《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes

Organic Chemistry, ORGANIC 8th Edition CHEMISTRY L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 7 Lecture Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Rizalia Klausmeyer Baylor University Waco,TX 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. ALWAYS LEARNING PEARSON
Chapter 7 Lecture Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Rizalia Klausmeyer Baylor University Waco, TX 1

Introduction to Alkenes Alkenes:Hydrocarbons with C=C double bonds. Alkenes are unsaturated. Alkenes also called olefins,meaning "oil-forming gas.” Alkene FG is the reactive C=C double bond. CH; Example: CH,=CH-CH一CH 3-methyl-1-butene 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Introduction to Alkenes • Alkenes: Hydrocarbons with C=C double bonds. • Alkenes are unsaturated. • Alkenes also called olefins, meaning “oil-forming gas.” • Alkene FG is the reactive C=C double bond. © 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 2
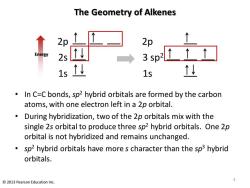
The Geometry of Alkenes 2p 2p Energy 2s 3sp2↑↑↑ 15 1s 型 In C=C bonds,sp2 hybrid orbitals are formed by the carbon atoms,with one electron left in a 2p orbital. During hybridization,two of the 2p orbitals mix with the single 2s orbital to produce three sp2 hybrid orbitals.One 2p orbital is not hybridized and remains unchanged. sp2 hybrid orbitals have more s character than the sp3 hybrid orbitals. 3 2013 Pearson Education Inc
The Geometry of Alkenes • In C=C bonds, sp2 hybrid orbitals are formed by the carbon atoms, with one electron left in a 2p orbital. • During hybridization, two of the 2p orbitals mix with the single 2s orbital to produce three sp2 hybrid orbitals. One 2p orbital is not hybridized and remains unchanged. • sp2 hybrid orbitals have more s character than the sp3 hybrid orbitals. 2p 2s 1s Energy 2p 3 sp2 1s 3 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
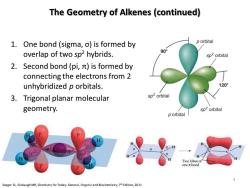
The Geometry of Alkenes(continued) 1.One bond (sigma,o)is formed by p orbital overlap of two sp2 hybrids. 90° sp2orbital 2.Second bond(pi,it)is formed by connecting the electrons from 2 unhybridized p orbitals. 1209 3.Trigonal planar molecular sp2 orbital geometry. sp2 orbital p orbital l H Two lobes of one i bond Seager SL,Slabaugh MR,Chemistry for Today:General,Organic and Biochemistry,7th Edition,2011
The Geometry of Alkenes (continued) 1. One bond (sigma, σ) is formed by overlap of two sp2 hybrids. 2. Second bond (pi, π) is formed by connecting the electrons from 2 unhybridized p orbitals. 3. Trigonal planar molecular geometry. 2p 2s 1s Energy 2p 3 sp2 1s Seager SL, Slabaugh MR, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic and Biochemistry, 7th Edition, 2011 4
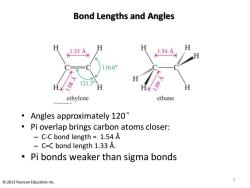
Bond Lengths and Angles H 1.33A 1.54A 116.6° 121.79 ethylene ethane Angles approximately 120 Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer: C-C bond length 1.54 A C=C bond length 1.33 A. Pi bonds weaker than sigma bonds 5 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Bond Lengths and Angles • Angles approximately 120° • Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer: – C-C bond length = 1.54 Å – C=C bond length 1.33 Å. • Pi bonds weaker than sigma bonds 5 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
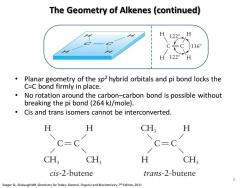
The Geometry of Alkenes(continued) 16 H 122° Planar geometry of the sp2 hybrid orbitals and pi bond locks the C=C bond firmly in place. No rotation around the carbon-carbon bond is possible without breaking the pi bond(264 kJ/mole). Cis and trans isomers cannot be interconverted. H H CH H C=C C=C CH; CH H CH, cis-2-butene trans-2-butene 6 Seager SLSlabaugh MR,Chemistry for Today:General,Organicand Biochemistry,Edition,2011
The Geometry of Alkenes (continued) • Planar geometry of the sp2 hybrid orbitals and pi bond locks the C=C bond firmly in place. • No rotation around the carbon–carbon bond is possible without breaking the pi bond (264 kJ/mole). • Cis and trans isomers cannot be interconverted. Seager SL, Slabaugh MR, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic and Biochemistry, 7th Edition, 2011 6
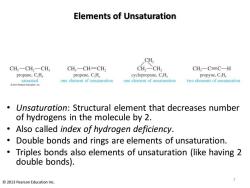
Elements of Unsaturation CH, CH,一CH2一CH CH3一CH=CH CH2-CH, CH,一C=C-H propane,C.H propene,C,H。 cyclopropane,C,H propyne,C.H saturated one element of unsaturation one element of unsaturation two elements of unsaturation 2013 Pearson Education.inc Unsaturation:Structural element that decreases number of hydrogens in the molecule by 2. Also called index of hydrogen deficiency. Double bonds and rings are elements of unsaturation. Triples bonds also elements of unsaturation (like having 2 double bonds). 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Elements of Unsaturation • Unsaturation: Structural element that decreases number of hydrogens in the molecule by 2. • Also called index of hydrogen deficiency. • Double bonds and rings are elements of unsaturation. • Triples bonds also elements of unsaturation (like having 2 double bonds). 7 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

