上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(1/2)

上充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Lecture 4-1 Nutrition,Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms CHAPTER 4 iness BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS AO TONG Zhao Liping,Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Lecture 4-1 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms Zhao Liping, Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology Shanghai Jiao Tong University CHAPTER 4 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

上泽充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University What does a cell need to be a successful chemical machine? The cell needs energy Chemical transformations ·Movement The cell needs building materials Precursors for monomers Growth factors etc. ae Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University What does a cell need to be a successful chemical machine? The cell needs energy • Chemical transformations • Movement The cell needs building materials • Precursors for monomers • Growth factors etc

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University I.Nutrition and Culture of Microorganisms A key feature of cells is their ability to direct chemical reactions and organize molecules into specific structures:metabolism. © Metabolic reactions are either energy releasing, called catabolic reactions,or energy requiring. called anabolic reactions.代谢包括了异化作用 (释放能量)和同化作用(需要能量)两种. Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University I. Nutrition and Culture of Microorganisms A key feature of cells is their ability to direct chemical reactions and organize molecules into specific structures: metabolism. Metabolic reactions are either energy releasing, called catabolic reactions, or energy requiring, called anabolic reactions.代谢包括了异化作用 (释放能量)和同化作用(需要能量)两种

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 4.1 Microbial Nutrition Many prokaryotes require an organic compound as carbon source..Some prokaryotes are autotrophs自养型,use CO2 as C source. Nitrogen氮 A typical bacterial cell is about 12%nitrogen (by dry weight) Nitrogen is an important element in proteins,nucleic acids, and several other constituents in the cell. Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University 4.1 Microbial Nutrition Carbon碳 • Many prokaryotes require an organic compound as carbon source. Some prokaryotes are autotrophs自养型, use CO2 as C source. Nitrogen氮 • A typical bacterial cell is about 12% nitrogen (by dry weight) • Nitrogen is an important element in proteins, nucleic acids, and several other constituents in the cell

Other Macronutrients: ·Phosphorus磷:is required for synthesis of nucleic acids and phospholipids. o Sulfur:is required in amino acids cysteine and methionine, and present in a number of vitamins and coenzyme A. ·Potassium钾:required by enzymes,including those involved in protein synthesis. o Magnesium:stabilize ribosomes,cell membranes,and nucleic acids and is also required for the activity of many enzymes. e Calcium:stabilize cell wall and plays a key role in the heat stability of endospores.Is not essential for the growth of many microorganisms. ·Sodium钠:required by some organisms.Its needs often reflects the habitat of the organism
Other Macronutrients: • Phosphorus磷: is required for synthesis of nucleic acids and phospholipids. • Sulfur硫: is required in amino acids cysteine and methionine, and present in a number of vitamins and coenzyme A. • Potassium钾: required by enzymes, including those involved in protein synthesis. • Magnesium镁: stabilize ribosomes, cell membranes, and nucleic acids and is also required for the activity of many enzymes. • Calcium钙: stabilize cell wall and plays a key role in the heat stability of endospores. Is not essential for the growth of many microorganisms. • Sodium钠: required by some organisms. Its needs often reflects the habitat of the organism

上降充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University @lron铁 Plays a major role in cellular respiration,being a key component of the cytochromes and iron-sulfur proteins involved in electron transport.在细胞的呼吸中有重 要作用,是电子传递链中细胞色素和铁硫蛋白 的重要组分 @Micronutrients((trace Elements)微量元素 They are metals,many of which play a structural role in various enzymes. Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Iron铁 • Plays a major role in cellular respiration, being a key component of the cytochromes and iron-sulfur proteins involved in electron transport.在细胞的呼吸中有重 要作用, 是电子传递链中细胞色素和铁硫蛋白 的重要组分. Micronutrients (trace Elements)微量元素 • They are metals, many of which play a structural role in various enzymes

上泽充通大睾 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Growth Factors生长因子 Are organic compounds that are required in very small amounts and only by some cells. Include vitamins,amino acids,purines,and pyrimidines. Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Growth Factors 生长因子 • Are organic compounds that are required in very small amounts and only by some cells. • Include vitamins, amino acids, purines, and pyrimidines

