《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 1 Marketing

Chapter 1 Marketing -Creating and Capturing Customer Value 教学目的:本章从市场营销学对“市场”一词的理解出发,使学生了解市场的功能、作用, 并建立起市场营销的基本概念,明确认识市场营销的重要性和企业市场营销活动应树立 的指导思想即市场营销观念。 教学重点:市场的含义、类型:市场营销的含义及有关的概念:市场营销管理及其哲学 观念。 教学难点:区分市场营销与推销 学时分配: 教学内容 导入案例一一泰国东方饭店(通过此案例,了解市场营销的概念及市场营销的核心一 建立关系) 一、What is Marketing 1.Marketing defined:The process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return. 6R"定义法-Right:product.price place.promotion,time customer 2.The Marketing Process Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants Design a customer-driven marketing strategy Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value Build profitable relationships and create customer delight Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs 1.Customer Needs.Wants and Demands
Chapter 1 Marketing -Creating and Capturing Customer Value 教学目的:本章从市场营销学对“市场”一词的理解出发,使学生了解市场的功能、作用, 并建立起市场营销的基本概念,明确认识市场营销的重要性和企业市场营销活动应树立 的指导思想即市场营销观念。 教学重点:市场的含义、类型;市场营销的含义及有关的概念;市场营销管理及其哲学 观念。 教学难点:区分市场营销与推销 学时分配: 教学内容: 导入案例——泰国东方饭店(通过此案例,了解市场营销的概念及市场营销的核心—— 建立关系) 一、 What is Marketing 1. Marketing defined: The process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return. 6”R”定义法——Right: product, price, place, promotion, time, customer 2. The Marketing Process ⚫ Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants ⚫ Design a customer-driven marketing strategy ⚫ Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value ⚫ Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value ⚫ Build profitable relationships and create customer delight ⚫ Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity 二、 Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs 1. Customer Needs, Wants and Demands

(1)Needs-state of felt deprivation for basic items such as food and clothing and complex needs such as for belonging.ie.I am hungry (2)Wants-form that a human need takes as shaped by culture and individual personality.i.e.I want a hamburger,and a soft drink (3)Demands-human wants backed by buying power.i.e.I have money to buy this meal. 2.Marketingofferings-products,services and experiences (1)Products:Anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a need or want (2)Services:Activities or benefits offered for sale that are essentially intangible and don't result in the ownership of anything. 3.Value and satisfaction Value=benefit-cost=(physical+emotional)benefit-(money+time+energy)cost Satisfaction=result-expectation 4.Exchange,transactions and relationships (1)Relationships:Building a marketing network consisting of the company and all its supporting stakeholders-Parties with an interest in a firm's decision-making. ie.employees,customers,suppliers,competitors,shareholders,etc. 5.Markets:the set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service Markets=actural+potential buyers ◆Needs resources for exchange willingness to exchange 3.Modern marketingsystem(P32) 三、 Designing a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy Marketing management:The art science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them. (-)Selecting Customersto Serve ()Choosinga Value Proposition (三) Marketing management orientations