Calculating Unsaturation To calculate number of unsaturations: Find the number of hydrogens the carbons would have if the compounds were saturated(CnH2n+2) Subtract the actual number of hydrogens and divide by 2. This calculation cannot distinguish between unsaturations from multiple bonds and those from rings. 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Calculating Unsaturation To calculate number of unsaturations: • Find the number of hydrogens the carbons would have if the compounds were saturated (CnH2n+2). • Subtract the actual number of hydrogens and divide by 2. • This calculation cannot distinguish between unsaturations from multiple bonds and those from rings. 8 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

Example:Calculate the Unsaturations for a Compound with Formula CsHa. Calculate the number of hydrogen atoms for a saturated compound with five carbons: (2XC)+2 (2×5)+2=12 Now subtract from this number the actual number of hydrogen atoms in the formula and divide by 2: 12-8 =4=2 unsaturations 22 The compound has two unsaturations.They can be two double bonds,two rings,one double bond and one ring, or 1 triple bond. 9 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Example: Calculate the Unsaturations for a Compound with Formula C5H8. • Calculate the number of hydrogen atoms for a saturated compound with five carbons: (2 x C) + 2 (2 x 5) + 2 = 12 • Now subtract from this number the actual number of hydrogen atoms in the formula and divide by 2: 12 – 8 = 4 = 2 unsaturations 2 2 • The compound has two unsaturations. They can be two double bonds, two rings, one double bond and one ring, or 1 triple bond. 9 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
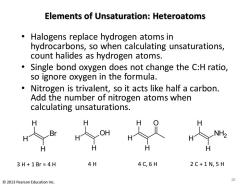
Elements of Unsaturation:Heteroatoms Halogens replace hydrogen atoms in hydrocarbons,so when calculating unsaturations, count halides as hydrogen atoms. Single bond oxygen does not change the C:H ratio, so ignore oxygen in the formula. Nitrogen is trivalent,so it acts like half a carbon. Add the number of nitrogen atoms when calculating unsaturations. H OH NH2 3H+1Br≈4H 4H 4C,6H 2C+1N,5H 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 0
Elements of Unsaturation: Heteroatoms • Halogens replace hydrogen atoms in hydrocarbons, so when calculating unsaturations, count halides as hydrogen atoms. • Single bond oxygen does not change the C:H ratio, so ignore oxygen in the formula. • Nitrogen is trivalent, so it acts like half a carbon. Add the number of nitrogen atoms when calculating unsaturations. 10 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc. H H H Br 3 H + 1 Br ≈ 4 H H H H OH 4 H H O H H 4 C, 6 H H H H NH2 2 C + 1 N, 5 H
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 22 Condensations and Alpha Substitutions of Carbonyl Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 21 Part 1 - Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 04 Organic Compounds - Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 11 Structure Determination - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 10 Structure Determination - Mass Spectrometry, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 12 Organohalides - Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
