《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers

Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 26 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Synthetic Polymers

Introduction A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units. First synthetic polymers: Poly(vinyl chloride)in 1838. ■Polystyrene in1839. Now,250 billion pounds are produced annually,worldwide. Chapter 26 2
Chapter 26 2 Introduction ▪ A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units. ▪ First synthetic polymers: ▪ Poly(vinyl chloride) in 1838. ▪ Polystyrene in 1839. ▪ Now, 250 billion pounds are produced annually, worldwide
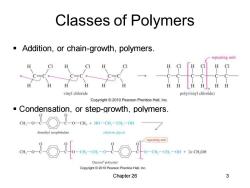
Classes of Polymers Addition,or chain-growth,polymers. repeating unit H CI H H H vinyl chloride poly(vinyl chloride) Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Condensation,or step-growth,polymers. C0o-ct wo cn.on limethyl terephthalate repeating unit 0-CH-CH一OH+2nCH,OH Dacron"polyester Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc. Chapter 26 3
Chapter 26 3 Classes of Polymers ▪ Addition, or chain-growth, polymers. ▪ Condensation, or step-growth, polymers

TABLE 26-1 Some of the Most Important Addition Polymers Polymer Polymer Uses Monomer Formula Polymer Repeating Unit polyethylene hottles.bags,films H,C-CH, 十CH,一CH+ polypropylene plastics,olefin fibers polystyrene plastics.foam insuation -cH,-CH poly(isobutylene) specialired rubbers CH poly(vinylchloride) vinyl plastics.films,water pipe poly(acrylonitrile) Orion",Acrilan"tiber 1-81 poly(methyl a-mcthacrylate) acrylic fibers, Plexiglas Lucite paints CH,- C-OCH poly(methyl a-cyanoacrylate) uper”gho poly(tetrafluoroethylene) +CF-CF士 Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 26 4
Chapter 26 4

Addition Polymers -Three kinds of intermediates: ·Free radicals ·Carbocations Carbanions Examples of addition polymers: Polypropylene plastics Polystyrene foam insulation ·Poly(acrylonitrile),Orlon®fiber -Poly(methyl a-methacrylate),Plexiglas Chapter 26 5
Chapter 26 5 Addition Polymers ▪ Three kinds of intermediates: ▪ Free radicals ▪ Carbocations ▪ Carbanions ▪ Examples of addition polymers: ▪ Polypropylene plastics ▪ Polystyrene foam insulation ▪ Poly(acrylonitrile), Orlon® fiber ▪ Poly(methyl -methacrylate), Plexiglas®
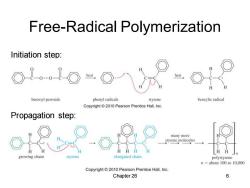
Free-Radical Polymerization Initiation step: O---O兰O benzoyl peroxide phenyl radicals styrene benzylie radical Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Propagation step: many more styrene molecules H HH growing chain styrene elongated chain polystyrene n=about 100 to 10,000 Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 26 6
Chapter 26 6 Free-Radical Polymerization Initiation step: Propagation step:
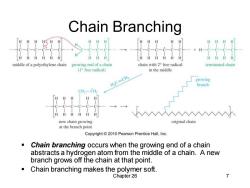
Chain Branching 厘 H 日日H middle of a polyethylene chain growing end of a chain chain with 2 free radical terminated chain (I free radical) in the middle HC=CH2 growing branch CH2-CH, HH H new chain growing original chain at the branch point Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chain branching occurs when the growing end of a chain abstracts a hydrogen atom from the middle of a chain.A new branch grows off the chain at that point. Chain branching makes the polymer soft. Chapter 26 7
Chapter 26 7 Chain Branching ▪ Chain branching occurs when the growing end of a chain abstracts a hydrogen atom from the middle of a chain. A new branch grows off the chain at that point. ▪ Chain branching makes the polymer soft
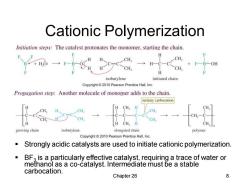
Cationic Polymerization Initiation steps:The catalyst protonates the monomer,starting the chain CH B+H,0: cH,→H-9 OH CH, CH H isobutylene initiated chain Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. tertiary carbocation CH CH CH H CH,H growing chain isobutylene elongated chain Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Strongly acidic catalysts are used to initiate cationic polymerization. ■ BFa is a particularly effective catalyst,requiring a trace of water or methanol as a co-catalyst.Intermediate must be a stable carbocation. Chapter 26 8
Chapter 26 8 Cationic Polymerization ▪ Strongly acidic catalysts are used to initiate cationic polymerization. ▪ BF3 is a particularly effective catalyst, requiring a trace of water or methanol as a co-catalyst. Intermediate must be a stable carbocation
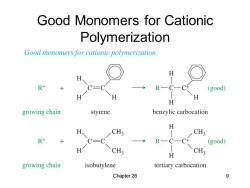
Good Monomers for Cationic Polymerization Good monomers for cationic polymerization H R+ R-C—( (good) H H growing chain styrene benzylic carbocation H H、 CH3 CH3 R+ C-C R一C一C+ (good) CH3 CH3 H growing chain isobutylene tertiary carbocation Chapter 26 9
Chapter 26 9 Good Monomers for Cationic Polymerization

Anionic Polymerization Initiation step:The initiator adds to the monomer to the form an anion. H、 CN CN Bu一C一C: Li butyllithium acrylonitrile stabilized anion Copyright2010 Pearson Prentioe Hall,Inc. Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. T8 CN growing chain acrylonitrile elongated chain Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc. Alkene must have an electron-withdrawing group like C=O, C≡N,orNO2: The reaction is initiated by a Grignard or organolithium reagent. Chapter 26 10
Chapter 26 10 Anionic Polymerization ▪ Alkene must have an electron-withdrawing group like C═O, CN, or NO2 . ▪ The reaction is initiated by a Grignard or organolithium reagent
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 22 Condensations and Alpha Substitutions of Carbonyl Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 21 Part 1 - Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 04 Organic Compounds - Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
