《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 6 FREEZING AND FROZEN-FOOD STORAGE

Chpter 6 FREEZING AND FROZEN-FOOD STORAGE Principles of freezing DESCRIPTION OF FOOD FREEZING SYSTEMS INDRECT-CONTACT FREEZING SYSTEMS DIRECT-CONTACT FREEZING SYSTEMS INDIVIDUAL QUICK FREEZING (IQF) ESTIMATION OF FREEZING TIME FOOD FREEZING AND PRODUCT QUALITY SUMMARY
Chpter 6 FREEZING AND FROZEN-FOOD STORAGE Principles of freezing DESCRIPTION OF FOOD FREEZING SYSTEMS INDRECT-CONTACT FREEZING SYSTEMS DIRECT-CONTACT FREEZING SYSTEMS INDIVIDUAL QUICK FREEZING (IQF) ESTIMATION OF FREEZING TIME FOOD FREEZING AND PRODUCT QUALITY SUMMARY

Problem ◼ Explain the cause of freezing temperature depression. ◼ Why should we use rapid freezing process? ◼ How many factors influence the freezing time? What are they? ◼ What changes occur to the product during freezing? ◼ Why the storage temp. should be kept in constant?
Problem ◼ Explain the cause of freezing temperature depression. ◼ Why should we use rapid freezing process? ◼ How many factors influence the freezing time? What are they? ◼ What changes occur to the product during freezing? ◼ Why the storage temp. should be kept in constant?

vocabulary ◼ freeze, ice crystals , irreversible, negative changes, latent heat of fusion , depression of the freezing temperature , supercooling region , freezing plateau , solutes , depression of the freezing temperature, freezing-point depression , freezing- temperature depression, eutectic temperature
vocabulary ◼ freeze, ice crystals , irreversible, negative changes, latent heat of fusion , depression of the freezing temperature , supercooling region , freezing plateau , solutes , depression of the freezing temperature, freezing-point depression , freezing- temperature depression, eutectic temperature

vocabulary ◼ barrier, air blat system, spiral conveyor, fluidized bed, immersion, cryogenic, tunnel, spray of liquid refrigerant, intimate contact , fundamental, estimation, critical, individual, freezing medium, Plank's equation, temperature gradient, thermal conductivity, cylinder, cylindrical, sphere, spherical, infinite plate, convective heat transfer coefficients
vocabulary ◼ barrier, air blat system, spiral conveyor, fluidized bed, immersion, cryogenic, tunnel, spray of liquid refrigerant, intimate contact , fundamental, estimation, critical, individual, freezing medium, Plank's equation, temperature gradient, thermal conductivity, cylinder, cylindrical, sphere, spherical, infinite plate, convective heat transfer coefficients

Freezing Process ◼ The freezing process is the removal of thermal energy from the food product to the extent required to reduce the temperature below the freezing temperature of water. The thermal energy removed as a part of freezing is primarily latent heat of fusion required to convert water to ice within the product
Freezing Process ◼ The freezing process is the removal of thermal energy from the food product to the extent required to reduce the temperature below the freezing temperature of water. The thermal energy removed as a part of freezing is primarily latent heat of fusion required to convert water to ice within the product

DEFINITION OF FREEZING AND FROZEN-FOOD STORAGE ◼ Food freezing is the preservation process that depends on the reduction of product temperature to levels well below the temperature at which ice crystals begin to form within the food. By reducing the temperature of the product to -10 to -20℃, the normal reactions that cause deterioration of foods are reduced to negligible or minimal rates
DEFINITION OF FREEZING AND FROZEN-FOOD STORAGE ◼ Food freezing is the preservation process that depends on the reduction of product temperature to levels well below the temperature at which ice crystals begin to form within the food. By reducing the temperature of the product to -10 to -20℃, the normal reactions that cause deterioration of foods are reduced to negligible or minimal rates

