《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 4 Managing Marketing Information to Gain Customer Insights

Chapter 4 Managing Marketing Information to Gain Customer Insights 教学目的:通过本章学习,使学生了解营销信息系统的含义,掌握开发营销信息 系统的步骤和营销调研的基本方法,学会分析和使用营销信息。 教学重点:营销信息系统的开发 教学难点:分析和使用营销信息 学时分配 教学内容: Marketing Information and Customer Insights Marketing information by itself has little value.The value is in the customer insighis gained from the information and how these insights are used to make better marketing decisions. Marketing Information To create value for customers and to build meaningful relationships with them,marketers must first gain fresh,deep insights into what customers need and want.Companies use such customer insights to develop competitive advantage Although customer and market insights are important for building customer value and relationships,these insights can be very difficult to obtain. Today's marketers have ready access to plenty of marketing information.With the recent explosion of information technologies companies can now generate information in great quantities 2.Customer Insights A company's marketing research and information system must do more than information lies in how it is used-in the customer
1 Chapter 4 Managing Marketing Information to Gain Customer Insights 教学目的:通过本章学习,使学生了解营销信息系统的含义,掌握开发营销信息 系统的步骤和营销调研的基本方法,学会分析和使用营销信息。 教学重点:营销信息系统的开发 教学难点:分析和使用营销信息 学时分配: 教学内容: 一、 Marketing Information and Customer Insights 1. Marketing Information ⚫ To create value for customers and to build meaningful relationships with them, marketers must first gain fresh, deep insights into what customers need and want. Companies use such customer insights to develop competitive advantage. ⚫ Although customer and market insights are important for building customer value and relationships, these insights can be very difficult to obtain. ⚫ Today’s marketers have ready access to plenty of marketing information. With the recent explosion of information technologies, companies can now generate information in great quantities. 2. Customer Insights ⚫ A company’s marketing research and information system must do more than information lies in how it is used—in the customer Marketing information by itself has little value. The value is in the customer insights gained from the information and how these insights are used to make better marketing decisions

insights (fresh understandings of customers and the marketplace derived from marketing information that become the basis for creating customer value and relationships)that it provides. Based on such thinking,many companies are now restructuring and renaming their marketing research and information functions. In gathering and using customer insights,companies must be careful not to go too far and become customer controlled.The idea is to understand customers to the core and give them what they need-to create value for customers as s means of capturing value for the firm in retum Companies must design effective marketing information systems that give managers the right information,in the right form,at the right time and help them to use this information to create customer value and stronger customer relationships 3.Marketing Information System A marketing information system(MIS)consists of people and procedures for assessing informational needs developing the needed information and helping decision makers to use the information to generate and validate actionable customer and market insights Figure 4.1 The Marketing Information System(Page 125) 二、 Assessing Marketing Information Needs The marketing information system begins and ends with users-with assessing their information needs and then delivering information that meets those needs. The marketing information system primarily serves the company's
2 insights (fresh understandings of customers and the marketplace derived from marketing information that become the basis for creating customer value and relationships) that it provides. ⚫ Based on such thinking, many companies are now restructuring and renaming their marketing research and information functions. ⚫ In gathering and using customer insights, companies must be careful not to go too far and become customer controlled. The idea is to understand customers to the core and give them what they need—to create value for customers as s means of capturing value for the firm in return. ⚫ Companies must design effective marketing information systems that give managers the right information, in the right form, at the right time and help them to use this information to create customer value and stronger customer relationships. 3. Marketing Information System ⚫ A marketing information system (MIS) consists of people and procedures for assessing informational needs developing the needed information and helping decision makers to use the information to generate and validate actionable customer and market insights. Figure 4.1 The Marketing Information System (Page 125) 二、 Assessing Marketing Information Needs ⚫ The marketing information system primarily serves the company’s The marketing information system begins and ends with users—with assessing their information needs and then delivering information that meets those needs

