《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 8 Products, Services, and Brands

Chapter 8 Products,Services,and Brands -Building Customer Value 教学目的:通过本章的学习,应使学生了解产品生命周期理论的内涵,能能够运 用生命周期理论分析产品所处的阶段,并能够制定相应的营销战略。 教学重点:产品整体概念、品牌管理、品牌策略、服务营销,产品生命周期。 教学难点:品牌策略,服务营销,产品生命周期。 学时分配: 教学内容: -、What is a Product? (一) Product,Services and Experiences 1.Product:anything that can be offered to a market for attention,acquisition, use.or consumption and that might satisfy a want or need 2.Service:any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything. Products,Services,and Experiences TangiNicnGood Good Minor Goo Auto With Tric Soap mpanying Restaurant services The Product-Service Continuum 4.Companies that market experiences realize that customers are really buying much more than just products and services.They are buying what those offers will do for them. (Levels of Productand Services
1 Chapter 8 Products, Services, and Brands -Building Customer Value 教学目的:通过本章的学习,应使学生了解产品生命周期理论的内涵,能能够运 用生命周期理论分析产品所处的阶段,并能够制定相应的营销战略。 教学重点:产品整体概念、品牌管理、品牌策略、服务营销,产品生命周期。 教学难点:品牌策略,服务营销,产品生命周期。 学时分配: 教学内容: 一、 What is a Product? (一) Product, Services and Experiences 1. Product: anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption and that might satisfy a want or need. 2. Service: any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything. 3. Products, Services, and Experiences Pure Tangible Good Pure Service Soap Tangible Good With Accompanying Services Auto With Accompanying Repair Services Hybrid Offer Restaurant Service With Accompanying Minor Goods Airline Trip With Accompanying Snacks Doctor’s Exam 4. Companies that market experiences realize that customers are really buying much more than just products and services. They are buying what those offers will do for them. (二) Levels of Product and Services
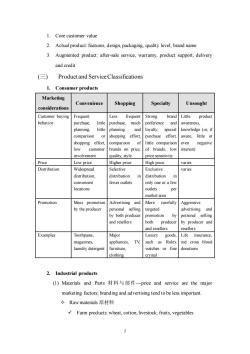
1.Core customer value 2.Actual product:features,design,packaging.quality level,brand name 3.Augmented product:after-sale service,warranty,product support,delivery and credit (三) Product and ServiceClassifications 1.Consumer products Marketing Convenienc considerations Shopping Specialty Unsought Customer buying Frequent Less frequent Strong brand Little product behavior purchase. little purchase.much preference and awareness. planning. little planning and lovalty. special knowledge (or,if comparison shopping effort purchase effort aware,little or shopping effort comparison e comparis even negative custome brands on price. of brands, interest) involvement quality.stvle price sensitivity Price Low price Higher price High price varies Distribution Wides ead Selective Exclus ive varies distribution distribution distribution convenient fewer outlets only one or a few 1ocat山ons outlets pe market area Promotion Mass promotion Advertising and More carefully Aggressive by the producer person targeted advertising by both produce promotion 6 personal selling and resellers both producer by producer and and resellers resellers Examples Toothpaste Maior Luxury goods, Life insurance appliances. such as Role red cross bloo aundry detergent furniture, watches or Tin donations clothing crystal 2.Industrial products (I)Materials and Parts材料与部件一price and service are the major marketing factors,branding and advertising tend to be less important 令Raw materials原材料 Farm products:wheat,cotton,livestock,fruits,vegetables
2 1. Core customer value 2. Actual product: features, design, packaging, quality level, brand name 3. Augmented product: after-sale service, warranty, product support, delivery and credit (三) Product and Service Classifications 1. Consumer products Marketing considerations Convenience Shopping Specialty Unsought Customer buying behavior Frequent purchase, little planning, little comparison or shopping effort, low customer involvement Less frequent purchase, much planning and shopping effort, comparison of brands on price, quality, style Strong brand preference and loyalty, special purchase effort, little comparison of brands, low price sensitivity Little product awareness, knowledge (or, if aware, little or even negative interest) Price Low price Higher price High price varies Distribution Widespread distribution, convenient locations Selective distribution in fewer outlets Exclusive distribution in only one or a few outlets per market area varies Promotion Mass promotion by the producer Advertising and personal selling by both producer and resellers More carefully targeted promotion by both producer and resellers Aggressive advertising and personal selling by producer and resellers Examples Toothpaste, magazines, laundry detergent Major appliances, TV, furniture, clothing Luxury goods, such as Rolex watches or fine crystal Life insurance, red cross blood donations 2. Industrial products (1) Materials and Parts 材料与部件—price and service are the major marketing factors; branding and advertising tend to be less important. Raw materials 原材料 ✓ Farm products: wheat, cotton, livestock, fruits, vegetables