(1) Needs - state of felt deprivation for basic items such as food and clothing and complex needs such as for belonging. i.e. I am hungry. (2) Wants - form that a human need takes as shaped by culture and individual personality. i.e. I want a hamburger, and a soft drink. (3) Demands - human wants backed by buying power. i.e. I have money to buy this meal. 2. Marketing offerings-products, services and experiences (1) Products: Anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a need or want (2) Services: Activities or benefits offered for sale that are essentially intangible and don’t result in the ownership of anything. 3. Value and satisfaction ⚫ Value=benefit-cost=(physical+emotional)benefit-(money+time+energy)cost ⚫ Satisfaction=result-expectation 4. Exchange, transactions and relationships (1) Relationships: Building a marketing network consisting of the company and all its supporting stakeholders-Parties with an interest in a firm’s decision-making. i.e. employees, customers, suppliers, competitors, shareholders, etc. 5. Markets: the set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service. ⚫ Markets=actural+potential buyers Needs resources for exchange willingness to exchange 3. Modern marketing system (P32) 三、 Designing a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy Marketing management: The art & science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them. (一) Selecting Customers to Serve (二) Choosing a Value Proposition (三) Marketing management orientations
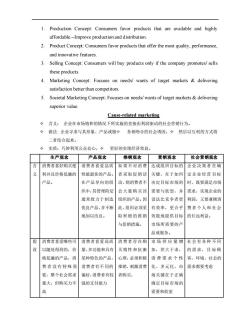
1. Production Concept:Consumers favor products that are available and highly affordable-Improve production and distribution 2.Product Concept:Consumers favor products that offer the most quality.performance, and innovative features. 3.Selling Concept:Consumers will buy products only if the company promotes/sells these products. 4.Marketing Concept:Focuses on needs/wants of target markets delivering satisfaction better than competitors 5. Societal Marketing Concept:Focuses on needs/wants of target markets&delivering superior value. Cause-related marketing 令含义:企业在市场饱和的情况下所实施的直接由利润驱动的社会营销行为。 ◇做法:企业寻求与其形象、产品或服◇务相吻合的社会诱因,◆然后以互利的方式将 二者结合起来。 令实质:巧妙利用公众良心,夕更好的实现经济效益。 生产观念 产品观念 推销观念 营销观念 社会营销观念 消费者喜好购买使消费者喜爱品质 如果不对消费达成组织目标的企业决策者在确 利并且价格低廉的 性能最佳的产品 者采取促销活 关键,在于如何 定企业经营目标 产品。 在产品导向的组 动,则消费者不 决定目标市场的 时,既要满足市场 织中,其管理阶层 会大量购买该 需要与欲望,并 需求,实现企业的 通常致力于制造 组织的产品。因 设法比竞争者更 利润,又要兼顾消 优良产品,并不断 此,组织必须采 有效率,更合乎 费者个人和社会 地加以改良。 取积极的推销 效能地提供目标 的长远利益。 与促销措施。 市场所需要的 品或服务。 假消费者喜爱哪些可消费者喜爱高质 消费者存在购市场供应量增社会有各种不同 设 以随处得到的,价量、多功能和具有 买惰性和抗衡加,供大于求, 的需求,目标顾 格低廉的产品,消 某种特色的产品, 心理,必须积极消费需求个性客、环境、社会的 费者没有特殊需 消费者有不同的 推销,刺激消费化、多元化,市需求都要考虑 要,整个社会需求 偏好,消费者有较 者购买, 场关键在于正确 量大,但购买力不 强的支付能力 确定目标市场的 需要和欲望
1. Production Concept: Consumers favor products that are available and highly affordable.-Improve production and distribution. 2. Product Concept: Consumers favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and innovative features. 3. Selling Concept: Consumers will buy products only if the company promotes/ sells these products. 4. Marketing Concept: Focuses on needs/ wants of target markets & delivering satisfaction better than competitors. 5. Societal Marketing Concept: Focuses on needs/ wants of target markets & delivering superior value. Cause-related marketing 含义: 企业在市场饱和的情况下所实施的直接由利润驱动的社会营销行为。 做法: 企业寻求与其形象、产品或服 务相吻合的社会诱因, 然后以互利的方式将 二者结合起来。 实质:巧妙利用公众良心, 更好的实现经济效益。 生产观念 产品观念 推销观念 营销观念 社会营销观念 含 义 消费者喜好购买便 利并且价格低廉的 产品。 消费者喜爱品质 性能最佳的产品。 在产品导向的组 织中,其管理阶层 通常致力于制造 优良产品,并不断 地加以改良。 如果不对消费 者采取促销活 动,则消费者不 会大量购买该 组织的产品。因 此,组织必须采 取积极的推销 与促销措施。 达成组织目标的 关键,在于如何 决定目标市场的 需要与欲望,并 设法比竞争者更 有效率,更合乎 效能地提供目标 市场所需要的产 品或服务。 企业决策者 在确 定企业经营 目标 时,既要满足市场 需求,实现企业的 利润,又要兼顾消 费者个人和 社会 的长远利益。 假 设 消费者喜爱哪些可 以随处得到的,价 格低廉的产品,消 费 者 没有 特殊 需 要,整个社会需求 量大,但购买力不 高 消费者喜爱高质 量、多功能和具有 某种特色的产品, 消费者有不同的 偏好,消费者有较 强的支付能力 消费者存在购 买惰性和抗衡 心理,必须积极 推销,刺激消费 者购买, 市场供应量增 加,供大于求, 消费需求个性 化、多元化,市 场关键在于正确 确定目标市场的 需要和欲望 社会有各种 不同 的需求,目 标顾 客、环境、社会的 需求都要考虑
