertising investment 1. Communication effects 2. Sales and profit effects 三、 Public Relations

()Public Relations:Involves Building Good Relations With the Company's Various Publics by Obtaining Favorable Publicity,Building Up a Good Corporate Image,and Handling or Heading Off Unfavorable Rumors,Stories,and Events. ·广告是让别人知道你(单面宣传),公关是让别人喜欢你(双向交流) ●公关=沟通+销售 ·公关的核心:制造时间,制造新闻(造势,借势) ·内求团结,外塑形象 (二)Functions 1.Press relations or press agency:creating and placing newsworthy information in the news media to attract attention to a person,product,or service. 2.Product publicity:publicizing specific products 3.Product affairs:building and maintaining relations with legislators and government officials to influence legislation and regulation. 4.Investor relations:maintaining relationships with shareholders and others in the financial community 5.Development:public relations with donors or members of nonprofit organizations to gain financial or volunteer support. (Major Public Relations Tools >News Speeches >Special Events >Written Materials >Audiovisual Materials >Corporate Identity Materials >Public Service Activities >Web Site 四、Personal Selling
10 (一) Public Relations: Involves Building Good Relations With the Company’s Various Publics by Obtaining Favorable Publicity, Building Up a Good Corporate Image, and Handling or Heading Off Unfavorable Rumors, Stories, and Events. ⚫ 广告是让别人知道你(单面宣传),公关是让别人喜欢你(双向交流) ⚫ 公关=沟通+销售 ⚫ 公关的核心:制造时间,制造新闻(造势,借势) ⚫ 内求团结,外塑形象 (二) Functions 1. Press relations or press agency: creating and placing newsworthy information in the news media to attract attention to a person, product, or service. 2. Product publicity: publicizing specific products 3. Product affairs: building and maintaining relations with legislators and government officials to influence legislation and regulation. 4. Investor relations: maintaining relationships with shareholders and others in the financial community. 5. Development: public relations with donors or members of nonprofit organizations to gain financial or volunteer support. (三) Major Public Relations Tools ➢ News ➢ Speeches ➢ Special Events ➢ Written Materials ➢ Audiovisual Materials ➢ Corporate Identity Materials ➢ Public Service Activities ➢ Web Site 四、 Personal Selling
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 8 Products, Services, and Brands.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 7 Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 6 Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 9 Pricing and Pricing Strategies.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 10 Marketing Channels.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第1章 营销与营销过程.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第3章 营销系统与营销环境分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第4章 消费者市场与购买行为分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第2章 顾客价值与顾客满意.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第9章 市场传播与促销.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第10章 产品生命周期与营销战略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第6章 产品决策.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第5章 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第7章 价格策略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第8章 分销管理.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014第二学期试卷A(答案).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014第二学期试卷A(试题).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第二学期试卷B(答案).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第二学期试卷B(试题).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第一学期试卷A(答案).doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 2 Company and Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 4 Managing Marketing Information to Gain Customer Insights.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 5 Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 3 Analyzing the Marketing Environment.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 1 Marketing.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第8章案例 分销渠道策略-通用公司打造全球供应链.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第9章案例 促销策略-中国肥皂泡戏煞东瀛人.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第6章案例 产品决策-广东太阳神的产品组合.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第7章案例 价格决策-海信空调的价格策略.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第5章案例 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位- “红高粱”的启示.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第3章案例 市场营销环境-恒伟药业信息调研出效益.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第4章案例 分析消费者市场与购买行为-小阿华的“精确营销”.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第2章案例 规划企业战略与市场营销管理-雅戈尔,选择没有对错.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第1章案例 营销与营销管理-亚马逊名震全球之道.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)The Pepsi and Coca-Cola Challenge-A Cola with Breakfast.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Van Der Steen Candy Company.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Summit Ski Produc.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Who will go to Saudi Arabia.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Egle Steel Supply Company.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Selling Whoppers In Japan.doc