Natural products:fish,lumber,crude petroleum,iron ore Manufactured materials √Component materials(构料):iron,yam,cement,.wires √Component parts(构件):small motors,.tires,castings (2)Capital Items资本项目 ◇Installations Major purchases:buildings(factories,offices) Fixed equipment:generators,drill presses,large computer systems. elevators 令Accessory equipment附属设备 Portable factory equipment and tools:hand tools,lift trucks √Office equipment办公设备:computers,fax machines,.desks (3)Supplies and Services供应品与服务 ◇Supplies, √Operating supplies作业供应品:lubricants,.coal,paper,pencils √Repair and maintenance item维修维护品:paint,.nails,brooms ◇Services: Maintenance and repair services:window cleaning.computer repair Business advisory services:legal,management consulting. advertising 3.Organizations,persons,places and ideas (1)Organization marketing Activities undertaken to create.maintain,or change the attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward an organization (2)Person marketing Activities undertaken to create,maintain,or change attitudes or behavior toward particular people (3)Place marketing Activities undertaken to create,maintain,or change attitudes or 3
3 ✓ Natural products: fish, lumber, crude petroleum, iron ore Manufactured materials ✓ Component materials(构料): iron, yarn, cement, wires ✓ Component parts(构件): small motors, tires, castings (2) Capital Items 资本项目 Installations ✓ Major purchases: buildings (factories, offices) ✓ Fixed equipment: generators, drill presses, large computer systems, elevators Accessory equipment 附属设备 ✓ Portable factory equipment and tools: hand tools, lift trucks ✓ Office equipment 办公设备: computers, fax machines, desks (3) Supplies and Services 供应品与服务 Supplies: ✓ Operating supplies 作业供应品: lubricants, coal, paper, pencils ✓ Repair and maintenance item 维修维护品:paint, nails, brooms Services: ✓ Maintenance and repair services: window cleaning, computer repair ✓ Business advisory services: legal, management consulting, advertising 3. Organizations, persons, places and ideas (1) Organization marketing Activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change the attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward an organization. (2) Person marketing Activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes or behavior toward particular people. (3) Place marketing Activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes or

behavior toward particular places. (4)④Social marketing The use of commercial marketing concepts and tools in programs designed to influence individuals'behavior to improve their well-being and that of society. 二、Product and Service Decisions ()Individual Product Decisions 1.Product and Service Attributes (1)Product Quality:the characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied customer needs Level:the ability of a product to perform its functions. Consistency:freedom from defects and consistency in delivering a targeted level of performance (2)Product Features:Help to Differentiate the Product from Those of the Competition (3)Product Style&Design:Process of Designing a Product's Style& Function Style:describes the appearance of a product Design:goes to the very heart of a product.Design begins with a deep understanding of customer needs 2.Branding ·品牌=品类(一组、一类东西)+品质(与众不同的差异化质量)+ 品味 ·品牌=商标(主动权在企业,及时、合情合理的抢先注册)+商誉(知 名度、美誉度、忠诚度,主动权在顾客) (1)Brand:a name,term,sign,or combination of these,that identifies the maker or seller of a product or service. (2)Branding helps buyers in many ways: Help consumers identify products that might benefit them
4 behavior toward particular places. (4) Social marketing The use of commercial marketing concepts and tools in programs designed to influence individuals’ behavior to improve their well-being and that of society. 二、 Product and Service Decisions (一) Individual Product Decisions 1. Product and Service Attributes (1) Product Quality: the characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied customer needs. Level: the ability of a product to perform its functions. Consistency: freedom from defects and consistency in delivering a targeted level of performance. (2) Product Features: Help to Differentiate the Product from Those of the Competition (3) Product Style & Design: Process of Designing a Product’s Style & Function Style: describes the appearance of a product Design: goes to the very heart of a product. Design begins with a deep understanding of customer needs. 2. Branding ⚫ 品牌=品类(一组、一类东西)+品质(与众不同的差异化质量)+ 品味 ⚫ 品牌=商标(主动权在企业,及时、合情合理的抢先注册)+商誉(知 名度、美誉度、忠诚度,主动权在顾客) (1) Brand: a name, term, sign, or combination of these, that identifies the maker or seller of a product or service. (2) Branding helps buyers in many ways: Help consumers identify products that might benefit them

