《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination

Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 6 Alkyl Halides:Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 6 Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc
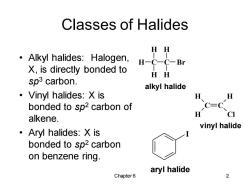
Classes of Halides HH Alkyl halides:Halogen, H-C一C-Br X,is directly bonded to HH sp3 carbon. alkyl halide ·Vinyl halides:Xis H H bonded to sp2 carbon of C=C H CI alkene. vinyl halide ·Aryl halides:Xis bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. aryl halide Chapter 6 2
Chapter 6 2 Classes of Halides • Alkyl halides: Halogen, X, is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. • Vinyl halides: X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. • Aryl halides: X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. C C H H H Cl vinyl halide C H H H C H H Br alkyl halide I aryl halide
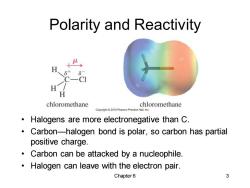
Polarity and Reactivity H 6+ -CI chloromethane chloromethane Halogens are more electronegative than C. Carbon-halogen bond is polar,so carbon has partial positive charge. Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. Halogen can leave with the electron pair. Chapter6 3
Chapter 6 3 Polarity and Reactivity • Halogens are more electronegative than C. • Carbon—halogen bond is polar, so carbon has partial positive charge. • Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. • Halogen can leave with the electron pair
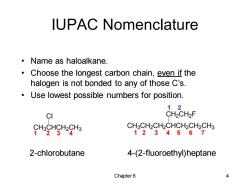
IUPAC Nomenclature 。Name as haloalkane. Choose the longest carbon chain,even if the halogen is not bonded to any of those C's. Use lowest possible numbers for position. 12 CI CH2CH2F HgHgHH CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 1234567 2-chlorobutane 4-(2-fluoroethyl)heptane Chapter6 4
Chapter 6 4 IUPAC Nomenclature • Name as haloalkane. • Choose the longest carbon chain, even if the halogen is not bonded to any of those C’s. • Use lowest possible numbers for position. CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 CH2CH2 F 1 2 3 4 2-chlorobutane 4-(2-fluoroethyl)heptane 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 CH3CHCH2CH3 Cl
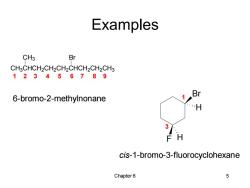
Examples CH3 Br CH3CHCH2CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 123456789 Br 6-bromo-2-methylnonane H 3 F H cis-1-bromo-3-fluorocyclohexane Chapter6 5
Chapter 6 5 Examples CH3CHCH2CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 CH3 Br Br F H H 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6-bromo-2-methylnonane 1 3 cis-1-bromo-3-fluorocyclohexane
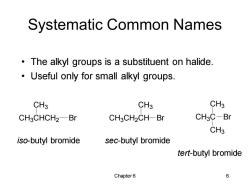
Systematic Common Names The alkyl groups is a substituent on halide. Useful only for small alkyl groups. CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3CHCH2-Br CH3CH2CH-Br CH3C-Br CH3 iso-butyl bromide sec-butyl bromide tert-butyl bromide Chapter 6 6
Chapter 6 6 Systematic Common Names • The alkyl groups is a substituent on halide. • Useful only for small alkyl groups. CH3CHCH2 CH3 Br CH3CH2CH CH3 Br CH3C CH3 Br CH3 iso-butyl bromide sec-butyl bromide tert-butyl bromide

Common Names of Halides 。 CH2X2 called methylene halide. CHX3 is a haloform. 。 CX is carbon tetrahalide. Common halogenated solvents: CH2Cl2 is methylene chloride CHCla is chloroform CCl,is carbon tetrachloride. Chapter6 7
Chapter 6 7 Common Names of Halides • CH2X2 called methylene halide. • CHX3 is a haloform. • CX4 is carbon tetrahalide. • Common halogenated solvents: CH2Cl2 is methylene chloride CHCl3 is chloroform CCl4 is carbon tetrachloride

Alkyl Halides Classification Methyl halides:halide is attached to a methyl group. Primary alkyl halide:carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to only one other carbon. Secondary alkyl halide carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to two other carbons. 。 Tertiary alkyl halide carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to three other carbon. Chapter 6 8
Chapter 6 8 Alkyl Halides Classification • Methyl halides: halide is attached to a methyl group. • Primary alkyl halide: carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to only one other carbon. • Secondary alkyl halide : carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to two other carbons. • Tertiary alkyl halide : carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to three other carbon
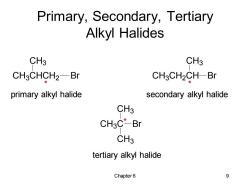
Primary,Secondary,Tertiary Alkyl Halides CH3 CH3 CH3CHCH2-Br CH3CH2CH-Br primary alkyl halide secondary alkyl halide CH3 CH3C*-Br CH3 tertiary alkyl halide Chapter 6 9
Chapter 6 9 primary alkyl halide secondary alkyl halide tertiary alkyl halide Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Alkyl Halides CH3 CHCH2 CH3 Br CH3 CH2 CH CH3 Br CH3 C CH3 Br CH3 * * *

Types of Dihalides 。Geminal dihalide: Br two halogen atoms CH3-CH-Br are bonded to the same carbon. geminal dihalide ·Vicinal dihalide: two halogen atoms Br-CH2CH2-Br are bonded to adjacent carbons. vicinal dihalide Chapter 6 10
Chapter 6 10 Types of Dihalides • Geminal dihalide: two halogen atoms are bonded to the same carbon. • Vicinal dihalide: two halogen atoms are bonded to adjacent carbons. CH3 CH Br Br Br CH2 CH2 Br geminal dihalide vicinal dihalide
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 21 Part 1 - Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 22 Condensations and Alpha Substitutions of Carbonyl Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
