《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 26 Orbitals and Organic Chemistry - Pericyclic Reactions

CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 26 Orbitals and Organic Chemistry: Pericyclic Reactions H IRD EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological applications
CHAPTER 26 Orbitals and Organic Chemistry: Pericyclic Reactions

Pericyclic Reactions -What Are They? Pericyclic reaction All bonding changes occur simultaneously through a cyclic transition state The combination of steps is called a concerted process; no intermediates are involved Why this chapter? Understanding of pericyclic reactions emerged in the latter half of the twentieth century Some biological pathways proceed through pericyclic reactions
Pericyclic reaction • All bonding changes occur simultaneously through a cyclic transition state • The combination of steps is called a concerted process; no intermediates are involved Why this chapter? • Understanding of pericyclic reactions emerged in the latter half of the twentieth century • Some biological pathways proceed through pericyclic reactions Pericyclic Reactions – What Are They?
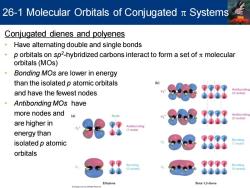
26-1 Molecular Orbitals of Conjugated Systems Conjugated dienes and polyenes Have alternating double and single bonds 。 p orbitals on sp2-hybridized carbons interact to form a set of molecular orbitals(MOs) 。 Bonding MOs are lower in energy than the isolated p atomic orbitals b Antibonding and have the fewest nodes 3 nodes ·Antibonding MOs have more nodes and (a) Antibonding 2 nodes) are higher in Antibonding (1 node) energy than isolated p atomic orbitals Bonding Bonding 0 nodes (0 nodes Ethylene Buta-1,3-diene
Conjugated dienes and polyenes • Have alternating double and single bonds • p orbitals on sp2 -hybridized carbons interact to form a set of p molecular orbitals (MOs) • Bonding MOs are lower in energy than the isolated p atomic orbitals and have the fewest nodes • Antibonding MOs have more nodes and are higher in energy than isolated p atomic orbitals 26-1 Molecular Orbitals of Conjugated p Systems

1,3,5-Hexatriene MO description for 1,3,5-Hexatriene -Three double bonds and six MOs -Only bonding orbitals,,w2,and wa,are filled in the ground state -On irradiation with ultraviolet light an electron is promoted from highest-energy filled orbital (y3)to the lowest-energy unfilled orbital (* Va and are each half-filled .This is the first (lowest energy)excited state
MO description for 1,3,5-Hexatriene •Three double bonds and six p MOs •Only bonding orbitals, ψ1 , ψ2 , and ψ3 , are filled in the ground state •On irradiation with ultraviolet light an electron is promoted from highest-energy filled orbital (ψ3 ) to the lowest-energy unfilled orbital (ψ4 *) •ψ3 and ψ4 * are each half-filled •This is the first (lowest energy) excited state 1,3,5-Hexatriene
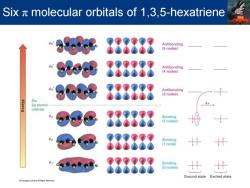
Six x molecular orbitals of 1,3,5-hexatriene 888888 Antibonding (5 nodes) 888888 Antibonding (4 nodes) 888888 Antibonding (3 nodes) Six 2p atomic orbitals Bonding (2 nodes) 888 Bonding 888888 Bonding (0 nodes 计 Ground state Excited state
Six π molecular orbitals of 1,3,5-hexatriene

