上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.3 Essentials of Molecular Biology(mRNA Transcription、PROTEIN SYNTHESIS)

泽克廷大学 上 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 7-3 Principles of Microbial Molecular Biology Chapter 6 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS JIAO TONG Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn Email:cf2001@sjtu.edu.cn
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 7-3 Principles of Microbial Molecular Biology Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn Email: cf2001@sjtu.edu.cn Chapter 6 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

上泽充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Transcription:Discuss the following questions 1.Why do we need a messenger RNA? 2.RNA polymerase:Any direction?Why? 3.RNA polymerase:Need a primer? 4.Initiation of RNA synthesis:How to find the right place? Where is the right place?Which DNA strand is the right strand for transcription? 5.Termination of RNA synthesis:where is the right place for termination? 6.Transcription:write down the relative position of promoter position,terminator,start codon,stop codon for a polycistronic mRNA No. 2 Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
No. 2 Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Transcription: Discuss the following questions 1. Why do we need a messenger RNA? 2. RNA polymerase: Any direction? Why? 3. RNA polymerase: Need a primer? 4. Initiation of RNA synthesis: How to find the right place? Where is the right place? Which DNA strand is the right strand for transcription? 5. Termination of RNA synthesis: where is the right place for termination? 6. Transcription: write down the relative position of promoter position, terminator, start codon, stop codon for a polycistronic mRNA

