上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.2)Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 How can a bacterium change itself by taking genes from other bacteria? Lecture 10-2 Bacterial genetics II.Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes Chapter 1o in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS IJIAO TONG UN Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 10-2 Bacterial genetics II. Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes How can a bacterium change itself by taking genes from other bacteria? Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn Chapter 10 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS

10.6 Genetic recombination遗传重组 The physical exchange of genetic material between genetic elements Genetic elements: ·Chromosomes ·Plasmids ·Viruses Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 10.6 Genetic recombination遗传重组 The physical exchange of genetic material between genetic elements Genetic elements: • Chromosomes • Plasmids • Viruses

Molecular Events in Homologous Recombination同源重组 General or homologous recombination同源重组 Genetic exchange between homologous DNA sequences from two different sources ©Homologous DNA sequences同源序列 Having the same or nearly the same sequence Extremely important for all organisms重要性 .25 genes involved in E.coli Several redundant pathways.Therefore,if one pathway is inhibited,.another may supply necessary functions..有数条替代 途径备用 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Molecular Events in Homologous Recombination 同源重组 General or homologous recombination同源重组 • Genetic exchange between homologous DNA sequences from two different sources Homologous DNA sequences同源序列 • Having the same or nearly the same sequence Extremely important for all organisms重要性 • 25 genes involved in E. coli • Several redundant pathways. Therefore, if one pathway is inhibited, another may supply necessary functions.有数条替代 途径备用
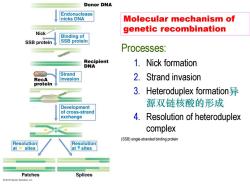
Donor DNA Endonuclease nicks DNA Molecular mechanism of genetic recombination Nick 0 Binding of SSB protein SSB protein Processes: 00000 Recipient DNA 1.Nick formation Strand RecA invasion 2.Strand invasion protein 000 3.Heteroduplex formation 源双链核酸的形成 Development of cross-strand exchange 4.Resolution of heteroduplex complex (SSB)single-stranded binding protein Resolution Resolution at sites at Vsites Patches Splices 2012 Pearson Education,Inc
Molecular mechanism of genetic recombination Processes: 1. Nick formation 2. Strand invasion 3. Heteroduplex formation异 源双链核酸的形成 4. Resolution of heteroduplex complex (SSB) single-stranded binding protein
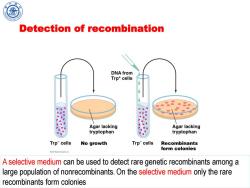
Detection of recombination DNA from Trp*cells Agar lacking Agar lacking tryptophan tryptophan Trp-cells No growth Trpcells Recombinants form colonies A selective medium can be used to detect rare genetic recombinants among a large population of nonrecombinants.On the selective medium only the rare recombinants form colonies
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Detection of recombination A selective medium can be used to detect rare genetic recombinants among a large population of nonrecombinants.On the selective medium only the rare recombinants form colonies

Processes leading to genetic recombination in prokaryotic cells原核生物遗传重组的类型 Transformation转化 Donor DNA is free in the environment Transduction转导 Donor DNA is transferred by a virus @Conjugation接合 Donor DNA is transferred via cell-to-cell contact and a conjugative plasmid Horizontal gene transfer Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Processes leading to genetic recombination in prokaryotic cells 原核生物遗传重组的类型 Transformation 转化 • Donor DNA is free in the environment Transduction 转导 • Donor DNA is transferred by a virus Conjugation 接合 • Donor DNA is transferred via cell-to-cell contact and a conjugative plasmid Horizontal gene transfer
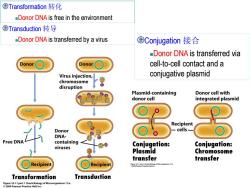
@Transformation转化 Donor DNA is free in the environment @Transduction转导 -Donor DNA is transferred by a virus ©Conjugation接合 Donor DNA is transferred via Donor Donor cell-to-cell contact and a Virus injection, conjugative plasmid chromosome disruption Plasmid-containing Donor cell with donor cell integrated plasmid Recipient Donor cells- DNA- Free DNA containing Conjugation: viruses Conjugation: Plasmid Chromosome transfer transfer Recipient Recipient Transformation Transduction Figure 10-11 part 1 Brock Biology of Microorganisms 11/e 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Transformation 转化 Donor DNA is free in the environment Transduction 转导 Donor DNA is transferred by a virus Conjugation 接合 Donor DNA is transferred via cell-to-cell contact and a conjugative plasmid