marketing and other managers.It may also provide information to external partners such as suppliers,resellers or marketing services agencies. A good marketing information system balances the information users would like to have against what they really need and what is feasible to offer. The MIS must monitor the marketing environment in order to provide decision makers with information they should have in order to better understand customers and make key marketing decisions. Sometimes the company cannot provide the needed information. either because it is not available or because of MIS limitations. The information on planned budgets probably is not available The company's MIS may not be advanced enough The costs of obtaining.analyzing,storing and delivering information can mount quickly. Marketers should not assume that additional information will always be worth obtaining.They should weigh carefully the costs of getting more information against the benefits resulting from it. 三、 Developing Marketing Information The problem is not finding information-the world is bursting with information from a glut of sources.The real challenge is to find the right information-from inside and outside sources-and to turn it into customer insights. 1.Internaldata (1)Internal databases Electronic collections of consumer and market information
3 marketing and other managers. It may also provide information to external partners such as suppliers, resellers or marketing services agencies. ⚫ A good marketing information system balances the information users would like to have against what they really need and what is feasible to offer. ⚫ The MIS must monitor the marketing environment in order to provide decision makers with information they should have in order to better understand customers and make key marketing decisions. ⚫ Sometimes the company cannot provide the needed information, either because it is not available or because of MIS limitations. The information on planned budgets probably is not available The company’s MIS may not be advanced enough. ⚫ The costs of obtaining, analyzing, storing and delivering information can mount quickly. Marketers should not assume that additional information will always be worth obtaining. They should weigh carefully the costs of getting more information against the benefits resulting from it. 三、 Developing Marketing Information 1. Internal data (1) Internal databases ⚫ Electronic collections of consumer and market information The problem is not finding information—the world is bursting with information from a glut of sources. The real challenge is to find the right information—from inside and outside sources—and to turn it into customer insights

obtained from data sources within the company network Marketing managers can readily access and work with information in the database to identify marketing opportunities and problems plan programs and evaluate performance. (2)Sources The marketing department:furnishes information on customer transactions,demographics,psychographics and buying behavior The customer service department:keeps records of customer satisfaction or service problems. The accounting department:prepares financial statements and keeps detailed records of sales,costs and cash flows. Operations:reports on production schedules,shipments and inventories. The sales force:reports on reseller reactions and competitor activities Marketing channel partners:provide data on point-of sale transactions Harnessing such information can provide powerful customer insights and competitive advantage. (3)Advantages Can be accessed more quickly and cheaply than other information sources. (4)Problems Incomplete or in the wrong form for making marketing decisions Data ages quickly:keeping the database current requires a majo effort A large company produces mountains of information,which must be well integrated and readily accessible so that managers can find it easily and use it effectively.Managing that much data requires highly sophisticated equipment and techniques
4 obtained from data sources within the company network. ⚫ Marketing managers can readily access and work with information in the database to identify marketing opportunities and problems, plan programs and evaluate performance. (2) Sources ⚫ The marketing department: furnishes information on customer transactions, demographics, psychographics and buying behavior. ⚫ The customer service department: keeps records of customer satisfaction or service problems. ⚫ The accounting department: prepares financial statements and keeps detailed records of sales, costs and cash flows. ⚫ Operations: reports on production schedules, shipments and inventories. ⚫ The sales force: reports on reseller reactions and competitor activities ⚫ Marketing channel partners: provide data on point-of sale transactions Harnessing such information can provide powerful customer insights and competitive advantage. (3) Advantages Can be accessed more quickly and cheaply than other information sources. (4) Problems ⚫ Incomplete or in the wrong form for making marketing decisions ⚫ Data ages quickly; keeping the database current requires a major effort ⚫ A large company produces mountains of information, which must be well integrated and readily accessible so that managers can find it easily and use it effectively. Managing that much data requires highly sophisticated equipment and techniques