Say something about product quality and consistency (3)Branding gives the seller several advantages: The seller's brand name and trademark provide legal protection for unique product features Helps the seller to segment markets 3.Packaging (1)Activity of designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product. (2)Numerous factors have made packaging an important marketing tool. (3)Poorly designed packages can cause headaches for consumers and lost sales for the company. (4)Innovative packaging can give a company an advantage over competitors and boost sales. (5)In recent years,product safety has also become a major packaging concern. 4.Labeling (1)Printed information appearing on or with the package (2)Performs several functions Identifies product or brand Describes several things about the product Promotes the product through attractive graphics 5.Product-Support Services (1)Companies should design its support services to profitably meet the needs of target customers and gain competitive advantage (2)How? Survey customers periodically to assess the value of current services and to obtain ideas for new ones. Take steps to fix problems and add new services that will both delight customers and yield profits to the company
5 Say something about product quality and consistency (3) Branding gives the seller several advantages: The seller’s brand name and trademark provide legal protection for unique product features Helps the seller to segment markets 3. Packaging (1) Activity of designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product. (2) Numerous factors have made packaging an important marketing tool. (3) Poorly designed packages can cause headaches for consumers and lost sales for the company. (4) Innovative packaging can give a company an advantage over competitors and boost sales. (5) In recent years, product safety has also become a major packaging concern. 4. Labeling (1) Printed information appearing on or with the package. (2) Performs several functions: ✓ Identifies product or brand ✓ Describes several things about the product ✓ Promotes the product through attractive graphics. 5. Product - Support Services (1) Companies should design its support services to profitably meet the needs of target customers and gain competitive advantage. (2) How? ✓ Survey customers periodically to assess the value of current services and to obtain ideas for new ones. ✓ Take steps to fix problems and add new services that will both delight customers and yield profits to the company

()Product Line Decisions 1.Product line A group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner,are sold to the same customer groups,are marketed through the same types ofoutlets,or fall within given price ranges. 2.Product line length (1)The number of items in the product line (2)Managers need to analyze their product lines periodically to assess each product item's sales and profits and to understand how each item contributes to the line's overall performance (3)Is influenced by company objectives and resources. 3.Expand product line (1)Product line filling 1)Adding more items within the present range of the line 2)Reasons: Reaching for extra profits √Satisfying dealers √Using excess capacity Being the leading full-line company Plugging holes to keep out competitors 3)The company should ensure that new items are noticeably different from existing ones. (2)Product line stretching-Lengthen product line beyond current range 1)Downward To plug a market hole that otherwise would attract a new competitor To respond to a competitor's attack on the upper end Find faster growth taking place in the low-end segments 2)Upward 6
6 (二) Product Line Decisions 1. Product line A group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups, are marketed through the same types of outlets, or fall within given price ranges. 2. Product line length (1) The number of items in the product line. (2) Managers need to analyze their product lines periodically to assess each product item’s sales and profits and to understand how each item contributes to the line’s overall performance. (3) Is influenced by company objectives and resources. 3. Expand product line (1) Product line filling 1) Adding more items within the present range of the line. 2) Reasons: ✓ Reaching for extra profits ✓ Satisfying dealers ✓ Using excess capacity ✓ Being the leading full-line company ✓ Plugging holes to keep out competitors 3) The company should ensure that new items are noticeably different from existing ones. (2) Product line stretching—Lengthen product line beyond current range 1) Downward ✓ To plug a market hole that otherwise would attract a new competitor ✓ To respond to a competitor’s attack on the upper end ✓ Find faster growth taking place in the low-end segments 2) Upward