10.7 Transformation Transformation Genetic transfer process by which DNA is incorporated into a recipient cell and brings about genetic change Discovered by Fredrick Griffith in the late 1920s Worked with Streptococcus pneumoniae(pneumococcus; Figure 10.12) This process set the stage for the discovery of DNA Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 10.7 Transformation Transformation • Genetic transfer process by which DNA is incorporated into a recipient cell and brings about genetic change Discovered by Fredrick Griffith in the late 1920s • Worked with Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus; Figure 10.12) This process set the stage for the discovery of DNA
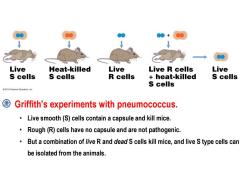
Live Heat-killed Live Live R cells Live S cells S cells R cells heat-killed S cells S cells 2012 Pearson Education,Inc Griffith's experiments with pneumococcus. Live smooth(S)cells contain a capsule and kill mice. Rough(R)cells have no capsule and are not pathogenic. But a combination of live R and dead S cells kill mice,and live S type cells can be isolated from the animals
Griffith's experiments with pneumococcus. • Live smooth (S) cells contain a capsule and kill mice. • Rough (R) cells have no capsule and are not pathogenic. • But a combination of live R and dead S cells kill mice, and live S type cells can be isolated from the animals

10.7 Transformation Competent:cells capable of taking up DNA and being transformed感受态 In naturally transformable bacteria,competence is regulated In other strains,specific procedures are necessary to make cells competent Electricity can be used to force cells to take up dNA (electroporation) Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 10.7 Transformation Competent: cells capable of taking up DNA and being transformed感受态 • In naturally transformable bacteria, competence is regulated • In other strains, specific procedures are necessary to make cells competent • Electricity can be used to force cells to take up DNA (electroporation)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.1)Mutation and Recombination.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 1 Microorganisms & Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Introduction to Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)虫草属(Cordyceps)真菌研究概况.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)植物生物反应器的研究进展.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)绪论(周选围).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第8章 生物技术发明的保护.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第7章 现代生物技术伦理与安全..pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第6章 生物技术与人类生存环境.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第5章 生物技术与人类健康.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第4章 能源开发中的生物技术.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第3章 日常生活(食品)中的生物技术.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第2章 农业生产中的生物技术.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)第1章 现代生物技术总论.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第四章 生物技术与能源.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第六章 生物技术与环境.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第八章 生物技术发明的保护.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第五章 生物技术与人类健康.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第七章 现代生物技术伦理与安全.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2015)第三章 日常生活(食品)中的生物技术.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.1 Genetic Engineering(Methods for Manipulating DNA).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.2 Genetic Engineering(Gene Cloning).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.1 Microbial Genomics(Genomes and Genomics).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.2 Microbial Genomics(Gene Function and Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.1 Metabolic diversity(Phototrophy)微生物代谢的多样性——光合生物 The Phototrophic Way of Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.2 Metabolic diversity(Chemolithotrophy)Chemolithotrophy:energy from the oxidation of inorganic electron donors 化能无机营养生物:通过氧化无机物而 获得能量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.3 Metabolic Diversity(Catabolism of Organic Compounds)The anaerobic way of life:Fermentation and syntrophy 无氧生活 方式:发酵与互养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.1 Methods in Microbial Ecology(Culture-dependent analysis of microbial communities 基于培养的微生物群落研究).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.2 Methods in Microbial Ecology and Test(MEASURING MICROBIAL ACTIVITIES IN NATURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.1 Microbial Ecology_Microbial Habitats and Diversity(MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS、Marine Microbiology).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.2 Microbial Ecology(Nutrient Cycles, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.3 Microbial Ecology(Microbial Symbioses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.2 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Fungi 真菌、Algae 藻类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 2 An Overview of Microbial Life.pdf