6.1 table Initial Freezing Temperatures of Foods Initial Water Freezing Content Temperature Product (by weight) (C) Apple juice 87.2 -1.44 Apple juice concentrate 49.8 -11.33 Apple sauce 82.8 -1.67 Asparagus 92.6 -0.67 Bilberries 85.1 -1.11 Bilberry juice 89.5 -1.11 Carrots 87.5 -1.11 Cherry juice 86.7 -1.44 Grape juice 84.7 -1.78 Onions 85.5 -1.44 Orange juice 89.0 -1.17 Peaches 85.1 -1.56 Pears 83.8 -1.61 Plums 80.3 -2.28 Raspberries 82.7 -1.22 Raspberry juice 88.5 -1.22 Spinach 90.2 -0.56 Strawberries 89.3 -0.89 Strawberry juice 91.7 -0.89 Sweet cherries 77.0 -2.61 Tall peas 75.8 -1.83 Tomato pulp 92.9 -0.72 From Heldman and Singh(1981)

◼ The two curves compare the characteristic temperature/time relationship during freezing of water with that of a food product. The first characteristic of the food- -freezing curve is the depression of the freezing temperature. All food products will exhibit an initial ice crystal formation temperature below that of pure water. The second feature of the food-freezing curve is the gradual decline in temperature during removal of the latent heat of fusion
◼ The two curves compare the characteristic temperature/time relationship during freezing of water with that of a food product. The first characteristic of the food- -freezing curve is the depression of the freezing temperature. All food products will exhibit an initial ice crystal formation temperature below that of pure water. The second feature of the food-freezing curve is the gradual decline in temperature during removal of the latent heat of fusion
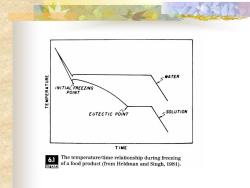
SWATER INITIAL FREEZING POINT EUTECTIC POINT SSOLUTION TIME 6.1 The temperature/time relationship during freezing figure of a food product(from Heldman and Singh,1981)

Freezing-temperature Depression ◼ The formation of ice crystals within the water phase results in a concentration of solutes within the water phase. The ice crystals are pure water in the solid state. The result of the increased concentration of the solute in the liquid phase causes depression of the freezing temp. , a lower temp. at which ice crystals will form. Since these changes occur on a continuous basis, the gradual temp. decline with time is a direct result of freezing-temperature depression
Freezing-temperature Depression ◼ The formation of ice crystals within the water phase results in a concentration of solutes within the water phase. The ice crystals are pure water in the solid state. The result of the increased concentration of the solute in the liquid phase causes depression of the freezing temp. , a lower temp. at which ice crystals will form. Since these changes occur on a continuous basis, the gradual temp. decline with time is a direct result of freezing-temperature depression
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 5 REFRIGERATED STORAGE.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 4 COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 3 PASTEURIZATION AND BLANCHING.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 2 THERMAL PROCESSING PRINCIPLES.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION.ppt
- 天津农学院:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(实验指导)食品工艺学实验任务书(共七章).doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五篇 软饮料工艺学.doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.5 第五章 瓶装水饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.4 第四章 植物蛋白饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.3 第三章 果蔬汁饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.2 第二章 碳酸饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.1 第一章 软饮料用原辅材料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学.doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.4 第四章 蔬菜腌制工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.3 第三章 果蔬干制工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.2 第二章 果蔬糖制工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.1 第一章 果蔬罐头工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三篇 面制食品工艺学.doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三篇 面制食品工艺学 3.3.4 第三章 焙烤食品工艺(四).ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三篇 面制食品工艺学 3.3.3 第三章 焙烤食品工艺(三).ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 7 LIQUID CONC.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 8 DEHYDRATION.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 9 OTHER SEPARATION PROCESSES.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)绪论、第一章 罐头食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第二章 软饮料工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第三章 糕点食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第四章 糖果食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第五章 酒类生产及酱油、食醋、酸奶的制作.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第六章 脱水食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第七章 食品冷加工工艺.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(主讲:夏文水、陈洁、许学勤、陶谦).ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 食品的脱水加工.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 食品的热处理与杀菌.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 食品的冷冻保藏.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 食品的腌渍发酵和烟熏处理.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 食品的化学保藏.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 食品的辐射保藏.ppt
- 广西工商职业技术学院:《食品分析与检验》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论(任课教师:陈宁春、蒲海燕、谢伟燕、谢洁、张国良).ppt
- 广西工商职业技术学院:《食品分析与检验》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论 1.1 溶液浓度的表示 1.2 实验数据的记录和理 1.3 实验室用水 1.4 化学试剂 1.5 实验室安全及防护.ppt
- 广西工商职业技术学院:《食品分析与检验》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论 1.6 样品采集、制备和保存.ppt