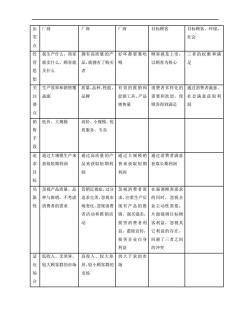
出厂商 厂商 一商 目标顾客 目标顾客、环境、 社会 点 我生产什么,商家 拥有高质量的产 好坏都要靠吆 顾客就是上帝 三者的权衡和满 营 就卖什么,顾客就 品,就拥有了购买 喝 以顾客为核心 足 思 买什么 者 关生产效率和销售覆质量、品种、性能、 有效的推销和消费者多样化的通过消费者满意、 注盖面 品牌 促销工具、产品需要和欲望,使 社会满意获取利 销售量 顾客得到满足 润 销低价、大规模 高价、小规模、优 售 质服务、专卖 追通过大规模生产来 通过高质量的 通过大规模销 通过消费者满意 求 获取短期利润 品来获取短期利 售来获取短期获取长期利润 润 利润 标 局忽视产品质量、品 营销近视症,过分 忽视消费者需在强调顾客需求 限 种与推销,不考虑 追求完美,忽视市 求,注重生产后的同时,忽视企 性 消费者的需求 场变化,忽视消费 现有产品的推业主动性需要, 者活动和推销活 销,强买强卖, 片面强调目标顾 损害消费者利客利益,忽视其 益,滥做宜传, 它利益的存在, 损苦企业自身回避了三者之间 利益 的冲突 适低收入、无差异、 高收入、较大差 供大于求的市 较大顾客群的市场异、较小顾客群的 市场
出 发 点 厂商 厂商 厂商 目标顾客 目标顾客、环境、 社会 经 营 思 想 我生产什么,商家 就卖什么,顾客就 买什么 拥有高质量的产 品,就拥有了购买 者 好坏都要靠吆 喝 顾客就是上帝, 以顾客为核心 三者的权衡 和满 足 关 注 要 点 生产效率和销售覆 盖面 质量、品种、性能、 品牌 有效的推销和 促销工具、产品 销售量 消费者多样化的 需要和欲望,使 顾客得到满足 通过消费者满意、 社会满意获 取利 润 销 售 手 段 低价、大规模 高价、小规模、优 质服务、专卖 追 求 目 标 通过大规模生产来 获取短期利润 通过高质量的产 品来获取短期利 润 通过大规模销 售来获取短期 利润 通过消费者满意 获取长期利润 局 限 性 忽视产品质量、品 种与推销,不考虑 消费者的需求 营销近视症,过分 追求完美,忽视市 场变化,忽视消费 者活动和推销活 动 忽视消费者需 求,注重生产后 现有产品的推 销,强买强卖, 损害消费者利 益,滥做宣传, 损害企业自身 利益 在强调顾客需求 的同时,忽视企 业主动性需要, 片面强调目标顾 客利益,忽视其 它利益的存在, 回避了三者之间 的冲突 适 应 场 合 低收入、无差异、 较大顾客群的市场 高收入、较大差 异、较小顾客群的 市场 供大于求的市 场

四、 Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program (一) Building Customer Relationships 1.Customer Relationship Management The overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction (1)Relationship building blocks:customer value and satisfaction ●Customer value Total customer value Product value:dependability,durability,security Service value:delivery,training.repair Personnel value:knowledge.experience,responsibility Image value:brand,Corporate image,goodwill ◇Total customer cost √Monetary cost √Time cost √Energy cost √Physical cost Customer satisfaction Today's most successful companies are raising expectations-and delivering performance to match These companies embrace total customer satisfaction. Firm that seeks total customer satisfaction doesn't have to attempt maximum customer satisfaction. Purpose of marketing is to generate customer value profitably-offer customer satisfaction without sacrificing profits. (2)Customer relationship levels and tools ●Levels 令basic relationships ◇full partnerships ·Tools: Frequency marketing programs
四、 Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program (一) Building Customer Relationships 1. Customer Relationship Management The overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction. (1) Relationship building blocks: customer value and satisfaction ⚫ Customer value Total customer value: ✓ Product value: dependability, durability, security ✓ Service value: delivery, training, repair ✓ Personnel value: knowledge, experience, responsibility ✓ Image value: brand, Corporate image, goodwill Total customer cost ✓ Monetary cost ✓ Time cost ✓ Energy cost ✓ Physical cost ⚫ Customer satisfaction Today’s most successful companies are raising expectations – and delivering performance to match. These companies embrace total customer satisfaction. Firm that seeks total customer satisfaction doesn’t have to attempt maximum customer satisfaction. Purpose of marketing is to generate customer value profitably – offer customer satisfaction without sacrificing profits. (2) Customer relationship levels and tools ⚫ Levels basic relationships full partnerships ⚫ Tools: Frequency marketing programs