2.Marketing Intelligence (1)Marketing Intelligence The systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information about consumers,competitors and developments in the marketing environment. The goal is to improve strategic decision making by understanding the consumer environment,assessing and tracking competitors actions and providing early warnings of opportunities and threats (2)Sources Companies also need to actively monitor competitors'activities. Much competitor intelligence can be collected from people inside the company Competitors often reveal intelligence information through their annual reports,business publications,trade show exhibits,press releases advertisements and Web pages (3)Advantage Good marketing intelligence can help marketers to gain insights into how consumers talk about and connect with their brands. (④)Problems The growing uses of marketing intelligence raises a number of ethical issues, 四、Marketing Research 9 Whereas marketing intelligence involves actively scanning the general m rketing environment,marketing research involves more focused studies to gain customer insights relating to specific marketing decisions
5 2. Marketing Intelligence (1) Marketing Intelligence ⚫ The systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information about consumers, competitors and developments in the marketing environment. ⚫ The goal is to improve strategic decision making by understanding the consumer environment, assessing and tracking competitors’ actions and providing early warnings of opportunities and threats. (2) Sources ⚫ Companies also need to actively monitor competitors’ activities. ⚫ Much competitor intelligence can be collected from people inside the company ⚫ Competitors often reveal intelligence information through their annual reports, business publications, trade show exhibits, press releases advertisements and Web pages. (3) Advantage ⚫ Good marketing intelligence can help marketers to gain insights into how consumers talk about and connect with their brands. (4) Problems ⚫ The growing uses of marketing intelligence raises a number of ethical issues, 四、 Marketing Research Whereas marketing intelligence involves actively scanning the general marketing environment, marketing research involves more focused studies to gain customer insights relating to specific marketing decisions

Marketing research is the systematic design,collection,analysis and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing an organization. Some large companies have their own research departments that work with marketing managers on marketing research projects. Sometimes firms simply purchase data collected by outside firms toaid in their decision making (-)Defining the Problem and Research Objectives 1.Marketing managers and researchers must work closely together to define the problem and agree on research objectives. (1)The manager:best understands the decision for which information is needed; (2)The researcher:best understands marketing research and how to obtain the information. 2.The manager and researcher must set the research objectives. (1)Exploratory research gather preliminary information that will help define the problem and suggest hypotheses. (2)Descriptive research:describe things,such as the market potential for a product or the demographics and attitudes of consumers who buy the product (3)Causal research:test hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships The statement of the problem and research objectives guides the entire research process ()Developing the Research Plan 1.Once the research problems and objectives have been defined,researchers must determine the exact information needed,develop a plan for gathering it efficiently and present the plan to management. 2.Research objectives must be translated into specific information needed 6
6 ⚫ Marketing research is the systematic design, collection, analysis and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing an organization. ⚫ Some large companies have their own research departments that work with marketing managers on marketing research projects. ⚫ Sometimes firms simply purchase data collected by outside firms to aid in their decision making. (一) Defining the Problem and Research Objectives 1. Marketing managers and researchers must work closely together to define the problem and agree on research objectives. (1) The manager: best understands the decision for which information is needed; (2) The researcher: best understands marketing research and how to obtain the information. 2. The manager and researcher must set the research objectives. (1) Exploratory research: gather preliminary information that will help define the problem and suggest hypotheses. (2) Descriptive research: describe things, such as the market potential for a product or the demographics and attitudes of consumers who buy the product. (3) Causal research: test hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships. The statement of the problem and research objectives guides the entire research process. (二) Developing the Research Plan 1. Once the research problems and objectives have been defined, researchers must determine the exact information needed, develop a plan for gathering it efficiently and present the plan to management. 2. Research objectives must be translated into specific information needed

3.The research plan should be presented in a written proposal ()Gathering Secondary Data 1.Secondary data:information that already exists somewhere,having been collected for another purpose. 2.Sources: (1)Buy secondary datareports from outside suppliers. (2)Use commercial online databases; (3)Web search engines can be a big help,but can also be very frustrating and inefficient. 3.Advantages (1)Can be obtained more quickly and at a lower cost than primary data (2)Can provide data an individual company cannot collect on its own-information that either is not directly available or would be too expensive to collect 4.Problems (1)The needed information may not exist (2)The information might not be very usable 5.The researcher must evaluate secondary information carefully to make certain it is relevant (fits research project needs),accurate (reliable collected and reported)curent(up-to-date enough for current decisions) and impartial (objectively collected and reported). (Primary Data Collection 1.Research approaches (1)Observational research Gathering primary data by observing relevant people,actions and situations. Observational research can obtain information that people are unwilling or unable to provide Ethnographic research involves sending trained observers to
7 3. The research plan should be presented in a written proposal. (三) Gathering Secondary Data 1. Secondary data: information that already exists somewhere, having been collected for another purpose. 2. Sources: (1) Buy secondary data reports from outside suppliers; (2) Use commercial online databases; (3) Web search engines can be a big help, but can also be very frustrating and inefficient. 3. Advantages (1) Can be obtained more quickly and at a lower cost than primary data (2) Can provide data an individual company cannot collect on its own—information that either is not directly available or would be too expensive to collect 4. Problems (1) The needed information may not exist (2) The information might not be very usable 5. The researcher must evaluate secondary information carefully to make certain it is relevant (fits research project needs), accurate (reliable collected and reported), current (up-to-date enough for current decisions) and impartial (objectively collected and reported). (四) Primary DataCollection 1. Research approaches (1) Observational research Gathering primary data by observing relevant people, actions and situations. Observational research can obtain information that people are unwilling or unable to provide. Ethnographic research involves sending trained observers to