Molecular Orbitals and Pericyclic Reactions Woodward-Hoffmann Rules for Pericyclic Reactions -Reaction can occur only if the symmetries of the reactant MOs are the same as the symmetries of the product MOs The lobes of reactant MOs must be of the correct algebraic sign for bonding to occur in the transition state leading to product If the symmetries of reactant and product orbitals correlate,the reaction is symmetry-allowed.Reactions conditions are relatively mild If the symmetries of the reactant and product orbitals do not correlate,the reaction is symmetry-disallowed and there are no low energy concerted paths Fukui's Simplification Frontier Orbitals -Consider only the frontier orbitals-the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)
Woodward-Hoffmann Rules for Pericyclic Reactions •Reaction can occur only if the symmetries of the reactant MOs are the same as the symmetries of the product MOs • The lobes of reactant MOs must be of the correct algebraic sign for bonding to occur in the transition state leading to product • If the symmetries of reactant and product orbitals correlate, the reaction is symmetry-allowed. Reactions conditions are relatively mild • If the symmetries of the reactant and product orbitals do not correlate, the reaction is symmetry-disallowed and there are no low energy concerted paths Fukui’s Simplification – Frontier Orbitals •Consider only the frontier orbitals – the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) Molecular Orbitals and Pericyclic Reactions

Worked Example 26.1 Predicting HOMO and LUMO Molecular Orbitals a)How many n MOs does 1,3,5,7-octatetraene have? b)What is the designation of its ground-state HOMO? c)What is the designation of its ground-state LUMO?
Worked Example 26.1 Predicting HOMO and LUMO Molecular Orbitals a) How many p MOs does 1,3,5,7-octatetraene have? b) What is the designation of its ground-state HOMO? c) What is the designation of its ground-state LUMO?

Worked Example 26.1 Predicting HOMO and LUMO Molecular Orbitals Strategy a)Two MOs result from the interaction of two atomic orbitals,a bonding MO and an antibonding MO. Therefore,the number of n MOs formed is equal to the number of p atomic orbitals that interact to form them b)Beginning with v,assign two electrons to each MO in order of increasing in energy and designate the highest occupied molecular orbital.There are eight x electrons derived from eight p atomic orbitals c)The LUMO is the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital that is the next highest-energy MO above the HOMO
Worked Example 26.1 Predicting HOMO and LUMO Molecular Orbitals Strategy a) Two MOs result from the interaction of two atomic orbitals, a bonding MO and an antibonding MO. Therefore, the number of p MOs formed is equal to the number of p atomic orbitals that interact to form them b) Beginning with ψ1 ,assign two electrons to each p MO in order of increasing in energy and designate the highest occupied molecular orbital. There are eight p electrons derived from eight p atomic orbitals c) The LUMO is the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital that is the next highest-energy MO above the HOMO

Worked Example 26.1 Predicting HOMO and LUMO Molecular Orbitals Solution a)Eight n molecular orbitals b)Ψ4 c)Ψ5
Worked Example 26.1 Predicting HOMO and LUMO Molecular Orbitals Solution a) Eight p molecular orbitals b) ψ4 c) ψ5
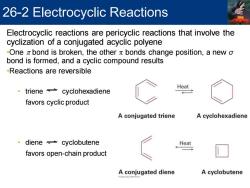
26-2 Electrocyclic Reactions Electrocyclic reactions are pericyclic reactions that involve the cyclization of a conjugated acyclic polyene -One z bond is broken,the other x bonds change position,a new o bond is formed,and a cyclic compound results -Reactions are reversible Heat triene cyclohexadiene favors cyclic product A conjugated triene A cyclohexadiene ·diene≠cyclobutene Heat favors open-chain product A conjugated diene A cyclobutene
Electrocyclic reactions are pericyclic reactions that involve the cyclization of a conjugated acyclic polyene •One p bond is broken, the other p bonds change position, a new σ bond is formed, and a cyclic compound results •Reactions are reversible • triene cyclohexadiene favors cyclic product • diene cyclobutene favors open-chain product 26-2 Electrocyclic Reactions
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 25 Secondary Metabolites - An Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 24 Biomolecules - Nucleic Acids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 23 Biomolecules - Lipids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 22 Carbohydrate Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 21 Biomolecules - Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 20 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 19 Biomolecules - Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 18 Amines and Heterocycles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 17 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution and Condensation Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 12 Organohalides - Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 10 Structure Determination - Mass Spectrometry, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 11 Structure Determination - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 27 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 03 Alkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 04 Rates & Kinetics.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 09 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 10 Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance(NMR)Spectroscopy.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 14 Ethers and Epoxides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 19 Amines.pdf
