上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.2 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Fungi 真菌、Algae 藻类

上帝充通大睾 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 通 Chapter 18-2 是后 Eukaryotic Microorganisms Chapter 14in 三8 BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS ALIAO TONG UNI Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 18-2 Eukaryotic Microorganisms Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn Chapter 14 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

Eukaryotic Microorganisms Molds Mushrooms Fungi Yeasts Slime molds Algae Protozoa Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Molds Mushrooms Fungi Yeasts Slime molds Algae Protozoa Eukaryotic Microorganisms

浒充通大学 Shanghai Jiao Tong University G UN 1896 1920 1987 2006 漏 及 18.10 Fungi真菌 月,度A是度 1annA。n 1日日6
1896 1920 1987 2006 18.10 Fungi 真菌
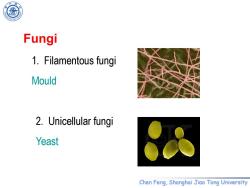
Fungi 1.Filamentous fungi Mould 2.Unicellular fungi Yeast Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1. Filamentous fungi Mould 2. Unicellular fungi Yeast Fungi

18.10.1 Fungal Physiology, Structure,and Symbioses ©Most fungi are multicellular,,forming a network of hyphae菌丝 Hyphae that extend above the surface can produce asexual spores called conidia分生孢子 Conidia are often pigmented and resistant to drying ©Hyphae form compact tufts called mycelia菌丝体 ©Most fungal cell walls are made of chitin几丁质细胞壁 ©Mycorrhizae help plant roots obtain phosphorus菌根 Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 18.10.1 Fungal Physiology, Structure, and Symbioses Most fungi are multicellular, forming a network of hyphae菌丝 Hyphae that extend above the surface can produce asexual spores called conidia 分生孢子 • Conidia are often pigmented and resistant to drying Hyphae form compact tufts called mycelia 菌丝体 Most fungal cell walls are made of chitin 几丁质细胞壁 Mycorrhizae help plant roots obtain phosphorus 菌根

Morphology of filamentous fungi The filamentous fungi consists of two parts: mycelium and spores.丝状真菌由菌丝体和孢子 组成. The filamentous fungi develop multicellular branching structures known as hyphae菌丝, which are connected filaments of vegetative cells.Integrated masses of hyphae are called a mycelium.分支结构为菌丝,菌丝组成菌丝体 Each hypha is about 5-10 um wide. Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Morphology of filamentous fungi The filamentous fungi consists of two parts: mycelium and spores.丝状真菌由菌丝体和孢子 组成. The filamentous fungi develop multicellular branching structures known as hyphae菌丝, which are connected filaments of vegetative cells. Integrated masses of hyphae are called a mycelium. 分支结构为菌丝,菌丝组成菌丝体 Each hypha is about 5-10 m wide
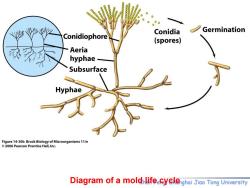
Conidia Germination Conidiophore (spores) Aeria hyphae Subsurface Hyphae Figure 14-30b Brock Biology of Microorganisms 11/e 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Diagram of a moldhlifeecyelenghai Jiao Tong University
Diagram of a mold life cycle Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
(a) 字 (b) 2012 Pearson Education,Inc
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc

Fungal Physiology,Structure,and Symbioses Some fungi produce macroscopic reproductive structures called fruiting bodies子实体 Mushrooms and puffballs are fruiting bodies Fungi can cause disease in plants and animals e Dutch elm trees were devastated by fungal infection of the ascomycete Ophiostoma ulmi Mycoses in humans range in severity from "athlete's foot"to histoplasmosis Chen Feng.Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Fungal Physiology, Structure, and Symbioses Some fungi produce macroscopic reproductive structures called fruiting bodies 子实体 • Mushrooms and puffballs are fruiting bodies Fungi can cause disease in plants and animals • Dutch elm trees were devastated by fungal infection of the ascomycete Ophiostoma ulmi • Mycoses in humans range in severity from “athlete’s foot” to histoplasmosis
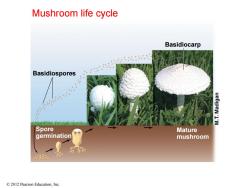
Mushroom life cycle Basidiocarp Basidiospores Spore Mature germination mushroom 然 2012 Pearson Education,Inc
Basidiospores Basidiocarp Spore germination Mature mushroom © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Mushroom life cycle
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.3 Microbial Ecology(Microbial Symbioses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.2 Microbial Ecology(Nutrient Cycles, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.1 Microbial Ecology_Microbial Habitats and Diversity(MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS、Marine Microbiology).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.2 Methods in Microbial Ecology and Test(MEASURING MICROBIAL ACTIVITIES IN NATURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.1 Methods in Microbial Ecology(Culture-dependent analysis of microbial communities 基于培养的微生物群落研究).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.3 Metabolic Diversity(Catabolism of Organic Compounds)The anaerobic way of life:Fermentation and syntrophy 无氧生活 方式:发酵与互养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.2 Metabolic diversity(Chemolithotrophy)Chemolithotrophy:energy from the oxidation of inorganic electron donors 化能无机营养生物:通过氧化无机物而 获得能量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.1 Metabolic diversity(Phototrophy)微生物代谢的多样性——光合生物 The Phototrophic Way of Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.2 Microbial Genomics(Gene Function and Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.1 Microbial Genomics(Genomes and Genomics).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.2 Genetic Engineering(Gene Cloning).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.1 Genetic Engineering(Methods for Manipulating DNA).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.2)Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.1)Mutation and Recombination.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 2 An Overview of Microbial Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.1)Microscopy and cell morphology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.2)Cell Membrances and Cell Walls.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.3)Cell Wall of Prokaryotes:Peptidoglycan and Related Molecules.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.4)Surface structures and inclusions of prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.1 Microbial Growth(Bacterial Cell Division、Growth of Bacterial Populations 细菌群体生长).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.2 Microbial Growth(Measuring Microbial Growth 微生物生长的测定(计数)).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.3 Microbial Growth(Environmental Effects on Microbial Growth).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.1 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(Physical Antimicrobial Control、Chemical Antimicrobial Control).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.2 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS USED IN VIVO 体内使用的抗微生物制剂、ANTIMICROBIAL DRUG RESISTANCE AND DRUG DISCOVERY 抗药性与新药研制).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.1 Essentials of Molecular Biology(Genes and Gene Experession、DNA STRUCTURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.3 Essentials of Molecular Biology(mRNA Transcription、PROTEIN SYNTHESIS).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.1 Regulation of Gene Expression(Overview、Regulation of Enzyme Activity、Transcriptional level regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.2 Metabolic Regulation(Regulation of Gene Expression).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.3 Metabolic Regulation(Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in gene expression、RNA-Based Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.1 Essentials of Virology(VIRUS AND VIRION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.2 Essentials of Virology(Viral Replication 病毒复制、Viral Diversity).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 9.3 Essentials of Virology and Test(Overview of Animal Viruses、Retroviruses).pdf
