《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 4 COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION

COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION • GENERAL CONCEPTS • DESCRIPTION OF COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION SYSTEMS • HEATING AND COOLING OF FOOD IN A CONTAINER • ESTABLISHMENT OF PROCESS TIMES • INFLUENCE OF COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION ON PRODUCT QUALITY • SUMMARY
COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION • GENERAL CONCEPTS • DESCRIPTION OF COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION SYSTEMS • HEATING AND COOLING OF FOOD IN A CONTAINER • ESTABLISHMENT OF PROCESS TIMES • INFLUENCE OF COMMERCIAL STERILIZATION ON PRODUCT QUALITY • SUMMARY

GENERAL CONCEPTS
GENERAL CONCEPTS

Factors influencing thermal process • product pH or acidity influencing the thermal resistance of the microbial spore. • The heating and cooling characteristics of the product in the container. • The decimal reduction time (D) and the thermal resistance constant (Z) for the microbial population in the product. • The size of the container and the types of heating and cooling media utilized
Factors influencing thermal process • product pH or acidity influencing the thermal resistance of the microbial spore. • The heating and cooling characteristics of the product in the container. • The decimal reduction time (D) and the thermal resistance constant (Z) for the microbial population in the product. • The size of the container and the types of heating and cooling media utilized
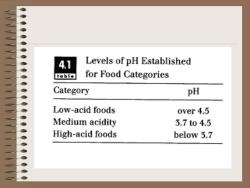
4.1 Levels of pH Established tobie for Food Categories Category pH Low-acid foods over 4.5 Medium acidity 3.7t04.5 High-acid foods below 5.7

• pH below 3.7, thermal process is based on the thermal resistance of microbial spores associated with economic spoilage. • pH over 4.5, thermal processes is based on thermal resistance of spores of microbial pathogens. • pH between 3.7 and 4.5, the processes may be similar to acid foods
• pH below 3.7, thermal process is based on the thermal resistance of microbial spores associated with economic spoilage. • pH over 4.5, thermal processes is based on thermal resistance of spores of microbial pathogens. • pH between 3.7 and 4.5, the processes may be similar to acid foods

• Clostridium botulinum, pH >4.5 toxin • 65% fatality after ingest • Minimum process :2.45 min/121℃ • Higher thermal resistance of nonpathogenic spores cause spoilage. • pH<3.7 spore-forming bacteria, yeasts, and molds are responsible for food spoilage • Conduction, mixed, convection
• Clostridium botulinum, pH >4.5 toxin • 65% fatality after ingest • Minimum process :2.45 min/121℃ • Higher thermal resistance of nonpathogenic spores cause spoilage. • pH<3.7 spore-forming bacteria, yeasts, and molds are responsible for food spoilage • Conduction, mixed, convection
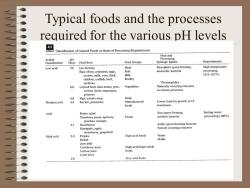
Typical foods and the processes required for the various pH levels
Typical foods and the processes required for the various pH levels

A minimum thermal process • All foods with pH greater than 4.5 must receive a minimum thermal process. This minimum process is indicated by the thermal death time versus temperature relationship, the typical reference process is 2.45 minutes at 121℃, and the thermal resistance constant (Z) is 10℃ to eliminate Clostridium botulinum
A minimum thermal process • All foods with pH greater than 4.5 must receive a minimum thermal process. This minimum process is indicated by the thermal death time versus temperature relationship, the typical reference process is 2.45 minutes at 121℃, and the thermal resistance constant (Z) is 10℃ to eliminate Clostridium botulinum
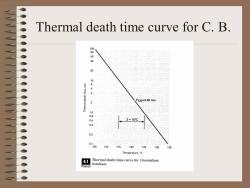
Thermal death time curve for C. B
Thermal death time curve for C. B

• With the growth and toxin production, Clostridium botulinum produce gas. the gas produced is sufficient to cause visible swelling of the container. This chara. represents the basis for an important quality control step used to eliminate the possibility of a canned food containing botulinum toxin from reaching a consumer
• With the growth and toxin production, Clostridium botulinum produce gas. the gas produced is sufficient to cause visible swelling of the container. This chara. represents the basis for an important quality control step used to eliminate the possibility of a canned food containing botulinum toxin from reaching a consumer
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 3 PASTEURIZATION AND BLANCHING.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 2 THERMAL PROCESSING PRINCIPLES.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION.ppt
- 天津农学院:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(实验指导)食品工艺学实验任务书(共七章).doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五篇 软饮料工艺学.doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.5 第五章 瓶装水饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.4 第四章 植物蛋白饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.3 第三章 果蔬汁饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.2 第二章 碳酸饮料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五篇 软饮料工艺学 5.1 第一章 软饮料用原辅材料.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学.doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.4 第四章 蔬菜腌制工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.3 第三章 果蔬干制工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.2 第二章 果蔬糖制工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四篇 果蔬食品加工学 4.1 第一章 果蔬罐头工艺.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三篇 面制食品工艺学.doc
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三篇 面制食品工艺学 3.3.4 第三章 焙烤食品工艺(四).ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三篇 面制食品工艺学 3.3.3 第三章 焙烤食品工艺(三).ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三篇 面制食品工艺学 3.3.2 第三章 焙烤食品工艺(二).ppt
- 河南农业大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三篇 面制食品工艺学 3.3.1 第三章 焙烤食品工艺(一).ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 5 REFRIGERATED STORAGE.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 6 FREEZING AND FROZEN-FOOD STORAGE.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 7 LIQUID CONC.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 8 DEHYDRATION.ppt
- 《食品加工原理》课程PPT教学课件(福建农林大学)Chapter 9 OTHER SEPARATION PROCESSES.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)绪论、第一章 罐头食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第二章 软饮料工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第三章 糕点食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第四章 糖果食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第五章 酒类生产及酱油、食醋、酸奶的制作.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第六章 脱水食品工艺.ppt
- 《食品工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第七章 食品冷加工工艺.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(主讲:夏文水、陈洁、许学勤、陶谦).ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 食品的脱水加工.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 食品的热处理与杀菌.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 食品的冷冻保藏.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 食品的腌渍发酵和烟熏处理.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 食品的化学保藏.ppt
- 江南大学:《食品工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 食品的辐射保藏.ppt
- 广西工商职业技术学院:《食品分析与检验》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论(任课教师:陈宁春、蒲海燕、谢伟燕、谢洁、张国良).ppt