To add prestige to their current products May be attracted by a faster growth rate or higher margins at the higher end 3)Both ways (Product Mix Decisions 1.Product Mix-all the product lines&items offered ()Width-一number of different product lines(产品线的数量) (2)Length-一total number of items in product lines(产品线中所包含的产品种类 或产品项目的数量) (3)Depth-一number of versions of each product(每条产品线内所包含的产品品 种、样式和数量) (4)Consistency-how closely related the various product lines are in the end use,production requirements,distribution channels or some other way. 同产品线之间在最终用途、生产要求、分销渠道及其他方面相互关联的紧密程 度) 2.Provide the handles for defining the company's product strategy.The company can increase its business in four ways (1)Add new product lines,widening its product mix-in this way,its new lines build on the company's reputation in its other lines (2)Can lengthen its existing product lines to become a more full-line company (3)Add more versions ofeach product and thus deepen its product mix (4)Pursue more product line consistency-or less-depending on whether it wants to have a strong reputation in a single field or in several fields. 三、 Branding Strategy:Building Strong Brands brand represents everything that a product or service means to consumers. As such,brands are valuable assets to a company
7 ✓ To add prestige to their current products ✓ May be attracted by a faster growth rate or higher margins at the higher end 3) Both ways (三) Product Mix Decisions 1. Product Mix –all the product lines & items offered (1) Width—number of different product lines(产品线的数量) (2) Length—total number of items in product lines(产品线中所包含的产品种类 或产品项目的数量) (3) Depth—number of versions of each product(每条产品线内所包含的产品品 种、样式和数量) (4) Consistency—how closely related the various product lines are in the end use, production requirements, distribution channels or some other way. (不 同产品线之间在最终用途、生产要求、分销渠道及其他方面相互关联的紧密程 度) 2. Provide the handles for defining the company’s product strategy. The company can increase its business in four ways: (1) Add new product lines, widening its product mix—in this way, its new lines build on the company’s reputation in its other lines (2) Can lengthen its existing product lines to become a more full-line company. (3) Add more versions of each product and thus deepen its product mix (4) Pursue more product line consistency—or less—depending on whether it wants to have a strong reputation in a single field or in several fields. 三、 Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands A brand represents everything that a product or service means to consumers. As such, brands are valuable assets to a company

(一)Brand Equity 1.Brand equity The differential effect that knowing the brand name has on customer response to the product or its marketing 2.Four consumer perception dimensions (1)Differentiation-what makes the brand stand out (2)Relevance-how consumer feel it meets their needs (3)Knowledge-how much consumers know about the brand (4)Esteem-how highly consumers regard and respect the brand 3.Brand valuation The process of estimating the total financial value ofa brand 4.Advantages (1)A powerful brand enjoys a high level of consumer brand awareness and loyalty. (2)A powerful brand offers the company some defense against fierce price competition. 5.The fundamental asset underlying brand equity is customer equity-the value of the customer relationships that the brand creates. ()Building Strong Brands ·建设品牌的两个方法:广告+公关 ●品牌建立的核心:品牌定位,即在顾客头脑中产生的联想 ·品牌建立的基础:稳定、持续、有保障的顾客可感知质量 1.Brand Positioning (1)Three levels 1)Product attributes Competitors can easily copy the attributes Customers are not interested in attributes;they are interested in what the attributes will do for them 2)Benefit
8 (一)Brand Equity 1. Brand equity The differential effect that knowing the brand name has on customer response to the product or its marketing 2. Four consumer perception dimensions (1) Differentiation—what makes the brand stand out (2) Relevance—how consumer feel it meets their needs (3) Knowledge—how much consumers know about the brand (4) Esteem—how highly consumers regard and respect the brand 3. Brand valuation The process of estimating the total financial value of a brand 4. Advantages (1) A powerful brand enjoys a high level of consumer brand awareness and loyalty. (2) A powerful brand offers the company some defense against fierce price competition. 5. The fundamental asset underlying brand equity is customer equity—the value of the customer relationships that the brand creates. (二)Building Strong Brands ⚫ 建设品牌的两个方法:广告+公关 ⚫ 品牌建立的核心:品牌定位,即在顾客头脑中产生的联想 ⚫ 品牌建立的基础:稳定、持续、有保障的顾客可感知质量 1. Brand Positioning (1) Three levels: 1) Product attributes ✓ Competitors can easily copy the attributes ✓ Customers are not interested in attributes; they are interested in what the attributes will do for them 2) Benefit

3)Beliefs and values (2)When positioning a brand,the marketer should establish a mission for the brand and a vision of what the brand must be and do. (3)A brand is the company's promise to deliver a specific set of features. benefits,services and experiences consistently to the buyers. (4)The brand promise must be simple and honest. 2.Brand Name Selection (1)Suggest something about the product's benefits and qualities (2)Easy to pronounce,recognize and remember. (3)Distinctive (4)Extendable (5)Translate easily into foreign languages (6)Capable of registration and legal protection 3.Brand Sponsorship (1)National brands VS store brands 1)Retailers have many advantages: √More control Price lower √Higher profit 2)To compete with store brands: Invest in R&D to bring out new brands,new features and continuous quality improvements Design strong advertising programs to maintain high awareness and preference Find ways to"partner"with major distributors in a search for distribution economies and improved joint performance. (2)Licensing 1)Some companies license names or symbols previously created by other manufacturers,names of well-known celebrities or characters from popular movies and books. 9
9 3) Beliefs and values (2) When positioning a brand, the marketer should establish a mission for the brand and a vision of what the brand must be and do. (3) A brand is the company’s promise to deliver a specific set of features, benefits, services and experiences consistently to the buyers. (4) The brand promise must be simple and honest. 2. Brand Name Selection (1) Suggest something about the product’s benefits and qualities. (2) Easy to pronounce, recognize and remember. (3) Distinctive (4) Extendable (5) Translate easily into foreign languages (6) Capable of registration and legal protection 3. Brand Sponsorship (1) National brands VS store brands 1) Retailers have many advantages: ✓ More control ✓ Price lower ✓ Higher profit 2) To compete with store brands: ✓ Invest in R&D to bring out new brands, new features and continuous quality improvements ✓ Design strong advertising programs to maintain high awareness and preference ✓ Find ways to “partner” with major distributors in a search for distribution economies and improved joint performance. (2) Licensing 1) Some companies license names or symbols previously created by other manufacturers, names of well-known celebrities or characters from popular movies and books

