《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 12 Organohalides - Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations

CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER12 Organohalides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Organic Chemistry with Biological applications
CHAPTER12 Organohalides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations

Alkyl Halides Alkyl halide or haloalkanes Compounds with a halogen atom bonded to a saturated sp3- hybridized carbon atom Widespread in nature Chloromethane is released in large amounts by ocean kelp,as well as by forest fires and volcanoes Vast array of industrial applications Use as inhaled anesthetics,refrigerants,pesticides,and solvents F Br H C三 F-C-C-H CI-C-F H-C-Br CI F CI CI H Trichloroethylene Halothane Dichlorodifluoromethane Bromomethane (a solvent) (an inhaled anesthetic) (a refrigerant) (a fumigant) Leang All Rights Reaorved
Alkyl halide or haloalkanes ▪ Compounds with a halogen atom bonded to a saturated sp3 - hybridized carbon atom ▪ Widespread in nature ▪ Chloromethane is released in large amounts by ocean kelp, as well as by forest fires and volcanoes ▪ Vast array of industrial applications ▪ Use as inhaled anesthetics, refrigerants, pesticides, and solvents Alkyl Halides
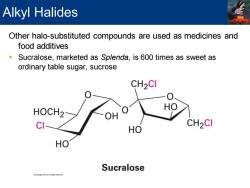
Alkyl Halides Other halo-substituted compounds are used as medicines and food additives Sucralose,marketed as Splenda,is 600 times as sweet as ordinary table sugar,sucrose CH2CI HOCH2 CI CH2CI HO HO Sucralose
Other halo-substituted compounds are used as medicines and food additives ▪ Sucralose, marketed as Splenda, is 600 times as sweet as ordinary table sugar, sucrose Alkyl Halides

Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are not often involved in the biochemical pathways of terrestrial organisms The kinds of reactions they undergo-nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations -are frequently involved Alkyl halide chemistry acts as a relatively simple model for many mechanistically similar but structurally more complex reactions found in biomolecules
Alkyl halides are not often involved in the biochemical pathways of terrestrial organisms ▪ The kinds of reactions they undergo – nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations – are frequently involved ▪ Alkyl halide chemistry acts as a relatively simple model for many mechanistically similar but structurally more complex reactions found in biomolecules Alkyl Halides

12-1 Naming Alkyl Halides Haloalkanes 0 Commonly called alkyl halides 。 The halogen is treated as a substituent on a parent alkane chain Alkyl halides can be named by following three steps: Step 1 Find the longest chain,and name it as the parent 。 If a double or triple bond is present,it must be included in the parent chain
Haloalkanes • Commonly called alkyl halides • The halogen is treated as a substituent on a parent alkane chain Alkyl halides can be named by following three steps: Step 1 Find the longest chain, and name it as the parent • If a double or triple bond is present, it must be included in the parent chain 12-1 Naming Alkyl Halides

Naming Alkyl Halides Step 2 Number the carbons of the parent chain beginning at the end nearer the first substituent,whether alkyl or halo Assign each substituent a number according to its position on the chain CH3 Br Br CH3 CH3CHCH2CHCHCH2CH3 CH3CHCH2CHCHCH2CH3 1°231456 7 1231 1456 CH3 CH3 5-Bromo-2,4-dimethylheptane 2-Bromo-4,5-dimethylheptane If different halogens are present,number all and list them in alphabetical order when writing the name
Step 2 Number the carbons of the parent chain beginning at the end nearer the first substituent, whether alkyl or halo • Assign each substituent a number according to its position on the chain If different halogens are present, number all and list them in alphabetical order when writing the name Naming Alkyl Halides
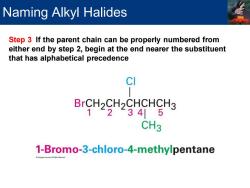
Naming Alkyl Halides Step 3 If the parent chain can be properly numbered from either end by step 2,begin at the end nearer the substituent that has alphabetical precedence CI BrCH2CH2CHCHCH3 1234|5 CH3 1-Bromo-3-chloro-4-methylpentane
Step 3 If the parent chain can be properly numbered from either end by step 2, begin at the end nearer the substituent that has alphabetical precedence Naming Alkyl Halides

Naming Alkyl Halides Many simple alkyl halides are also named by identifying first the alkyl group and then the halogen CH3l can either be called iodomethane or methyl iodide B CI CH3I CH3CHCH3 Iodomethane 2-Chloropropane Bromocyclohexane (or methyl iodide) (or isopropyl chloride) (or cyclohexyl bromide) Names shown in parentheses will not be used in this textbook
Many simple alkyl halides are also named by identifying first the alkyl group and then the halogen ▪ CH3 I can either be called iodomethane or methyl iodide ▪ Names shown in parentheses will not be used in this textbook Naming Alkyl Halides
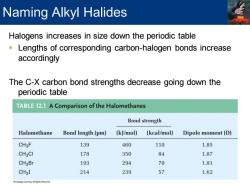
Naming Alkyl Halides Halogens increases in size down the periodic table Lengths of corresponding carbon-halogen bonds increase accordingly The C-X carbon bond strengths decrease going down the periodic table TABLE 12.1 A Comparison of the Halomethanes Bond strength Halomethane Bond length(pm) (kJ/mol) (kcal/mol) Dipole moment(D) CH3F 139 460 110 1.85 CH3CI 178 350 84 1.87 CH3Br 193 294 70 1.81 CH3I 214 239 57 1.62
Halogens increases in size down the periodic table ▪ Lengths of corresponding carbon-halogen bonds increase accordingly The C-X carbon bond strengths decrease going down the periodic table Naming Alkyl Halides

Naming Alkyl Halides The carbon-halogen bond of alkyl halides is polarized with the carbon atom bearing a slight positive charge(8+)and the halogen a slight negative charge(8-) The alkyl halide C-X carbon atom behaves as an electrophile in polar reactions Electrophilic carbon
The carbon-halogen bond of alkyl halides is polarized with the carbon atom bearing a slight positive charge (d+) and the halogen a slight negative charge (d-) ▪ The alkyl halide C-X carbon atom behaves as an electrophile in polar reactions Naming Alkyl Halides
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 10 Structure Determination - Mass Spectrometry, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 11 Structure Determination - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 04 Organic Compounds - Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 17 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution and Condensation Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 18 Amines and Heterocycles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 19 Biomolecules - Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 20 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 21 Biomolecules - Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 22 Carbohydrate Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 23 Biomolecules - Lipids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 24 Biomolecules - Nucleic Acids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 25 Secondary Metabolites - An Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 26 Orbitals and Organic Chemistry - Pericyclic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 27 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 03 Alkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 04 Rates & Kinetics.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.pdf
