上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学)

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 16-3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类 Chapter 16 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS AI JIAO TONG UNI Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 16-3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类 Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 16 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

III.Microbial Systematics微生物系统 分类学 @Phylogenetics系统发生学-the study of phylogeny family history of microbes ·Genotype-based Taxonomy:分类学-science of classification, consists of two major subdisciplines: 。Identification鉴定 ·Nomenclature命名 ·Phenotype-based Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University III. Microbial Systematics微生物系统 分类学 Phylogenetics系统发生学-the study of phylogeny • family history of microbes • Genotype-based Taxonomy分类学-science of classification, consists of two major subdisciplines: • Identification 鉴定 • Nomenclature 命名 • Phenotype-based

Conventional/Classical Taxonomy 传统/经典分类法 Characteristics of taxonomic value include Morphology,Motility,Nutrition, Pysiology&Ecology?分类学特征包括形态学、 运动性、营养需求、生理学、生态学特征 GC ratios can be a part of classical bacterial taxonomy Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Conventional/Classical Taxonomy 传统/经典分类法 Characteristics of taxonomic value include Morphology, Motility, Nutrition, Pysiology & Ecology分类学特征包括形态学、 运动性、营养需求、生理学、生态学特征 GC ratios can be a part of classical bacterial taxonomy
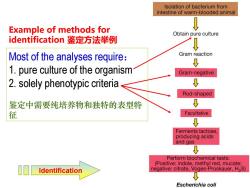
Isolation of bacterium from intestine of warm-blooded animal Example of methods for Obtain pure culture identification鉴定方法举例 Most of the analyses require: Gram reaction ↓ 1.pure culture of the organism Gram-negative 2.solely phenotypic criteria Rod-shaped 鉴定中需要纯培养物和独特的表型特 征 Facultative ↓ Ferments lactose, producing acids and gas ↓ Perform biochemical tests: (Positive:indole,methyl red,mucate; Identification negative:citrate,Voges-Proskauer,H2S) Escherichia coli
Example of methods for identification 鉴定方法举例 Most of the analyses require: 1. pure culture of the organism 2. solely phenotypic criteria 鉴定中需要纯培养物和独特的表型特 征 Identification