Club marketing programs Structural ties and financial and social benefits 2.The Changing nature of customer relationships (1)Relating with more carefully selected customers (2)Relating more deeply and interactively New technologies have profoundly changed the ways in which people relate to one another This changing communications environment also affects how consumers relate to companies and products. At the same time that the new communications tools create relationship-building opportunities for markets,they also create challenges. They give consumers greater power and control. 3.Partner Relationship Management (1)Partners inside the company Every functional area can interact with customers. Every employee must be customer-focused. Rather than letting each department go its own way,firms are linking all departments in the cause of creating customer value. (2)Marketing partners outside the firm Through supply chain management,many companies today are strengthening their connections with partners all along the supply chain. ·传统的是拉入式做经营,现代是全方位拉动做经营,即整合资源(自然、社会、 客户、行业内的存量资源) ·如何形成价值链一一整合资源。营销者是资源整合者。 ·行业内的存量资源整合包括收购、包销、贴牌生产等。 ·资源运作:你手上有了别人想要的资源,你就可以调动、利用、支配别人手中的 资源。具体做法:渠道互换、共同研发、生产等。资源运作是资源整合的基础。 ·水平战略:满足同一顾客不同需求的企业彼此之间形成的战略联盟。 ·水平战略是资源整合的一种形式。 ·水平战略往小了说叫联合促销,往大了说叫异业整合或混业经营。(苏宁与居然) (二) Capturing Value from Customers 1.Creating Customer loyalty and retention
Club marketing programs Structural ties and financial and social benefits 2. The Changing nature of customer relationships (1) Relating with more carefully selected customers (2) Relating more deeply and interactively ⚫ New technologies have profoundly changed the ways in which people relate to one another. ⚫ This changing communications environment also affects how consumers relate to companies and products. ⚫ At the same time that the new communications tools create relationship-building opportunities for markets, they also create challenges. They give consumers greater power and control. 3. Partner Relationship Management (1) Partners inside the company ⚫ Every functional area can interact with customers. ⚫ Every employee must be customer-focused. ⚫ Rather than letting each department go its own way, firms are linking all departments in the cause of creating customer value. (2) Marketing partners outside the firm ⚫ Through supply chain management, many companies today are strengthening their connections with partners all along the supply chain. ⚫ 传统的是拉入式做经营,现代是全方位拉动做经营,即整合资源(自然、社会、 客户、行业内的存量资源) ⚫ 如何形成价值链——整合资源。营销者是资源整合者。 ⚫ 行业内的存量资源整合包括收购、包销、贴牌生产等。 ⚫ 资源运作:你手上有了别人想要的资源,你就可以调动、利用、支配别人手中的 资源。具体做法:渠道互换、共同研发、生产等。资源运作是资源整合的基础。 ⚫ 水平战略:满足同一顾客不同需求的企业彼此之间形成的战略联盟。 ⚫ 水平战略是资源整合的一种形式。 ⚫ 水平战略往小了说叫联合促销,往大了说叫异业整合或混业经营。(苏宁与居然) (二) Capturing Value from Customers 1. Creating Customer loyalty and retention

(1)Highly satisfied(delighted)customers produce benefits They are less price sensitive, They remain customers longer, They talk favorably about the company and products to others. (2)Tremendous difference between the loyalty of satisfied customers and completely satisfied customers. (3)Delighted customers have emotional and rational preferences for products,and this creates high customer loyalty. ·保持顾客的1:5法则 ·争取一个新顾客所耗费的成本是保持一名现有顾客的5倍 ●原因 ·开发新顾客要花费相应的开发费用(宣传、评价顾客信用等) ·第一次交易时,很难向新顾客销售多种产品 ●新顾客很难将业务集中在一个企业购买 2.Building Lasting Customer Relationships (1)Financial Benefits:i.e.Frequency Marketing Programs (2)Social Benefits:i.e.Learning Individual Customer's Needs&Wants (3)Structural Ties:i.e.Supply Customers With Special Equipment 一个古老但非常有用的手段一口碑营销 特点:低成本投入、效果显著、信任度高 案例:国外一家银行出纳员的故事 这家银行地处偏远,在一个周五的晚上临下班前30分钟,把零钱用完了,可面前还有一群人等着兑换薪 水支票,这位出纳员怎么办?