上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 1 Microorganisms & Microbiology

上充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Lecture 1 Microorganisms Microbiology Chapter 1 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
Lecture 1 Microorganisms & Microbiology Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn Chapter 1 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

上游充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.1 Microbiology As a basic biological science,microbiology provides tools for probing the processes of life. As an applied biological science,microbiology deals with many important practical problems in medicine,agriculture,and industry. Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.1 Microbiology As a basic biological science, microbiology provides tools for probing the processes of life. As an applied biological science, microbiology deals with many important practical problems in medicine, agriculture, and industry

上游充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.Compartmentalization and metabolism Cells take up nutrients from the environment,transform them, and release wastes into the environment.The cell is thus an open system. 1.2 Microorganisms as Cells Cel 1.2.1 Characteristics of living Environment 2.Reproduction(growth) systems Chemicals from the environment are turned into new cells under the genetic direction of preexisting cells. ●→● Hallmarks /characteristics 3.Differentiation Some cells can form new cell structures such as a spore,usually as part of a cellular life cycle Spore 1.Metabolism代谢 4.Communication 2.Growth生长 Cells communicate or interact by means of chemicals that are released or taken up. 3.Differentiation.分化 4. Communication交流 5.Movement Some cells are capable of self-propulsion. 5. Movement运动 6. Evolution进化 6.Evolution Cells contain genes and evolve to display new biological properties.Phylogenetic trees show the evolutionary relationships between cells. heredity and mutation-information Distinct Ancestral species flow Distinct species Chen Fens Education,Inc.,publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.2 Microorganisms as Cells 1.2.1 Characteristics of living systems Hallmarks / characteristics 1. Metabolism代谢 2. Growth生长 3. Differentiation分化 4. Communication交流 5. Movement运动 6. Evolution进化 heredity and mutation-information flow

上游充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.2.2 Cells as chemical machines and as coding devices Cells are self-replicating entities可自我复制的主体, they can be viewed in two ways: 圈As chemical machines作为化学机器的细胞 carrying out chemical transformations of non-living materials to living materials to provide energy and precursors for cell reproduction As coding devices作为编码装置的细胞 serving as storehouses and processors of genetic information(DNA)to give the cell instructions to make new copies of itself Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.2.2 Cells as chemical machines and as coding devices Cells are self-replicating entities可自我复制的主体, they can be viewed in two ways: As chemical machines作为化学机器的细胞 • carrying out chemical transformations of non-living materials to living materials to provide energy and precursors for cell reproduction As coding devices作为编码装置的细胞 • serving as storehouses and processors of genetic information (DNA) to give the cell instructions to make new copies of itself
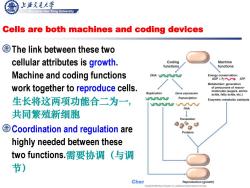
上游充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University Cells are both machines and coding devices The link between these two cellular attributes is growth. Coding Machine functions functions Machine and coding functions DNA NOTOTIT Energy conservation: ADP+PA◆ATP Metabolism:generation work together to reproduce cells. of precursors of macro- molecules (sugars,amino Replication Gene expression acids,fatty acids,etc.) 生长将这两项功能合二为一, 0T0000 Transcription Enzymes:metabolic catalysts 000形网mA RNA 共同繁殖新细胞 Translation Coordination and regulation are Proteins highly needed between these two functions.需要协调(与调 节) Cher Reproduction(growth) Coyt200 Pearson Education ine.pubishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Cells are both machines and coding devices The link between these two cellular attributes is growth. Machine and coding functions work together to reproduce cells. 生长将这两项功能合二为一, 共同繁殖新细胞 Coordination and regulation are highly needed between these two functions.需要协调(与调 节)
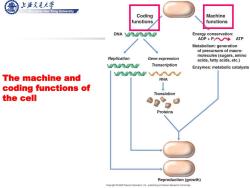
上游充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Coding Machine functions functions DNA YITUTOT Energy conservation: ADP+P ATP Metabolism:generation of precursors of macro- molecules(sugars,amino Replication Gene expression acids,fatty acids,etc.) 000 Transcription Enzymes:metabolic catalysts 000w%w The machine and RNA coding functions of Translation the cell 00g Proteins Reproduction(growth) Copyrigh2009 Pearson Education.Inc.,publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University The machine and coding functions of the cell

上降充通大睾 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.3 Microorganisms A large and diverse group of microscopic organisms that exist as single cells or cell clusters,it also include non-cellular life forms such as viruses and prions.微生物:微小的细胞或非细胞生物 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.3 Microorganisms A large and diverse group of microscopic organisms that exist as single cells or cell clusters, it also include non-cellular life forms such as viruses and prions.微生物:微小的细胞或非细胞生物