watch and interact with consumers in their natural habitat. Observational and ethnographic research often yield the kinds of details that just don't emerge from traditional research questionnaires or focus groups. (2)Survey research Gathering primary data by asking people questions about their knowledge,attitudes,preferences and buying behaviors Advantage:flexibility-it can be used to obtain many different kinds of information in many different situations. Problems:unable to answer,unwilling to respond,give the wrong answer or pleasing answers (3)Experimental research Gathering primary data by selecting matched groups of subjects, giving them different treatments,controlling related factors and checking for differences in group responses. Tries to explain cause-and-effect relationships.Best suited for gathering causal information. 2.Contact methods (1)Mail,telephone,and personal interviewing Mail Telephone Personal Online Flexibility Poor Good Excellent Good Quantity of data that Good Fair Excellent Good can be collected Control of Excellent Fair Poor Fair interviewer effects Control of sample Fair Excellent Good Excellent Speed of data Poor Excellent Good Excellent collection Response rate Poor Poor Good Good
8 watch and interact with consumers in their natural habitat. Observational and ethnographic research often yield the kinds of details that just don’t emerge from traditional research questionnaires or focus groups. (2) Survey research Gathering primary data by asking people questions about their knowledge, attitudes, preferences and buying behaviors. Advantage: flexibility—it can be used to obtain many different kinds of information in many different situations. Problems: unable to answer, unwilling to respond, give the wrong answer or pleasing answers. (3) Experimental research Gathering primary data by selecting matched groups of subjects, giving them different treatments, controlling related factors and checking for differences in group responses. Tries to explain cause-and-effect relationships. Best suited for gathering causal information. 2. Contact methods (1) Mail, telephone, and personal interviewing Mail Telephone Personal Online Flexibility Poor Good Excellent Good Quantity of data that can be collected Good Fair Excellent Good Control of interviewer effects Excellent Fair Poor Fair Control of sample Fair Excellent Good Excellent Speed of data collection Poor Excellent Good Excellent Response rate Poor Poor Good Good