是让这些人回去换好零钱再来?还是等明天备齐零钱再营业?出纳员的作 法是:根据最接近的数目来付款,当1美元钞用完后,就用最接近的5元的倍数付款,在关门之前,甚至用 10元的倍数来付款.结帐时发现出纳员总共多付了320美元,银行怎么办?银行不仅没有惩罚出纳 员,还特别把她塑造成为英雄人物,因为银行估计那天晚上,口碑效应大概为他们多争取了100个新 客户,她为银行带来的影响比320元昂贵得多。 顾客永远是正确的 √原则1:顾客永远是正确的。 √原则2:如果顾客错了,见原则1 企业竞争优势的关键来源 √企业正是通过比竞争对手更廉价或更出色地开展价值创造活动
(1) Highly satisfied (delighted) customers produce benefits: ⚫ They are less price sensitive, ⚫ They remain customers longer, ⚫ They talk favorably about the company and products to others. (2) Tremendous difference between the loyalty of satisfied customers and completely satisfied customers. (3) Delighted customers have emotional and rational preferences for products, and this creates high customer loyalty. ⚫ 保持顾客的1:5法则 ⚫ 争取一个新 顾客所耗费的成本是保持一名现有 顾客的5 倍 ⚫ 原因 ⚫ 开发新顾客要花费相应的开发费用(宣传、评价顾客信用等) ⚫ 第一次交易时,很难向新顾客销售多种产品 ⚫ 新顾客很难将业务集中在一个企业购买 2. Building Lasting Customer Relationships (1) Financial Benefits: i.e. Frequency Marketing Programs (2) Social Benefits: i.e. Learning Individual Customer’s Needs & Wants (3) Structural Ties: i.e. Supply Customers With Special Equipment 一个古老但非常有用的手段 ——口碑营销 特点: 低成本投入、效果显著、信任度高 案例:国外一家银行出纳员的故事 这家银行地处偏远,在一个周五的晚上临下班前30分钟,把零钱用完了,可面前还有一群人等着兑换薪 水支票,这位出纳员怎么办?是让这些人回去换好零钱再来?还是等明天备齐零钱再营业?出纳员的作 法是:根据最接近的数目来付款,当1美元钞用完后,就用最接近的5元的倍数付款,在关门之前,甚至用 10元的倍数来付款.结帐时发现出纳员总共多付了320美元,银行怎么办?银行不仅没有惩罚出纳 员,还特别把她塑造成为英雄人物,因为银行估计那天晚上,口碑效应大概为他们多争取了100个新 客户,她为银行带来的影响比320元昂贵得多。 顾客永远是正确的 ✓ 原则1:顾客永远是正确的。 ✓ 原则2:如果顾客错了,见原则1 企业竞争优势的关键来源 ✓ 企业正是通过比竞争对手更廉价或更出色地开展价值创造活动

√包括市场营销、销售、生产、服务、采购、技术开发、人力资源管理和企业决策 √竞争者的价值链之间的差异是竞争优势的关键来源。 为客户创造价值的途径 √降低客户成本 √增加客户效益 如何永久的赚钱? √赚所有的人一次钱,是运气: √赚一个人所有的钱,是学问。 忠诚的顾客哪里来? √频繁营销规划:设计向经常购买或大量购买的顾客提供奖励的方法 √俱乐部营销规划 √超越消费者的期望 √不断寻求改进、创新 如何提高客户的忠诚度 √对客户购买动机影响最大的因素: ■客户服务(37%) ■产品选择(37%) ■忠诚度计划(22%) √提供个性化的产品与服务 ■创造需求 ■创造客户 保持顾客的途径 √设置高的转换壁垒 √提供高的顾客满意 保持顾客的利器 √后营销管理关系营销先做朋友后做生意 What is Marketing?Pulling it all together(Page 53)
✓ 包括市场营销、销售、生产、服务、采购、技术开发、人力资源管理和企业决策 ✓ 竞争者的价值链之间的差异是竞争优势的关键来源。 为客户创造价值的途径 ✓ 降低客户成本 ✓ 增加客户效益 如何永久的赚钱? ✓ 赚所有的人一次钱,是运气; ✓ 赚一个人所有的钱,是学问。 忠诚的顾客哪里来? ✓ 频繁营销规划:设计向经常购买或大量购买的顾客提供奖励的方法 ✓ 俱乐部营销规划 ✓ 超越消费者的期望 ✓ 不断寻求改进、创新 如何提高客户的忠诚度 ✓ 对客户购买动机影响最大的因素: ◼ 客户服务(37%) ◼ 产品选择(37%) ◼ 忠诚度计划(22%) ✓ 提供个性化的产品与服务 ◼ 创造需求 ◼ 创造客户 保持顾客的途径 ✓ 设置高的转换壁垒 ✓ 提供高的顾客满意 保持顾客的利器 ✓ 后营销管理-关系营销-先做朋友后做生意 五、 What is Marketing? Pulling it all together (Page 53)

Discussing Applying the Concepts 1.What is marketing and what its primary foal? 2.What are the five different marketing management orientations?Which orientation do you believe your school follows when marketing itself? 3.How has the Internet changed consumers?Marketers? 4.In a small group,develop a marketing plan for a pet boarding service.Who is your target market?How will you enable customers to get the best value?Define what you mean by value and develop the value proposition of your offering for this target market. 5.Define the different relationship levels companies can build with customers.Pick a company and describe the types of relationships you have with it
