上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.1 Microbial Ecology_Microbial Habitats and Diversity(MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS、Marine Microbiology)

上降充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 15-1 Microbial Ecology:Major Microbial Habitats and Diversity CHAPTER 23in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS AO TON Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology Shanghai Jiao Tong University
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 15-1 Microbial Ecology: Major Microbial Habitats and Diversity Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology Shanghai Jiao Tong University CHAPTER 23 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

充通大警 上i Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 I.MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS 15.1 Populations,Guilds, HAI JIAO TONG UNIVER and Communities n
1896 1920 1987 2006 I. MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS 15.1 Populations, Guilds, and Communities

o→8→88+88 +88888 Population Components of Microbial Ecosystem Populations ·Individual cells grow to form populationsi群体由单个细 胞共同组成 ( uildsi种群 o Metabolically related populations constitute groupings called guilds代谢相关的一群同种生物构成种群 Communities群落 e Sets of guilds conducting complementary physiological processes interact to form microbial communities-一系列种群相互作用及生理互补构成群落 3 Microbiology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
3 Microbiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Components of Microbial Ecosystem Populations • Individual cells grow to form populations群体由单个细 胞共同组成 Guilds种群 • Metabolically related populations constitute groupings called guilds代谢相关的一群同种生物构成种群 Communities群落 • Sets of guilds conducting complementary physiological processes interact to form microbial communities一系列种群相互作用及生理互补构成群落

Guilds and communities种群与群落 Various microbial Light community structure in a Community 1 Community 2 lake ecosystem.湖泊生 Photic zone: Oxic zone: Oxygenic phototrophs Aerobes and facultative aerobes 态系统中的群落组成 6C02+6H20→ C6H1206+602 C6H1206+602→ 6C02+6H20 Energy yield Community 3 Anoxic sediments: 1.Guild 1:denitrifying bacteria (NON2) ferric iron-reducing bacteria(Fe3+-Fe2) 2.Guild 2:sulfate-reducing bacteria(SOH2S) sulfur-reducing bacteria(s°→H2S) 3.Guild 3:fermentative bacteria 4.Guild 4:methanogens(CO2-CH4) For the sediment community,major acetogens(CO2-acetate) guilds are indicated.层积层群落 2012 Prson Edcon ine 中的主要种群 4 Microbiology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
4 Microbiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Guilds and communities 种群与群落 Various microbial community structure in a lake ecosystem. 湖泊生 态系统中的群落组成 For the sediment community, major guilds are indicated.层积层群落 中的主要种群

Microbial ecology微生物生态学 Microbial ecologists primarily focus on two areas of study: Biodiversity of microorganisms in nature and how different guilds interact in microbial communities 生物的多样性 Activities of microorganisms in nature and monitor their effects on ecosystems微生物的活性 5 Microbiology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
5 Microbiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Microbial ecology 微生物生态学 Microbial ecologists primarily focus on two areas of study: • Biodiversity of microorganisms in nature and how different guilds interact in microbial communities微 生物的多样性 • Activities of microorganisms in nature and monitor their effects on ecosystems微生物的活性

15.2 Environments and Microenvironments 境与微环境 Growth of microorganisms in nature Resources(nutrients available) ·Proper Conditions 。·Temperature ·pH 。Vater availability ·Light Oxygen Slow growth in nature than in pure culture E.coli doubling time:12 hour in intestine,20 min in culture 6 Microbiology.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
6 Microbiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 15.2 Environments and Microenvironments 环 境与微环境 Growth of microorganisms in nature • Resources (nutrients available) • Proper Conditions • Temperature • pH • Water availability • Light • Oxygen Slow growth in nature than in pure culture • E. coli doubling time: 12 hour in intestine, 20 min in culture

Microenvironment微环境 ©Niche for microorganism微生物的小生境 (生态位) Prime niche:a habitat defined by the type and quantity of different resources and the physicochemical conditions in which a microorganism is most successful初始生态 位:自然界中微生物最适宜的小环境 Think small-microenvironment 3 mm to E.coli just as the same of 2 km to a man 7 Microbiology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
7 Microbiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Microenvironment 微环境 Niche for microorganism微生物的小生境 (生态位) • Prime niche: a habitat defined by the type and quantity of different resources and the physicochemical conditions in which a microorganism is most successful初始生态 位:自然界中微生物最适宜的小环境 Think small-microenvironment • 3 mm to E. coli just as the same of 2 km to a man

