《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 11 Structure Determination - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy

CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 11 Structure Determination: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance T H IR D E DI Spectroscopy Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 11 Structure Determination: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy

Introduction Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)Spectroscopy is the most valuable spectroscopic technique available to laboratory organic chemists Taken together,mass spectrometry,IR,UV and NMR make it possible to determine the structures of even very complex molecules Mass spectrometry molecular formula Infrared Spectroscopy functional groups UV Spectroscopy extent of conjugation NMR Spectroscopy map of carbon-hydrogen framework
• Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy is the most valuable spectroscopic technique available to laboratory organic chemists • Taken together, mass spectrometry, IR, UV and NMR make it possible to determine the structures of even very complex molecules Mass spectrometry - molecular formula Infrared Spectroscopy - functional groups UV Spectroscopy - extent of conjugation NMR Spectroscopy - map of carbon-hydrogen framework Introduction

11-1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Many atomic nuclei behave as if they spin on an axis of rotation -Nuclei are positively charged These spinning nuclei generate tiny magnetic fields Tiny magnets interact with an external magnetic field,denoted Bo Proton (1H)and carbon (13C)are the most important nuclear spins to organic chemists
Many atomic nuclei behave as if they spin on an axis of rotation ▪ Nuclei are positively charged ▪ These spinning nuclei generate tiny magnetic fields ▪ Tiny magnets interact with an external magnetic field, denoted B0 ▪ Proton (1H) and carbon (13C) are the most important nuclear spins to organic chemists 11-1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
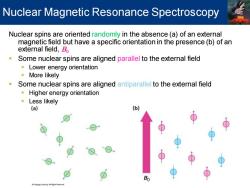
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear spins are oriented randomly in the absence (a)of an external magnetic field but have a specific orientation in the presence(b)of an external field,Bo n Some nuclear spins are aligned parallel to the external field Lower energy orientation More likely Some nuclear spins are aligned antiparallel to the external field Higher energy orientation Less likely (a) (b) 0
Nuclear spins are oriented randomly in the absence (a) of an external magnetic field but have a specific orientation in the presence (b) of an external field, B0 ▪ Some nuclear spins are aligned parallel to the external field ▪ Lower energy orientation ▪ More likely ▪ Some nuclear spins are aligned antiparallel to the external field ▪ Higher energy orientation ▪ Less likely Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy

Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy When nuclei that are aligned parallel with an external magnetic field are irradiated with the proper frequency of electromagnetic radiation the energy is absorbed and the nuclei“spin-flips”to the higher-energy antiparallel alignment Nuclei that undergo "spin-flips"in response to applied radiation are said to be in resonance with the applied radiation -nuclear magnetic resonance Frequency necessary for resonance depends on strength of external field and the identity of the nuclei
When nuclei that are aligned parallel with an external magnetic field are irradiated with the proper frequency of electromagnetic radiation the energy is absorbed and the nuclei “spin-flips” to the higher-energy antiparallel alignment ▪ Nuclei that undergo “spin-flips” in response to applied radiation are said to be in resonance with the applied radiation - nuclear magnetic resonance ▪ Frequency necessary for resonance depends on strength of external field and the identity of the nuclei Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy

Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy The energy difference AE between nuclear spin states depends on the strength of the applied magnetic field Absorption of energy with frequency vconverts a nucleus from a lower to a higher spin state -AE=8.0 x 10-5 kJ/mol for magnetic field strength of 4.7 T a For field strength of 4.7 T a radiofrequency (rf)of v=200 MHz is required to bring 1H nuclei into resonance For a field strength of 4.7 T a radiofrequency(rf)ofv=50 MHz is required to bring 13C nuclei into resonance (c) (b) Strength of applied field,Bo
The energy difference DE between nuclear spin states depends on the strength of the applied magnetic field ▪ Absorption of energy with frequency n converts a nucleus from a lower to a higher spin state ▪ DE = 8.0 x 10-5 kJ/mol for magnetic field strength of 4.7 T a ▪ For field strength of 4.7 T a radiofrequency (rf) of n = 200 MHz is required to bring 1H nuclei into resonance ▪ For a field strength of 4.7 T a radiofrequency (rf) of n = 50 MHz is required to bring 13C nuclei into resonance Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
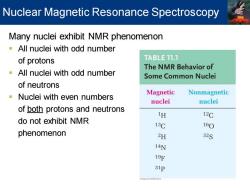
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Many nuclei exhibit NMR phenomenon -All nuclei with odd number of protons TABLE 11.1 The NMR Behavior of All nuclei with odd number Some Common Nuclei of neutrons Nuclei with even numbers Magnetic Nonmagnetic nuclei nuclei of both protons and neutrons 1H 12C do not exhibit NMR 13C 160 phenomenon 2H 32S 14N 19℉ 31p
Many nuclei exhibit NMR phenomenon ▪ All nuclei with odd number of protons ▪ All nuclei with odd number of neutrons ▪ Nuclei with even numbers of both protons and neutrons do not exhibit NMR phenomenon Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy

11-2 The Nature of NMR Absorptions The absorption frequency is not the same for all 1H and 13C nuclei Nuclei in molecules are surrounded by electrons Electrons set up tiny local magnetic fields that act in opposition to the applied field,shielding the nucleus from the full effect of the external magnetic field The effective field actually felt by the nucleus is the applied field reduced by the local shielding effects Beffective=Bapplied-Blocal
The absorption frequency is not the same for all 1H and 13C nuclei ▪ Nuclei in molecules are surrounded by electrons ▪ Electrons set up tiny local magnetic fields that act in opposition to the applied field, shielding the nucleus from the full effect of the external magnetic field ▪ The effective field actually felt by the nucleus is the applied field reduced by the local shielding effects Beffective = Bapplied – Blocal 11-2 The Nature of NMR Absorptions

The Nature of NMR Absorptions The absorption frequency is not the same for all 1H and 13C nuclei Each chemically distinct nucleus in a molecule has a slightly different electronic environment and consequently a different effective field Each chemically distinct 13C or 1H nucleus in a molecule experiences a different effective field and will exhibit a distinct 13C or 1H NMR signal
The absorption frequency is not the same for all 1H and 13C nuclei ▪ Each chemically distinct nucleus in a molecule has a slightly different electronic environment and consequently a different effective field ▪ Each chemically distinct 13C or 1H nucleus in a molecule experiences a different effective field and will exhibit a distinct 13C or 1H NMR signal The Nature of NMR Absorptions
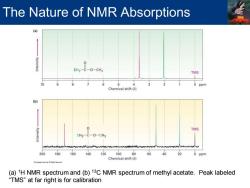
The Nature of NMR Absorptions CH3-C-0-CH3 TMS 6 A 2 0 ppm Chemical shift (8) (b) TMS CH3-C-O-CH3 200180 160 140 12010080 60 40 20 0 ppm Chemical shift(8) (a)1H NMR spectrum and(b)13C NMR spectrum of methyl acetate.Peak labeled “TMS”at far right is for calibration
(a) 1H NMR spectrum and (b) 13C NMR spectrum of methyl acetate. Peak labeled “TMS” at far right is for calibration The Nature of NMR Absorptions
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 04 Organic Compounds - Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 10 Structure Determination - Mass Spectrometry, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 12 Organohalides - Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 17 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution and Condensation Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 18 Amines and Heterocycles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 19 Biomolecules - Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 20 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 21 Biomolecules - Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 22 Carbohydrate Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 23 Biomolecules - Lipids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 24 Biomolecules - Nucleic Acids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 25 Secondary Metabolites - An Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 26 Orbitals and Organic Chemistry - Pericyclic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 27 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 03 Alkanes.pdf
