《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides

CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 13 Alcohols,Phenols,and Thiols;Ethers and Sulfides EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides

Alcohols,Phenols,and Ethers Alcohols,Phenols,and Ethers Organic derivatives of water in which one or both of the water hydrogens is replaced by an organic group:H-O-H versus R-O-H,Ar-O-H,and R-O-R' Thiols and sulfides Corresponding sulfur analogs,R-S-H and R-S-R
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers ▪ Organic derivatives of water in which one or both of the water hydrogens is replaced by an organic group: H-O-H versus R-O-H, Ar-O-H, and R-O-R’ Thiols and sulfides ▪ Corresponding sulfur analogs, R-S-H and R-S-R’ Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
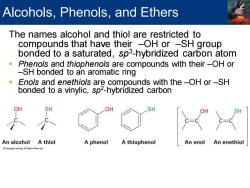
Alcohols,Phenols,and Ethers The names alcohol and thiol are restricted to compounds that have their -OH or -SH group bonded to a saturated,sp3-hybridized carbon atom Phenols and thiophenols are compounds with their-OH or -SH bonded to an aromatic ring 。 Enols and enethiols are compounds with the-OH or-SH bonded to a vinylic,sp2-hybridized carbon OH OH An alcohol A thiol A phenol A thiophenol An enol An enethiol
The names alcohol and thiol are restricted to compounds that have their –OH or –SH group bonded to a saturated, sp3 -hybridized carbon atom ▪ Phenols and thiophenols are compounds with their –OH or –SH bonded to an aromatic ring ▪ Enols and enethiols are compounds with the –OH or –SH bonded to a vinylic, sp2 -hybridized carbon Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers

Alcohols Alcohols occur widely and have many industrial and pharmaceutical applications Methanol is one of the most important of all industrial chemicals Called wood alcohol because historically it was prepared by heating wood in the absence of air Approximately 1.3 billion gallons are manufactured each year in the United States by catalytic reduction of carbon monoxide with hydrogen 400℃ C0+2H2 Zinc oxide/chromia CH3OH catalyst Toxic to humans Industrially used as a solvent and as a starting material for production of formaldehyde(CH2O)and acetic acid(CHCO2H)
Alcohols occur widely and have many industrial and pharmaceutical applications ▪ Methanol is one of the most important of all industrial chemicals ▪ Called wood alcohol because historically it was prepared by heating wood in the absence of air ▪ Approximately 1.3 billion gallons are manufactured each year in the United States by catalytic reduction of carbon monoxide with hydrogen ▪ Toxic to humans ▪ Industrially used as a solvent and as a starting material for production of formaldehyde (CH2O) and acetic acid (CH3CO2H) Alcohols

Alcohols Ethanol was one of the first organic chemicals to be prepared and purified Ethanol production by fermentation of grains and sugars has been carried out for about 9,000 years Its purification by distillation goes back at least as far as the 12th century Today,approximately 4 billion gallons are produced each year in the United States through the fermentation of corn,barley,and sorghum Ethanol for nonbeverage use as a chemical intermediate is obtained by acid-catalyzed hydration of ethylene Approximately 110 million gallons are produced each year in the United States H20 H2C=CH2 H3PO4 CH3CH2OH 250C
▪ Ethanol was one of the first organic chemicals to be prepared and purified ▪ Ethanol production by fermentation of grains and sugars has been carried out for about 9,000 years ▪ Its purification by distillation goes back at least as far as the 12th century ▪ Today, approximately 4 billion gallons are produced each year in the United States through the fermentation of corn, barley, and sorghum ▪ Ethanol for nonbeverage use as a chemical intermediate is obtained by acid-catalyzed hydration of ethylene ▪ Approximately 110 million gallons are produced each year in the United States Alcohols