上游充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University Compared with plant and animal cells, microorganisms are: ·Very small-bacteria0.5-5m,微小 ·Highly diverse-all kinds of morphology,形态多 样 ·leading an independent living独立生活 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Compared with plant and animal cells, microorganisms are: • Very small-bacteria 0.5-5μm,微小 • Highly diverse-all kinds of morphology,形态多 样 • leading an independent living独立生活

h 上海充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.4 The Impact of Microorganisms on Humans 生物对人类的影响 圈Disease agents病原物 Human,animal,plants ©Agriculture农业 ·Nitrogen fixation-root nodule:根瘤 ·Animal digestion-rumen:膪胃 ©Food industry食品工业 ·Spoilage ·Fermented food ©Energy能源 Biomass ·Biofuels 圈Environment:环境 。 Bioremediation生物修复 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1.4 The Impact of Microorganisms on Humans 微 生物对人类的影响 Disease agents病原物 • Human, animal, plants Agriculture农业 • Nitrogen fixation-root nodule根瘤 • Animal digestion-rumen瘤胃 Food industry食品工业 • Spoilage • Fermented food Energy能源 • Biomass • Biofuels Environment环境 • Bioremediation生物修复

上游充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Pathogens-harmful microorganisms Time:1350 A.D.Place:the European continent. "In less than two years'time,the Bubonic Plague wiped out half the population of Europe.Fleas bit rats and then bit man, but no one knew it.An estimated 25 million people died in 14 months.Some individual cities had a mortality as high as 90%. Bodies were piled into carts and dragged away to be burned in common graves.It was a most grotesque way to die:bleeding and screaming and having one's organs literally liquefy.From infection to death took perhaps one week. 1350年黑死病流行于欧洲,2500万人在14个月内死亡。 Bubonic Plague.黑死病,淋巴腺鼠疫 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Pathogens-harmful microorganisms Time: 1350 A.D. Place: the European continent. “In less than two years' time, the Bubonic Plague wiped out half the population of Europe. Fleas bit rats and then bit man, but no one knew it. An estimated 25 million people died in 14 months. Some individual cities had a mortality as high as 90%. Bodies were piled into carts and dragged away to be burned in common graves. It was a most grotesque way to die: bleeding and screaming and having one's organs literally liquefy. From infection to death took perhaps one week. ” 1350年黑死病流行于欧洲,2500万人在14个月内死亡。 Bubonic Plague黑死病, 淋巴腺鼠疫
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Introduction to Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)虫草属(Cordyceps)真菌研究概况.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)植物生物反应器的研究进展.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)绪论(周选围).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第8章 生物技术发明的保护.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第7章 现代生物技术伦理与安全..pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第6章 生物技术与人类生存环境.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第5章 生物技术与人类健康.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第4章 能源开发中的生物技术.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第3章 日常生活(食品)中的生物技术.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第2章 农业生产中的生物技术.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第1章 现代生物技术总论.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第四章 生物技术与能源.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第六章 生物技术与环境.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第八章 生物技术发明的保护.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第五章 生物技术与人类健康.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第七章 现代生物技术伦理与安全.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第三章 日常生活(食品)中的生物技术.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第二章 生物技术与农业.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)绪论、第一章 生物技术概论.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.1)Mutation and Recombination.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.2)Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.1 Genetic Engineering(Methods for Manipulating DNA).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.2 Genetic Engineering(Gene Cloning).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.1 Microbial Genomics(Genomes and Genomics).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.2 Microbial Genomics(Gene Function and Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.1 Metabolic diversity(Phototrophy)微生物代谢的多样性——光合生物 The Phototrophic Way of Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.2 Metabolic diversity(Chemolithotrophy)Chemolithotrophy:energy from the oxidation of inorganic electron donors 化能无机营养生物:通过氧化无机物而 获得能量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.3 Metabolic Diversity(Catabolism of Organic Compounds)The anaerobic way of life:Fermentation and syntrophy 无氧生活 方式:发酵与互养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.1 Methods in Microbial Ecology(Culture-dependent analysis of microbial communities 基于培养的微生物群落研究).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.2 Methods in Microbial Ecology and Test(MEASURING MICROBIAL ACTIVITIES IN NATURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.1 Microbial Ecology_Microbial Habitats and Diversity(MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS、Marine Microbiology).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.2 Microbial Ecology(Nutrient Cycles, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.3 Microbial Ecology(Microbial Symbioses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