2)Licensing can be a highly profitable business for many companies. (3)Co-branding 1)The practice of using the established brand names of two different companies on the same product. 2)Advantages: Create broader consumer appeal and greater brand equity Allows a company to expand its existing brand into a category it might otherwise have difficulty entering alone 3)Limitations: Involve complex legal contracts and licenses Partners must carefully coordinate their advertising.sales promotion and other marketing efforts. Each partner must trust that the other will take good care of its brand. 4.Brand Development (1)Line Extensions: 1)Existing brand names extended to new forms,sizes,and flavors of an existing product category 2)Purposes: Asa low-cost,low-risk way to introduce new products Want to meet consumer desires for variety To use excess capacity To command more shelf space from resellers 3)Risks An overextended brand name might lose its specific meaning Sales of an extension may come at the expense of other items in the line. (2)Brand Extensions 1)Existing brand names extended to new or modified product categories. 2)Advantages
10 2) Licensing can be a highly profitable business for many companies. (3) Co-branding 1) The practice of using the established brand names of two different companies on the same product. 2) Advantages: ✓ Create broader consumer appeal and greater brand equity ✓ Allows a company to expand its existing brand into a category it might otherwise have difficulty entering alone 3) Limitations: ✓ Involve complex legal contracts and licenses ✓ Partners must carefully coordinate their advertising, sales promotion and other marketing efforts. ✓ Each partner must trust that the other will take good care of its brand. 4. Brand Development (1) Line Extensions: 1) Existing brand names extended to new forms, sizes, and flavors of an existing product category 2) Purposes: ✓ As a low-cost, low-risk way to introduce new products ✓ Want to meet consumer desires for variety ✓ To use excess capacity ✓ To command more shelf space from resellers 3) Risks ✓ An overextended brand name might lose its specific meaning ✓ Sales of an extension may come at the expense of other items in the line. (2) Brand Extensions: 1) Existing brand names extended to new or modified product categories. 2) Advantages
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 7 Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 6 Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 9 Pricing and Pricing Strategies.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 10 Marketing Channels.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第1章 营销与营销过程.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第3章 营销系统与营销环境分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第4章 消费者市场与购买行为分析.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第2章 顾客价值与顾客满意.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第9章 市场传播与促销.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第10章 产品生命周期与营销战略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第6章 产品决策.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第5章 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第7章 价格策略.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程授课教案(中文)第8章 分销管理.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014第二学期试卷A(答案).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014第二学期试卷A(试题).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第二学期试卷B(答案).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第二学期试卷B(试题).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第一学期试卷A(答案).doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《市场营销学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013第一学期试卷B(答案).doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 11 Communicating Customer Value.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 2 Company and Marketing Strategy.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 4 Managing Marketing Information to Gain Customer Insights.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 5 Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer Behavior.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 3 Analyzing the Marketing Environment.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程授课教案(双语)Chapter 1 Marketing.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第8章案例 分销渠道策略-通用公司打造全球供应链.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第9章案例 促销策略-中国肥皂泡戏煞东瀛人.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第6章案例 产品决策-广东太阳神的产品组合.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第7章案例 价格决策-海信空调的价格策略.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第5章案例 市场细分、决定目标市场与定位- “红高粱”的启示.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第3章案例 市场营销环境-恒伟药业信息调研出效益.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第4章案例 分析消费者市场与购买行为-小阿华的“精确营销”.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第2章案例 规划企业战略与市场营销管理-雅戈尔,选择没有对错.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(中文)第1章案例 营销与营销管理-亚马逊名震全球之道.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)The Pepsi and Coca-Cola Challenge-A Cola with Breakfast.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Van Der Steen Candy Company.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Summit Ski Produc.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Who will go to Saudi Arabia.doc
- 《市场营销学》课程教学案例(双语)Egle Steel Supply Company.doc