Phenols Phenols occur widely in living organisms and are intermediates in the industrial synthesis of products as diverse as adhesives and antiseptics Phenols are general disinfectants found in coal tar Methyl salicylate is a flavoring agent found in oil of wintergreen Urushiols are the allergenic constituents of poison oak and poison ivy The word phenol is the name both of a specific compound and of a class of compounds OH OH OH CO2CH3 OH Phenol Methyl salicylate Urushiols (also known as (R different C15 alkyl carbolic acid) and alkenyl chains)
▪ Phenols occur widely in living organisms and are intermediates in the industrial synthesis of products as diverse as adhesives and antiseptics ▪ Phenols are general disinfectants found in coal tar ▪ Methyl salicylate is a flavoring agent found in oil of wintergreen ▪ Urushiols are the allergenic constituents of poison oak and poison ivy ▪ The word phenol is the name both of a specific compound and of a class of compounds Phenols
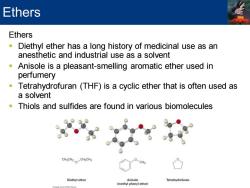
Ethers Ethers Diethyl ether has a long history of medicinal use as an anesthetic and industrial use as a solvent Anisole is a pleasant-smelling aromatic ether used in perfumery Tetrahydrofuran (THF)is a cyclic ether that is often used as a solvent Thiols and sulfides are found in various biomolecules CHaCH2CHaCHa CH Diethyl ether Anisole Tetrahydrofuran (methyl phenyl ether)
Ethers ▪ Diethyl ether has a long history of medicinal use as an anesthetic and industrial use as a solvent ▪ Anisole is a pleasant-smelling aromatic ether used in perfumery ▪ Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a cyclic ether that is often used as a solvent ▪ Thiols and sulfides are found in various biomolecules Ethers
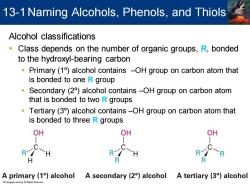
13-1 Naming Alcohols,Phenols,and Thiols Alcohol classifications Class depends on the number of organic groups,R,bonded to the hydroxyl-bearing carbon Primary(1)alcohol contains -OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to one R group Secondary (2)alcohol contains -OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to two R groups Tertiary(3)alcohol contains-OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to three R groups OH OH OH R -H R -R H R A primary(1)alcohol A secondary(2)alcohol A tertiary (3)alcohol
Alcohol classifications ▪ Class depends on the number of organic groups, R, bonded to the hydroxyl-bearing carbon ▪ Primary (1º) alcohol contains –OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to one R group ▪ Secondary (2º) alcohol contains –OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to two R groups ▪ Tertiary (3º) alcohol contains –OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to three R groups 13-1Naming Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols

Naming Alcohols,Phenols,and Thiols Simple alcohols are named in the IUPAC system as derivatives of the parent alkane,using the suffix -o/: Rule 1 Select the longest carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group,and derive the parent name by replacing the -e ending of the corresponding alkane with -o/ The -e is deleted to prevent the occurrence of two adjacent vowels Rule 2 Number the alkane chain beginning at the end nearer the hydroxyl group
Simple alcohols are named in the IUPAC system as derivatives of the parent alkane, using the suffix –ol: Rule 1 Select the longest carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group, and derive the parent name by replacing the –e ending of the corresponding alkane with –ol ▪ The –e is deleted to prevent the occurrence of two adjacent vowels Rule 2 Number the alkane chain beginning at the end nearer the hydroxyl group Naming Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols
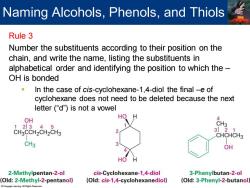
Naming Alcohols,Phenols,and Thiols Rule 3 Number the substituents according to their position on the chain,and write the name,listing the substituents in alphabetical order and identifying the position to which the- OH is bonded In the case of cis-cyclohexane-1,4-diol the final -e of cyclohexane does not need to be deleted because the next letter ("d")is not a vowel OH 4 123 4 CH3 CH3CCH2CH2CH3 321 CHCHCH3 CH3 OH HO 2-Methylpentan-2-ol cis-Cyclohexane-1,4-diol 3-Phenylbutan-2-ol Old:2-Methyl-2-pentanol) (Old:cis-1,4-cyclohexanediol) (Old:3-Phenyl-2-butanol
Rule 3 Number the substituents according to their position on the chain, and write the name, listing the substituents in alphabetical order and identifying the position to which the – OH is bonded ▪ In the case of cis-cyclohexane-1,4-diol the final –e of cyclohexane does not need to be deleted because the next letter (“d”) is not a vowel Naming Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 12 Organohalides - Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 10 Structure Determination - Mass Spectrometry, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 11 Structure Determination - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 04 Organic Compounds - Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 17 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution and Condensation Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 18 Amines and Heterocycles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 19 Biomolecules - Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 20 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 21 Biomolecules - Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 22 Carbohydrate Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 23 Biomolecules - Lipids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 24 Biomolecules - Nucleic Acids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 25 Secondary Metabolites - An Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 26 Orbitals and Organic Chemistry - Pericyclic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 27 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 03 Alkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 04 Rates & Kinetics.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides.pdf