16.10 Phenotypic Analysis:Fatty Acid Methyl Ester(FAME)脂肪酸甲酯分析法 FAME:Identification through characterizations of the types and proportions of fatty acids present in membrane and outer membrane(G-) lipids of cells.通过细胞膜/外膜的脂肪酸类型 来鉴定细菌 More than 200 different fatty acids have been discovered from bacterial sources. Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 16.10 Phenotypic Analysis: Fatty Acid Methyl Ester (FAME) 脂肪酸甲酯分析法 FAME: Identification through characterizations of the types and proportions of fatty acids present in membrane and outer membrane (G- ) lipids of cells.通过细胞膜/外膜的脂肪酸类型 来鉴定细菌 More than 200 different fatty acids have been discovered from bacterial sources
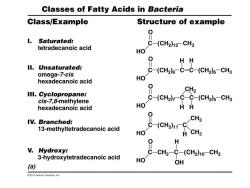
Classes of Fatty Acids in Bacteria Class/Example Structure of example 0 l. Saturated: C-(CH2)12-CH3 tetradecanoic acid HO HH II.Unsaturated: C-(CH2)6-C=C-(CH2)6-CH3 omega-7-cis hexadecanoic acid HO 0 CH2 III.Cyclopropane: cis-7,8-methylene C-(CH2)7-C-C-(CH2)5-CH3 hexadecanoic acid HO HH IV.Branched: 13-methyltetradecanoic acid HO -( HCHg 0 H V.Hydroxy: C-CH2-C-(CH2)10-CH3 3-hydroxytetradecanoic acid HO OH (a) 2012 Pearson Education.Inc
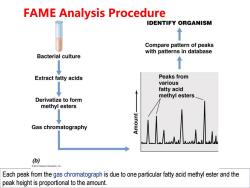
FAME Analysis Procedure IDENTIFY ORGANISM ↑ Compare pattern of peaks with patterns in database Bacterial culture Extract fatty acids Peaks from various fatty acid methyl esters Derivatize to form methyl esters Gas chromatography (b) 2012 Pearson Education,inc Each peak from the gas chromatograph is due to one particular fatty acid methyl ester and the peak height is proportional to the amount
FAME Analysis Procedure Each peak from the gas chromatograph is due to one particular fatty acid methyl ester and the peak height is proportional to the amount
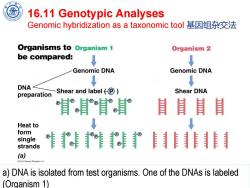
16.11 Genotypic Analyses Genomic hybridization as a taxonomic tool基因组杂交法 Organisms to organism 1 Organism 2 be compared: ↓ Genomic DNA Genomic DNA ↓ ↓ DNA preparation Shear and label®) Shear DNA Iee官 Heat to form single ®® strands (a) 2012 Pearson Education,Inc. a)DNA is isolated from test organisms.One of the DNAs is labeled (Organism 1)
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 16.11 Genotypic Analyses Genomic hybridization as a taxonomic tool 基因组杂交法 a) DNA is isolated from test organisms. One of the DNAs is labeled (Organism 1)
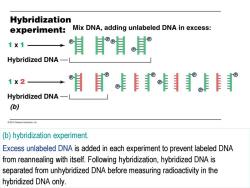
Hybridization experiment: Mix DNA,adding unlabeled DNA in excess: ® 1X1 Hybridized DNA- 1×2 Hybridized DNA- (b) 2012 Pearson Education.Inc. (b)hybridization experiment. Excess unlabeled DNA is added in each experiment to prevent labeled DNA from reannealing with itself.Following hybridization,hybridized DNA is separated from unhybridized DNA before measuring radioactivity in the hybridized DNA only
(b) hybridization experiment. Excess unlabeled DNA is added in each experiment to prevent labeled DNA from reannealing with itself. Following hybridization, hybridized DNA is separated from unhybridized DNA before measuring radioactivity in the hybridized DNA only
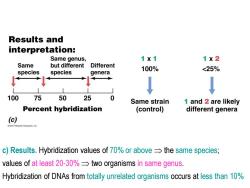
Results and interpretation: Same genus, 1X1 1X2 Same but different Different 100% <25% species species genera 100 75 50 25 0 Same strain 1 and 2 are likely Percent hybridization (control) different genera (c) 2012 Pearson Education,Inc. c)Results.Hybridization values of 70%or above=the same species; values of at least 20-30%two organisms in same genus. Hybridization of DNAs from totally unrelated organisms occurs at less than 10%
c) Results. Hybridization values of 70% or above the same species; values of at least 20-30% two organisms in same genus. Hybridization of DNAs from totally unrelated organisms occurs at less than 10%
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.3 Microbial Ecology(Microbial Symbioses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.2 Microbial Ecology(Nutrient Cycles, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.1 Microbial Ecology_Microbial Habitats and Diversity(MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS、Marine Microbiology).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.2 Methods in Microbial Ecology and Test(MEASURING MICROBIAL ACTIVITIES IN NATURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.1 Methods in Microbial Ecology(Culture-dependent analysis of microbial communities 基于培养的微生物群落研究).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.3 Metabolic Diversity(Catabolism of Organic Compounds)The anaerobic way of life:Fermentation and syntrophy 无氧生活 方式:发酵与互养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.2 Metabolic diversity(Chemolithotrophy)Chemolithotrophy:energy from the oxidation of inorganic electron donors 化能无机营养生物:通过氧化无机物而 获得能量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.1 Metabolic diversity(Phototrophy)微生物代谢的多样性——光合生物 The Phototrophic Way of Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.2 Microbial Genomics(Gene Function and Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.1 Microbial Genomics(Genomes and Genomics).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.2 Genetic Engineering(Gene Cloning).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.1 Genetic Engineering(Methods for Manipulating DNA).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.2)Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.1)Mutation and Recombination.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 1 Microorganisms & Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Introduction to Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)虫草属(Cordyceps)真菌研究概况.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)植物生物反应器的研究进展.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.2 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Fungi 真菌、Algae 藻类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 2 An Overview of Microbial Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.1)Microscopy and cell morphology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.2)Cell Membrances and Cell Walls.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.3)Cell Wall of Prokaryotes:Peptidoglycan and Related Molecules.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.4)Surface structures and inclusions of prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.1 Microbial Growth(Bacterial Cell Division、Growth of Bacterial Populations 细菌群体生长).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.2 Microbial Growth(Measuring Microbial Growth 微生物生长的测定(计数)).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.3 Microbial Growth(Environmental Effects on Microbial Growth).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.1 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(Physical Antimicrobial Control、Chemical Antimicrobial Control).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.2 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS USED IN VIVO 体内使用的抗微生物制剂、ANTIMICROBIAL DRUG RESISTANCE AND DRUG DISCOVERY 抗药性与新药研制).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.1 Essentials of Molecular Biology(Genes and Gene Experession、DNA STRUCTURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.3 Essentials of Molecular Biology(mRNA Transcription、PROTEIN SYNTHESIS).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.1 Regulation of Gene Expression(Overview、Regulation of Enzyme Activity、Transcriptional level regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.2 Metabolic Regulation(Regulation of Gene Expression).pdf