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University IV mRNA Transcription Why do we need a messenger RNA? ·The genetic information needs to be read“one sentence at a time",just like we speak in sentences.Genes are“sentences”in genetic information Protein synthesis takes place away from where chromosome exists No.3 Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
No. 3 Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University IV. mRNA Transcription Why do we need a messenger RNA? • The genetic information needs to be read “one sentence at a time”, just like we speak in sentences. Genes are “sentences” in genetic information • Protein synthesis takes place away from where chromosome exists
上泽充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 7.7 Overview of transcription 7.7.1 RNA polymerase RNA polymerase requires DNA as a template Direction:5'→3'. Do not need primer:RNA polymerase can start chains Triphosphate-containing:The initial nucleotide in an RNA retains 3 phosphate The first base in the rNa is always a purine. No.4 Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
No. 4 Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 7.7 Overview of transcription RNA polymerase requires DNA as a template Direction: 5’ 3’. Do not need primer: RNA polymerase can start chains Triphosphate-containing: The initial nucleotide in an RNA retains 3 phosphate The first base in the RNA is always a purine. 7.7.1 RNA polymerase
上泽克通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Overview of Transcription Transcription(DNA to RNA)is carried out by RNA polymerase RNA polymerase uses DNA as template RNA precursors are ATP,GTP,CTP,and UTP Chain growth is 5'to 3'just like DNA replication No.5 2012 Pearson Education,Inc. Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
No. 5 Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Overview of Transcription Transcription (DNA to RNA) is carried out by RNA polymerase • RNA polymerase uses DNA as template • RNA precursors are ATP, GTP, CTP, and UTP • Chain growth is 5′ to 3′ just like DNA replication © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc
上帝充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Overview of Transcription Only one of the two strands of DNA are transcribed by RNA polymerase for any gene Genes are present on both strands of DNA,but at different locations RNA polymerase has five different subunits RNA polymerase recognizes DNA sites called promoters No.6 Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
No. 6 Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Only one of the two strands of DNA are transcribed by RNA polymerase for any gene Genes are present on both strands of DNA, but at different locations RNA polymerase has five different subunits RNA polymerase recognizes DNA sites called promoters Overview of Transcription
上帝充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Overview of Transcription Promoters:site of initiation of transcription Recognized by sigma factor of RNA polymerase Transcription stops at specific sites called transcription terminators Unlike DNA replication,transcription involves smaller units of DNA Often as small as a single gene Allows cell to transcribe different genes at different rates No.7 Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
No. 7 Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Promoters: site of initiation of transcription • Recognized by sigma factor of RNA polymerase Transcription stops at specific sites called transcription terminators Unlike DNA replication, transcription involves smaller units of DNA • Often as small as a single gene • Allows cell to transcribe different genes at different rates Overview of Transcription
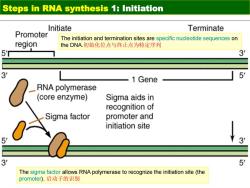
Steps in RNA synthesis 1:Initiation Initiate Terminate Promoter The initiation and termination sites are specific nucleotide sequences on region the DNA.初始化位点与终止点为特定序列 5' 3 1 Gene 5 RNA polymerase (core enzyme) Sigma aids in recognition of Sigma factor promoter and initiation site 5 3 3 5 The sigma factor allows RNA polymerase to recognize the initiation site(the promoter').启动子的识别
Steps in RNA synthesis 1: Initiation The initiation and termination sites are specific nucleotide sequences on the DNA.初始化位点与终止点为特定序列 The sigma factor allows RNA polymerase to recognize the initiation site (the promoter). 启动子的识别
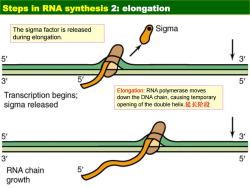
Steps in RNA synthesis 2:elongation The sigma factor is released Sigma during elongation. 5 3 3 5' Transcription begins; Elongation:RNA polymerase moves down the DNA chain,causing temporary sigma released opening of the double helix..a延长阶段 5 3 3 5 RNA chain 5 growth
Elongation: RNA polymerase moves down the DNA chain, causing temporary opening of the double helix.延长阶段 The sigma factor is released during elongation. Steps in RNA synthesis 2: elongation
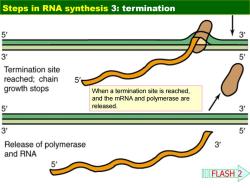
Steps in RNA synthesis 3:termination 5 3 3 5 Termination site reached:chain 5 growth stops When a termination site is reached, and the mRNA and polymerase are 5 released. 3 3 5 Release of polymerase 3 and RNA 5 FLASH 2
When a termination site is reached, and the mRNA and polymerase are released. Steps in RNA synthesis 3: termination FLASH 2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.1 Essentials of Molecular Biology(Genes and Gene Experession、DNA STRUCTURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.2 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS USED IN VIVO 体内使用的抗微生物制剂、ANTIMICROBIAL DRUG RESISTANCE AND DRUG DISCOVERY 抗药性与新药研制).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.1 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(Physical Antimicrobial Control、Chemical Antimicrobial Control).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.3 Microbial Growth(Environmental Effects on Microbial Growth).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.2 Microbial Growth(Measuring Microbial Growth 微生物生长的测定(计数)).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.1 Microbial Growth(Bacterial Cell Division、Growth of Bacterial Populations 细菌群体生长).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.4)Surface structures and inclusions of prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.3)Cell Wall of Prokaryotes:Peptidoglycan and Related Molecules.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.2)Cell Membrances and Cell Walls.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.1)Microscopy and cell morphology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 2 An Overview of Microbial Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.2 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Fungi 真菌、Algae 藻类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.1 Regulation of Gene Expression(Overview、Regulation of Enzyme Activity、Transcriptional level regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.2 Metabolic Regulation(Regulation of Gene Expression).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.3 Metabolic Regulation(Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in gene expression、RNA-Based Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.1 Essentials of Virology(VIRUS AND VIRION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.2 Essentials of Virology(Viral Replication 病毒复制、Viral Diversity).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.3 Essentials of Virology and Test(Overview of Animal Viruses、Retroviruses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源_常见微生物名称中英文索引.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第1章 绪论(主讲:陈峰).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第10章 微生物与基因工程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第11章 微生物生态.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第2章 纯培养和显微技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第3章 微生物细胞的结构与功能.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第4章 微生物的营养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第5章 微生物的代谢.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第6章 微生物的生长繁殖及其控制.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第7章 病毒学概论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第8章 微生物遗传.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(中文课件)第9章 微生物基因表达的调控.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物的世界 Microbial World》通识教育课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 微生物的生长繁殖及其控制.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物的世界 Microbial World》通识教育课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 绪论(陈峰).pdf
