《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers

CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 5 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers T H I R D E DI TION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 5 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers

Handedness Right and left hands are not identical Right and left hands are mirror images of each other they are nonsuperimposable mirror images Almost all the molecules in the human body are handed Handedness primarily arises from the tetrahedral stereochemistry of sp3-hybridized carbon atoms Handedness is crucial to understanding biological chemistry Left hand Right hand
Right and left hands are not identical ▪ Right and left hands are mirror images of each other – they are nonsuperimposable mirror images ▪ Almost all the molecules in the human body are handed ▪ Handedness primarily arises from the tetrahedral stereochemistry of sp3 -hybridized carbon atoms ▪ Handedness is crucial to understanding biological chemistry Handedness
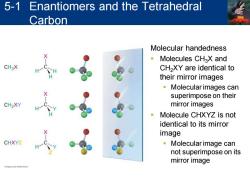
5-1 Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon Molecular handedness Molecules CHaX and CH3X CH2XY are identical to their mirror images 。Molecular images can superimpose on their CH2XY mirror images Molecule CHXYZ is not identical to its mirror image CHXYZ 。Molecular image can not superimpose on its mirror image
Molecular handedness ▪ Molecules CH3X and CH2XY are identical to their mirror images ▪ Molecular images can superimpose on their mirror images ▪ Molecule CHXYZ is not identical to its mirror image ▪ Molecular image can not superimpose on its mirror image 5-1 Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon

Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon Enantiomers "From the Greek enantio,meaning“opposite'” Stereoisomers in which molecules are not identical to their mirror images Result whenever a tetrahedral carbon is bonded to four different substituents CHXYZ (one need not be H) Lactic acid(2-hydroxypropanoic acid)has four different groups (-H,-OH,-CH3,-CO2H)bonded to the central carbon atoms and exists as a pair of enantiomers
Enantiomers ▪ From the Greek enantio, meaning “opposite” ▪ Stereoisomers in which molecules are not identical to their mirror images ▪ Result whenever a tetrahedral carbon is bonded to four different substituents CHXYZ (one need not be H) ▪ Lactic acid (2-hydroxypropanoic acid) has four different groups (-H, -OH, -CH3 , -CO2H) bonded to the central carbon atoms and exists as a pair of enantiomers Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon
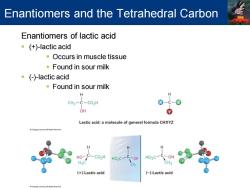
Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon Enantiomers of lactic acid (+)-lactic acid Occurs in muscle tissue Found in sour milk ()-lactic acid ·Found in sour milk H CH2- C-CO2H OH Lactic acid:a molecule of general formula CHXYZ H C02H HO,C- HO2C- (+)-Lactic acid (-)-Lactic acid
Enantiomers of lactic acid ▪ (+)-lactic acid ▪ Occurs in muscle tissue ▪ Found in sour milk ▪ (-)-lactic acid ▪ Found in sour milk Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon
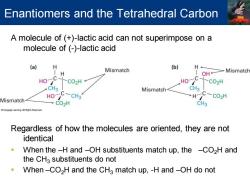
Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon A molecule of (+)-lactic acid can not superimpose on a molecule of (-)-lactic acid (a) Mismatch (b) H H OH Mismatch HO >C02H HO C -CO2H CH3 Mismatch C Mismatch HO-C-CH3 HC-CO2H →C02H CH3 Regardless of how the molecules are oriented,they are not identical When the-H and -OH substituents match up,the -CO2H and the CHa substituents do not When-CO2H and the CH3 match up,-H and-OH do not
A molecule of (+)-lactic acid can not superimpose on a molecule of (-)-lactic acid Regardless of how the molecules are oriented, they are not identical ▪ When the –H and –OH substituents match up, the –CO2H and the CH3 substituents do not ▪ When –CO2H and the CH3 match up, -H and –OH do not Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon

5-2 The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality Chiral -From the Greek cheir meaning "hand" Molecules that are not identical to their mirror images,and thus exist in two enantiomeric forms A molecule is not chiral if it has a plane of symmetry Plane of symmetry A plane that cuts through the middle of an object (or molecule)so that one half of the object is a mirror image of the other half
Chiral ▪ From the Greek cheir meaning “hand” ▪ Molecules that are not identical to their mirror images, and thus exist in two enantiomeric forms ▪ A molecule is not chiral if it has a plane of symmetry Plane of symmetry ▪ A plane that cuts through the middle of an object (or molecule) so that one half of the object is a mirror image of the other half 5-2 The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality
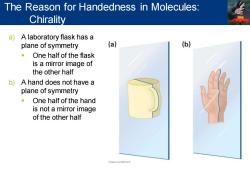
The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality a)A laboratory flask has a plane of symmetry (a) (b) One half of the flask is a mirror image of the other half b)A hand does not have a plane of symmetry One half of the hand is not a mirror image of the other half FORWLEINNAPm
a) A laboratory flask has a plane of symmetry ▪ One half of the flask is a mirror image of the other half b) A hand does not have a plane of symmetry ▪ One half of the hand is not a mirror image of the other half The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality
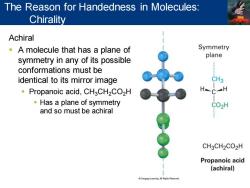
The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality Achiral -A molecule that has a plane of Symmetry plane symmetry in any of its possible conformations must be identical to its mirror image CH3 Propanoic acid,CH3CH2CO2H HC一H Has a plane of symmetry CO2H and so must be achiral CH3CH2CO2H Propanoic acid (achiral) Cengage Leaming.All Fighis Reoerved
Achiral ▪ A molecule that has a plane of symmetry in any of its possible conformations must be identical to its mirror image ▪ Propanoic acid, CH3CH2CO2H ▪ Has a plane of symmetry and so must be achiral The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality
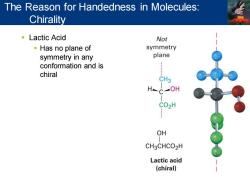
The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality ■Lactic Acid Not Has no plane of symmetry symmetry in any plane conformation and is chiral CH3 OH CO2H OH CH3CHCO2H Lactic acid (chiral)
▪ Lactic Acid ▪ Has no plane of symmetry in any conformation and is chiral The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 04 Organic Compounds - Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 22 Condensations and Alpha Substitutions of Carbonyl Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 11 Structure Determination - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 10 Structure Determination - Mass Spectrometry, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 12 Organohalides - Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 17 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution and Condensation Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 18 Amines and Heterocycles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 19 Biomolecules - Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 20 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 21 Biomolecules - Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 22 Carbohydrate Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 23 Biomolecules - Lipids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 24 Biomolecules - Nucleic Acids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 25 Secondary Metabolites - An Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry.ppt
