《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds

Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 17 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
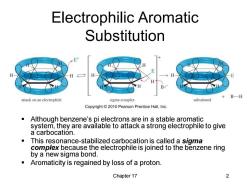
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution E H H B-H attack on an electrophile sigma complex substituted Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Although benzene's pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system,they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give a carbocation. This resonance-stabilized carbocation is called a sigma complex because the electrophile is joined to the benzene ring by a new sigma bond. Aromaticity is regained by loss of a proton. Chapter 17 2
Chapter 17 2 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution ▪ Although benzene’s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give a carbocation. ▪ This resonance-stabilized carbocation is called a sigma complex because the electrophile is joined to the benzene ring by a new sigma bond. ▪ Aromaticity is regained by loss of a proton

Mechanism of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Step 1:Attack on the electrophile forms the sigma complex. H 6 H H E+ H H H sigma complex(arenium ion) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Step 2:Loss of a proton gives the substitution product. H H H H H base: base-H H H H H Copyright @2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 17 3
Chapter 17 3 Mechanism of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
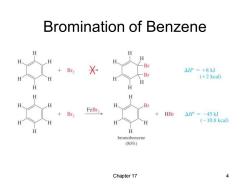
Bromination of Benzene H H H H Br +Br2 △P=+8kJ Br H H (+2 kcal) H H H Br FeBr3> +HBr △HP=-45kJ H H (-10.8kcal) bromobenzene (80%)】 Chapter 17 4
Chapter 17 4 Bromination of Benzene

Mechanism for the Bromination of Benzene:Step 1 :Br--Br:FeBra3→ 十 Br-Br-FeBr3 (stronger electrophile than Br2) Before the electrophilic aromatic substitution can take place,the electrophile must be activated. A strong Lewis acid catalyst,such as FeBra,should be used. Chapter 17 5
Chapter 17 5 Mechanism for the Bromination of Benzene: Step 1 ▪ Before the electrophilic aromatic substitution can take place, the electrophile must be activated. ▪ A strong Lewis acid catalyst, such as FeBr3 , should be used. Br Br FeBr3 Br Br FeBr3 + - (stronger electrophile than Br2)
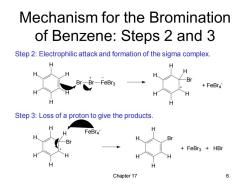
Mechanism for the Bromination of Benzene:Steps 2 and 3 Step 2:Electrophilic attack and formation of the sigma complex. H H -FeBr3 Br FeBr4 H H Step 3:Loss of a proton to give the products. FeBr4 H Br Br FeBr3 +HBr H H H Chapter 17 6
Chapter 17 6 H H H H H H Br Br FeBr3 H H H H H H Br + FeBr4 - H H H H H H Br FeBr4 - Br H H H H H + FeBr3 + HBr Step 2: Electrophilic attack and formation of the sigma complex. Step 3: Loss of a proton to give the products. Mechanism for the Bromination of Benzene: Steps 2 and 3
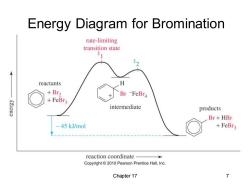
Energy Diagram for Bromination rate-limiting transition state reactants H +Br2 Br -FeBr4 +FeBr3 K3I3u3 intermediate products Br+HBr 45 kJ/mol +FeBr3 reaction coordinate Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 17 7
Chapter 17 7 Energy Diagram for Bromination

Chlorination and lodination Chlorination is similar to bromination. AICla is most often used as catalyst,but FeCla will also work. lodination requires an acidic oxidizing agent,like nitric acid,to produce iodide cation. H+HNO3 +712I*+NO2 H2O Chapter 17 8
Chapter 17 8 Chlorination and Iodination ▪ Chlorination is similar to bromination. AlCl3 is most often used as catalyst, but FeCl3 will also work. ▪ Iodination requires an acidic oxidizing agent, like nitric acid, to produce iodide cation. H + + HNO3 + ½ I2 I + + NO2 + H2O
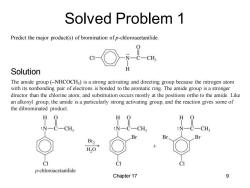
Solved Problem 1 Predict the major product(s)of bromination of p-chloroacetanilide. C-CH Solution The amide group(-NHCOCH3)is a strong activating and directing group because the nitrogen atom with its nonbonding pair ofelectrons is bonded to the aromatic ring.The amide group is a stronger director than the chlorine atom,and substitution occurs mostly at the positions ortho to the amide.Like an alkoxyl group,the amide is a particularly strong activating group,and the reaction gives some of the dibrominated product. H O H :N-C-CH3 :N- CH N C一CH Br2 H2O CI p-chloroacetanilide Chapter 17 9
Chapter 17 9 Predict the major product(s) of bromination of p-chloroacetanilide. The amide group (–NHCOCH3 ) is a strong activating and directing group because the nitrogen atom with its nonbonding pair of electrons is bonded to the aromatic ring. The amide group is a stronger director than the chlorine atom, and substitution occurs mostly at the positions ortho to the amide. Like an alkoxyl group, the amide is a particularly strong activating group, and the reaction gives some of the dibrominated product. Solved Problem 1 Solution
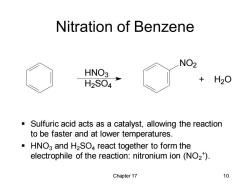
Nitration of Benzene NO2 HNO3 H2S04 H2O Sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst,allowing the reaction to be faster and at lower temperatures. HNO3 and H2SO4 react together to form the electrophile of the reaction:nitronium ion(NO2). Chapter 17 10
Chapter 17 10 Nitration of Benzene ▪ Sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst, allowing the reaction to be faster and at lower temperatures. ▪ HNO3 and H2SO4 react together to form the electrophile of the reaction: nitronium ion (NO2 + ). HNO3 H2 SO4 NO2 + H2 O
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 21 Part 1 - Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 22 Condensations and Alpha Substitutions of Carbonyl Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
