上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(MICROBIAL EVOLUTION)

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 16-2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类 Chapter 16 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS GH Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 16-2 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类 Chapter 16 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS Chen Feng School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn

上泽充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1896 1920 1987 2006 。© II.MICROBIAL EVOLUTION 月 CUAGUALIAO IONG UNIVEG
1896 1920 1987 2006 II. MICROBIAL EVOLUTION

12.5 The Evolutionary Process演化过程 Adaptive mutations are those that improve the fitness of an organism,increasing its survival capacity or reproductive success compared with that of competing organisms. Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 12.5 The Evolutionary Process演化过程 Adaptive mutations are those that improve the fitness of an organism, increasing its survival capacity or reproductive success compared with that of competing organisms
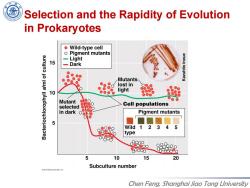
Selection and the Rapidity of Evolution in Prokaryotes Wild-type cell Pigment mutants Light 15 -Dark Mutants lost in 10 light 部8 Mutant Cell populations selected in dark Pigment mutants 5 Wild 1 2 3 45 type P880 pooo 5 10 15 20 Subculture number 2012 Pearson Education.inc Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Selection and the Rapidity of Evolution in Prokaryotes

11.6 Evolutionary Analysis:Theoretial Aspects Evolutionary chronometer-a molecule,such as rRNA, whose molecular sequence can be used as a comparative measure of evolutionary divergence. 分子序列可代表相对演化分岐的分子,如RNA,可作为演 化指针。 Criteria for being chronometers 1.Universal distribution across the group chosen for study广泛分布 2.Functionally homologous in each organisms.功能同源 3.Can be properly aligned to in order to identify sequence homology and variance.线性 4.Should change at a rate commensurate with the evolutionary distance measured.与进化距离相称的变化速率 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 11.6 Evolutionary Analysis: Theoretial Aspects Evolutionary chronometer- a molecule, such as rRNA, whose molecular sequence can be used as a comparative measure of evolutionary divergence. 分子序列可代表相对演化分岐的分子,如rRNA,可作为演 化指针。 Criteria for being chronometers 1. Universal distribution across the group chosen for study广泛分布 2. Functionally homologous in each organisms功能同源 3. Can be properly aligned to in order to identify sequence homology and variance. 线性 4. Should change at a rate commensurate with the evolutionary distance measured.与进化距离相称的变化速率