cost Good Fair Poor Excellent (2)Online marketing research Forms:Internet surveys,online panels,experiments,online focus groups. Well suited to quantitative research ◇Advantages: √speed and low costs more interactive and engaging.easier to complete.less intrusive 令Drawbacks: Restricted Internet access can make it difficult to get a broad cross section of respondents Another problem is controlling who is in the online sample Online surveys can be dry and lacking in dynamics compared with other,more-personal approaches 令Online focus groups Gathering a small group of people online with a trained moderator to chat about a product,service or organization and gain qualitative insights about consumer attitudes and behavior. Advantages:participants can log in from anywhere; researchers can conduct and monitor online focus groups from just about anywhere,eliminating travel,lodging and facility costs,although online focus groups require some advance scheduling.results are almost immediate. Problem:lack the real-world dynamics of more personal approaches 3.Sampling plan
9 cost Good Fair Poor Excellent (2) Online marketing research Forms:Internet surveys, online panels, experiments, online focus groups. Well suited to quantitative research Advantages: ✓ speed and low costs ✓ more interactive and engaging, easier to complete, less intrusive Drawbacks: ✓ Restricted Internet access can make it difficult to get a broad cross section of respondents ✓ Another problem is controlling who is in the online sample. ✓ Online surveys can be dry and lacking in dynamics compared with other, more-personal approaches Online focus groups ✓ Gathering a small group of people online with a trained moderator to chat about a product, service or organization and gain qualitative insights about consumer attitudes and behavior. ✓ Advantages: participants can log in from anywhere; researchers can conduct and monitor online focus groups from just about anywhere, eliminating travel, lodging and facility costs; although online focus groups require some advance scheduling, results are almost immediate. ✓ Problem: lack the real-world dynamics of more personal approaches. 3. Sampling plan
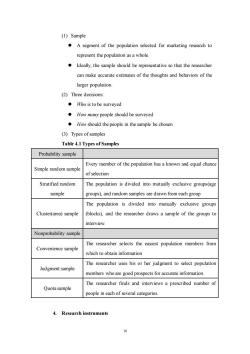
(1)Sample A segment of the population selected for marketing research to represent the population as a whole. Ideally,the sample should be representative so that the researcher can make accurate estimates of the thoughts and behaviors of the larger population. (2)Three decisions ·Who is to be surveyed How many people should be surveyed How should the people in the sample be chosen (3)Types of samples Table 4.1 Types of Samples Probability sample Every member of the population has a known and equal chanc Simple random sample ofselection Stratified random The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups(age sample groups).and random samples are drawn from each group The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups Cluster(area)sample (blocks),and the researcher draws a sample of the groups to interview. Nonprobability sample The researcher selects the easiest population members from Convenience sample which to obtain information The researcher uses his or her judgment to select population Judgment sample members who are good prospects for accurate information. The researcher finds and interviews a prescribed number of Quotasample people in each of several categories. 4.Research instruments 0
10 (1) Sample ⚫ A segment of the population selected for marketing research to represent the population as a whole. ⚫ Ideally, the sample should be representative so that the researcher can make accurate estimates of the thoughts and behaviors of the larger population. (2) Three decisions: ⚫ Who is to be surveyed ⚫ How many people should be surveyed ⚫ How should the people in the sample be chosen (3) Types of samples Table 4.1 Types of Samples Probability sample Simple random sample Every member of the population has a known and equal chance of selection Stratified random sample The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups(age groups), and random samples are drawn from each group Cluster(area) sample The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (blocks), and the researcher draws a sample of the groups to interview. Nonprobability sample Convenience sample The researcher selects the easiest population members from which to obtain information Judgment sample The researcher uses his or her judgment to select population members who are good prospects for accurate information. Quota sample The researcher finds and interviews a prescribed number of people in each of several categories. 4. Research instruments
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 2 Company and Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 11 Communicating Customer Value.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 8 Products, Services, and Brands.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 7 Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 6 Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 9 Pricing and Pricing Strategies.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 10 Marketing Channels.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第1章 营销与营销过程.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第3章 营销系统与营销环境分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第4章 消费者市场与购买行为分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第2章 顾客价值与顾客满意.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第9章 市场传播与促销.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第10章 产品生命周期与营销战略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第6章 产品决策.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第5章 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第7章 价格策略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第8章 分销管理.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014第二学期试卷A(答案).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014第二学期试卷A(试题).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第二学期试卷B(答案).doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 5 Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 3 Analyzing the Marketing Environment.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 1 Marketing.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第8章案例 分销渠道策略-通用公司打造全球供应链.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第9章案例 促销策略-中国肥皂泡戏煞东瀛人.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第6章案例 产品决策-广东太阳神的产品组合.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第7章案例 价格决策-海信空调的价格策略.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第5章案例 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位- “红高粱”的启示.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第3章案例 市场营销环境-恒伟药业信息调研出效益.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第4章案例 分析消费者市场与购买行为-小阿华的“精确营销”.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第2章案例 规划企业战略与市场营销管理-雅戈尔,选择没有对错.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第1章案例 营销与营销管理-亚马逊名震全球之道.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)The Pepsi and Coca-Cola Challenge-A Cola with Breakfast.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Van Der Steen Candy Company.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Summit Ski Produc.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Who will go to Saudi Arabia.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Egle Steel Supply Company.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Selling Whoppers In Japan.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程作业习题(分章)市场营销学练习及答案(共九章).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程作业习题(综合)综合习题九.doc