上帝充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Nutritional requirements of different microbes Different microorganisms can have vastly different nutritional requirements because they have different biosynthetic capacities E.coli:capable of synthesizing all organic compounds it needs Leuconostoc mesenteroides:need many externally provided organic compounds-extremely fastidious(nutritionally demanding)肠膜明串珠菌(需要极复杂营养的) Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Nutritional requirements of different microbes Different microorganisms can have vastly different nutritional requirements because they have different biosynthetic capacities • E. coli: capable of synthesizing all organic compounds it needs • Leuconostoc mesenteroides: need many externally provided organic compounds-extremely fastidious (nutritionally demanding)肠膜明串珠菌(需要极复杂营养的)

上帝充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 4.2 Culture media:培养基 Culture media are the nutrient solutions used to grow microorganisms in the laboratory. Chemically defined the exact chemical composition is known化学限定的培养基 ·Synthetic media合成培养基 Minimal media限制性培养基 Basal media基础培养基 ©Chemically undefined非化学限定的培养基 ·Complex media复合培养基 ·Natural media天然培养基 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University 4.2 Culture media培养基 Culture media are the nutrient solutions used to grow microorganisms in the laboratory. Chemically defined(the exact chemical composition is known)化学限定的培养基 • Synthetic media合成培养基 • Minimal media限制性培养基 • Basal media基础培养基 Chemically undefined非化学限定的培养基 • Complex media复合培养基 • Natural media天然培养基
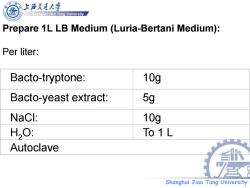
帝克通大学 上 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Prepare 1L LB Medium (Luria-Bertani Medium): Per liter: Bacto-tryptone: 10g Bacto-yeast extract: 5g NaCl: 10g H,O: To 1 L Autoclave Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Prepare 1L LB Medium (Luria-Bertani Medium): Per liter: Bacto-tryptone: 10g Bacto-yeast extract: 5g NaCl: 10g H2O: To 1 L Autoclave
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.4)Surface structures and inclusions of prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.3)Cell Wall of Prokaryotes:Peptidoglycan and Related Molecules.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.2)Cell Membrances and Cell Walls.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.1)Microscopy and cell morphology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 2 An Overview of Microbial Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.2 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Fungi 真菌、Algae 藻类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.3 Microbial Ecology(Microbial Symbioses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.2 Microbial Ecology(Nutrient Cycles, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.1 Microbial Ecology_Microbial Habitats and Diversity(MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS、Marine Microbiology).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.2 Methods in Microbial Ecology and Test(MEASURING MICROBIAL ACTIVITIES IN NATURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.1 Methods in Microbial Ecology(Culture-dependent analysis of microbial communities 基于培养的微生物群落研究).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.3 Metabolic Diversity(Catabolism of Organic Compounds)The anaerobic way of life:Fermentation and syntrophy 无氧生活 方式:发酵与互养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.2 Metabolic diversity(Chemolithotrophy)Chemolithotrophy:energy from the oxidation of inorganic electron donors 化能无机营养生物:通过氧化无机物而 获得能量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.1 Metabolic diversity(Phototrophy)微生物代谢的多样性——光合生物 The Phototrophic Way of Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.1 Microbial Growth(Bacterial Cell Division、Growth of Bacterial Populations 细菌群体生长).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.2 Microbial Growth(Measuring Microbial Growth 微生物生长的测定(计数)).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.3 Microbial Growth(Environmental Effects on Microbial Growth).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.1 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(Physical Antimicrobial Control、Chemical Antimicrobial Control).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.2 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS USED IN VIVO 体内使用的抗微生物制剂、ANTIMICROBIAL DRUG RESISTANCE AND DRUG DISCOVERY 抗药性与新药研制).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.1 Essentials of Molecular Biology(Genes and Gene Experession、DNA STRUCTURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.3 Essentials of Molecular Biology(mRNA Transcription、PROTEIN SYNTHESIS).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.1 Regulation of Gene Expression(Overview、Regulation of Enzyme Activity、Transcriptional level regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.2 Metabolic Regulation(Regulation of Gene Expression).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.3 Metabolic Regulation(Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in gene expression、RNA-Based Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.1 Essentials of Virology(VIRUS AND VIRION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.2 Essentials of Virology(Viral Replication 病毒复制、Viral Diversity).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.3 Essentials of Virology and Test(Overview of Animal Viruses、Retroviruses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源_常见微生物名称中英文索引.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第1章 绪论(主讲:陈峰).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第10章 微生物与基因工程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第11章 微生物生态.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第2章 纯培养和显微技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第3章 微生物细胞的结构与功能.pdf