15.3 Microbial Growth on Surfaces and Biofilms 表面生长与生物膜 Surfaces are important microbial habitats because:固体表面是重要的微生物生活环境: ·Nutrients can adsorb to them;营养可吸附于表面 In the microenvironment of a surface,nutrient level may be much higher than they are in the bulk solution. 微环境的固体表面有更高的营养物水平(与水环境相 比)。 A surface may itself also be a nutrient,such as a particle of organic matter.固体表面可能本身就是营养 8 Microbiology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
8 Microbiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 15.3 Microbial Growth on Surfaces and Biofilms 表面生长与生物膜 Surfaces are important microbial habitats because:固体表面是重要的微生物生活环境: • Nutrients can adsorb to them;营养可吸附于表面; • In the microenvironment of a surface, nutrient level may be much higher than they are in the bulk solution. 微环境的固体表面有更高的营养物水平(与水环境相 比)。 • A surface may itself also be a nutrient, such as a particle of organic matter.固体表面可能本身就是营养
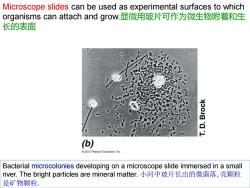
Microscope slides can be used as experimental surfaces to which organisms can attach and grow.显微用玻片可作为微生物附着和生 长的表面 (b) 2012 Pearson Education,Inc. Bacterial microcolonies developing on a microscope slide immersed in a small river..The bright particles are mineral matter..小河中玻片长出的微菌落,亮颗粒 是矿物颗粒
Bacterial microcolonies developing on a microscope slide immersed in a small river. The bright particles are mineral matter. 小河中玻片长出的微菌落,亮颗粒 是矿物颗粒. Microscope slides can be used as experimental surfaces to which organisms can attach and grow.显微用玻片可作为微生物附着和生 长的表面

(b)Fluorescence photomicrograph of a natural microbial community Microcolonies colonizing plant roots in soil. Root Note microcolony development.荧光照片:土 壤根际的自然微生物群 落,注意其中的微菌落 (a) 2012 Pearson Education,Inc. (stained with acridine orange)丫啶橙染色
(b) Fluorescence photomicrograph of a natural microbial community colonizing plant roots in soil. Note microcolony development. 荧光照片:土 壤根际的自然微生物群 落,注意其中的微菌落. (stained with acridine orange)丫啶橙染色
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.2 Methods in Microbial Ecology and Test(MEASURING MICROBIAL ACTIVITIES IN NATURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.1 Methods in Microbial Ecology(Culture-dependent analysis of microbial communities 基于培养的微生物群落研究).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.3 Metabolic Diversity(Catabolism of Organic Compounds)The anaerobic way of life:Fermentation and syntrophy 无氧生活 方式:发酵与互养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.2 Metabolic diversity(Chemolithotrophy)Chemolithotrophy:energy from the oxidation of inorganic electron donors 化能无机营养生物:通过氧化无机物而 获得能量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.1 Metabolic diversity(Phototrophy)微生物代谢的多样性——光合生物 The Phototrophic Way of Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.2 Microbial Genomics(Gene Function and Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.1 Microbial Genomics(Genomes and Genomics).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.2 Genetic Engineering(Gene Cloning).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.1 Genetic Engineering(Methods for Manipulating DNA).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.2)Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.1)Mutation and Recombination.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 1 Microorganisms & Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Introduction to Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)虫草属(Cordyceps)真菌研究概况.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)植物生物反应器的研究进展.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)绪论(周选围).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第8章 生物技术发明的保护.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第7章 现代生物技术伦理与安全..pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第6章 生物技术与人类生存环境.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第5章 生物技术与人类健康.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.2 Microbial Ecology(Nutrient Cycles, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.3 Microbial Ecology(Microbial Symbioses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.2 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Fungi 真菌、Algae 藻类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 2 An Overview of Microbial Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.1)Microscopy and cell morphology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.2)Cell Membrances and Cell Walls.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.3)Cell Wall of Prokaryotes:Peptidoglycan and Related Molecules.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.4)Surface structures and inclusions of prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.1 Microbial Growth(Bacterial Cell Division、Growth of Bacterial Populations 细菌群体生长).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.2 Microbial Growth(Measuring Microbial Growth 微生物生长的测定(计数)).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.3 Microbial Growth(Environmental Effects on Microbial Growth).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.1 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(Physical Antimicrobial Control、Chemical Antimicrobial Control).pdf