Discussing & Applying the Concepts 1. What is marketing and what its primary foal? 2. What are the five different marketing management orientations? Which orientation do you believe your school follows when marketing itself? 3. How has the Internet changed consumers? Marketers? 4. In a small group, develop a marketing plan for a pet boarding service. Who is your target market? How will you enable customers to get the best value? Define what you mean by value and develop the value proposition of your offering for this target market. 5. Define the different relationship levels companies can build with customers. Pick a company and describe the types of relationships you have with it
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 3 Analyzing the Marketing Environment.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 5 Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 4 Managing Marketing Information to Gain Customer Insights.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 2 Company and Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 11 Communicating Customer Value.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 8 Products, Services, and Brands.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 7 Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 6 Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 9 Pricing and Pricing Strategies.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 10 Marketing Channels.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第1章 营销与营销过程.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第3章 营销系统与营销环境分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第4章 消费者市场与购买行为分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第2章 顾客价值与顾客满意.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第9章 市场传播与促销.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第10章 产品生命周期与营销战略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第6章 产品决策.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第5章 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第7章 价格策略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第8章 分销管理.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第8章案例 分销渠道策略-通用公司打造全球供应链.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第9章案例 促销策略-中国肥皂泡戏煞东瀛人.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第6章案例 产品决策-广东太阳神的产品组合.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第7章案例 价格决策-海信空调的价格策略.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第5章案例 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位- “红高粱”的启示.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第3章案例 市场营销环境-恒伟药业信息调研出效益.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第4章案例 分析消费者市场与购买行为-小阿华的“精确营销”.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第2章案例 规划企业战略与市场营销管理-雅戈尔,选择没有对错.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第1章案例 营销与营销管理-亚马逊名震全球之道.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)The Pepsi and Coca-Cola Challenge-A Cola with Breakfast.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Van Der Steen Candy Company.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Summit Ski Produc.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Who will go to Saudi Arabia.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Egle Steel Supply Company.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Selling Whoppers In Japan.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程作业习题(分章)市场营销学练习及答案(共九章).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程作业习题(综合)综合习题九.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程作业习题(综合)综合习题九答案.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程作业习题(综合)综合习题十.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程作业习题(综合)综合习题十答案.doc