Evolutionary chronometer Evolutionary distance between two organisms can be measured by differences in the nucleotide or amino acid sequence of homologous macromolecules isolated from them两物种的进化距离可通过比较来自它们的同 源大分子的核苷酸序列或氨基酸序列而测定 Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Evolutionary chronometer Evolutionary distance between two organisms can be measured by differences in the nucleotide or amino acid sequence of homologous macromolecules isolated from them 两物种的进化距离可通过比较来自它们的同 源大分子的核苷酸序列或氨基酸序列而测定
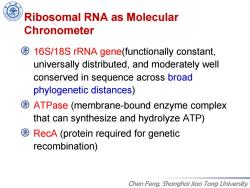
Ribosomal RNA as Molecular Chronometer 16S/18S rRNA gene(functionally constant, universally distributed,and moderately well conserved in sequence across broad phylogenetic distances) ATPase (membrane-bound enzyme complex that can synthesize and hydrolyze ATP) RecA(protein required for genetic recombination) Chen Feng,Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Chen Feng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Ribosomal RNA as Molecular Chronometer 16S/18S rRNA gene(functionally constant, universally distributed, and moderately well conserved in sequence across broad phylogenetic distances) ATPase (membrane-bound enzyme complex that can synthesize and hydrolyze ATP) RecA (protein required for genetic recombination)
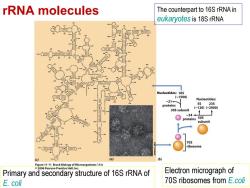
rRNA molecules The counterpart to 16S rRNA in eukaryotes is 18S rRNA Nucleotides:16S (~1500) Nucleotides: -21+ proteins 55 235 (~120)(~2900) 30S subunit ~34← proteins 50S subunit 705 ribosome (c) (a) (b) Figure 11-11 Brock Biology of Microorganisms 11/e 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Primary and secondary structure of 16S rRNA of Electron micrograph of E.coli 70S ribosomes from E.coli
rRNA molecules Electron micrograph of 70S ribosomes from E.coli Primary and secondary structure of 16S rRNA of E. coli The counterpart to 16S rRNA in eukaryotes is 18S rRNA
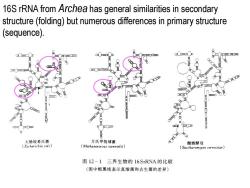
16S rRNA from Archea has general similarities in secondary structure(folding)but numerous differences in primary structure (sequence). 大肠埃希氏菌 万氏甲烷球菌 酿酒酵母 Escherichia coli) Methanococcus vannielii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae 图12-1三界生物的16 SrRNA的比较 (图中粗黑线表示真细菌和古生菌的差异)
16S rRNA from Archea has general similarities in secondary structure (folding) but numerous differences in primary structure (sequence)
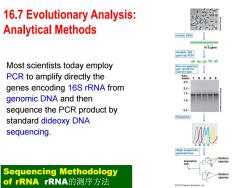
16.7 Evolutionary Analysis: Analytical Methods Isolate DNA 16S gene Amplify 16S gene by PCR Most scientists today employ Run on agarose gel:check for correct size PCR to amplify directly the Kilo- bases 1 2 3.0- genes encoding 16S rRNA from 2.0- 1.5- genomic DNA and then 1.0- sequence the PCR product by 0.5- Sequence standard dideoxy DNA sequencing Align sequences; generate tree Distinct Ancestral species cell Sequencing Methodology Distinct species of rRNArRNA的测序方法 2012 Pearson Education,Inc
Most scientists today employ PCR to amplify directly the genes encoding 16S rRNA from genomic DNA and then sequence the PCR product by standard dideoxy DNA sequencing. Sequencing Methodology of rRNA rRNA的测序方法 16.7 Evolutionary Analysis: Analytical Methods
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.1 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物演化与系统分类(EARLY EARTH, THE ORIGIN OF LIFE, AND MICROBIAL DIVERSIFICATION).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.3 Microbial Ecology(Microbial Symbioses).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.2 Microbial Ecology(Nutrient Cycles, Biodegradation, and Bioremediation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 15.1 Microbial Ecology_Microbial Habitats and Diversity(MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEMS、Marine Microbiology).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.2 Methods in Microbial Ecology and Test(MEASURING MICROBIAL ACTIVITIES IN NATURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 14.1 Methods in Microbial Ecology(Culture-dependent analysis of microbial communities 基于培养的微生物群落研究).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.3 Metabolic Diversity(Catabolism of Organic Compounds)The anaerobic way of life:Fermentation and syntrophy 无氧生活 方式:发酵与互养.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.2 Metabolic diversity(Chemolithotrophy)Chemolithotrophy:energy from the oxidation of inorganic electron donors 化能无机营养生物:通过氧化无机物而 获得能量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 13.1 Metabolic diversity(Phototrophy)微生物代谢的多样性——光合生物 The Phototrophic Way of Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.2 Microbial Genomics(Gene Function and Regulation).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 12.1 Microbial Genomics(Genomes and Genomics).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.2 Genetic Engineering(Gene Cloning).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 11.1 Genetic Engineering(Methods for Manipulating DNA).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.2)Genetic Exchange In Prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 10 Bacterial genetics(10.1)Mutation and Recombination.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 1 Microorganisms & Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Introduction to Microbiology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)虫草属(Cordyceps)真菌研究概况.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT讲座)植物生物反应器的研究进展.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术与人类》通识课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,2017)绪论(周选围).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 16.3 Microbial Evolution and Systematics 微生物进化与系统分类(Microbial Systematics 微生物系统分类学).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.1 Diversity of Bacteria(The Proteobacteria)The Phylogeny of Bacteria、Phototrophic, Chemolithotrophic, and Methanotrophic Proteobacteria、Aerobic and Facultatively Aerobic、Delta-and Epsilonproteobacteria.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 17.2 Diversity of Bacteria(Other Bacteria).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.1 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Eukaryotic cell structure function and genetics、Eukaryotic Microbial Diversity.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 18.2 Diversity of Eucaryotic Microbe(Eukaryotic Microorganisms)Fungi 真菌、Algae 藻类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 2 An Overview of Microbial Life.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.1)Microscopy and cell morphology.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.2)Cell Membrances and Cell Walls.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.3)Cell Wall of Prokaryotes:Peptidoglycan and Related Molecules.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Biology(3.4)Surface structures and inclusions of prokaryotes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 4 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.1 Microbial Growth(Bacterial Cell Division、Growth of Bacterial Populations 细菌群体生长).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.2 Microbial Growth(Measuring Microbial Growth 微生物生长的测定(计数)).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 5.3 Microbial Growth(Environmental Effects on Microbial Growth).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.1 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(Physical Antimicrobial Control、Chemical Antimicrobial Control).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 6.2 Microbial Growth Control in vitro and in vivo(ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS USED IN VIVO 体内使用的抗微生物制剂、ANTIMICROBIAL DRUG RESISTANCE AND DRUG DISCOVERY 抗药性与新药研制).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.1 Essentials of Molecular Biology(Genes and Gene Experession、DNA STRUCTURE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 7.3 Essentials of Molecular Biology(mRNA Transcription、PROTEIN SYNTHESIS).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微生物学 Microbiology》课程教学资源(双语课件)Lecture 8.1 Regulation of Gene Expression(Overview、Regulation of Enzyme Activity、Transcriptional level regulation).pdf
