《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding

CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 1 Structure and Bonding EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 1 Structure and Bonding

Scientific Revolution Scientific revolution leads to: Safer and more effective medicines Cures for genetic diseases ■Increased life span Improved quality of life Scientific advances in medicine and biology require an understanding of organic chemistry
Scientific revolution leads to: ▪ Safer and more effective medicines ▪ Cures for genetic diseases ▪ Increased life span ▪ Improved quality of life Scientific advances in medicine and biology require an understanding of organic chemistry Scientific Revolution

Organic Chemistry Organic and Biological Chemistry in Modern Medicine 。 Coronary artery disease(CAD)is directly correlated with blood cholesterol levels 75%of blood cholesterol (1000 mg each day)is biosynthesized Drugs known as Statins reduce the risk of CAD by lowering blood cholesterol levels 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A(HMG-CoA)to mevalonate conversion Crucial step in biosynthesis of cholesterol Atorvastatin(Lipitor)inactivates enzyme that catalyzes HMG-CoA to vevalonate conversion
Organic and Biological Chemistry in Modern Medicine ▪ Coronary artery disease (CAD) is directly correlated with blood cholesterol levels ▪ 75% of blood cholesterol (1000 mg each day) is biosynthesized ▪ Drugs known as Statins reduce the risk of CAD by lowering blood cholesterol levels ▪ 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) to mevalonate conversion ▪ Crucial step in biosynthesis of cholesterol ▪ Atorvastatin (Lipitor) inactivates enzyme that catalyzes HMG-CoA to vevalonate conversion Organic Chemistry
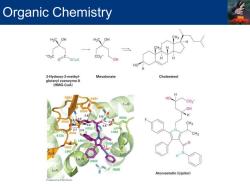
Organic Chemistry H3C OH H3C OH 02C C02 0 SCoA OH HO 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl- Mevalonate Cholesterol glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) HO C02 OH H CH3 7 K739 L967 508 Atorvastatin(Lipitor)
Organic Chemistry

Carbon Organic chemistry -All organic compounds contain the element carbon 4A element Shares four electrons Forms four strong covalent bonds Bonds to other carbons to create chains and rings Not all carbon compounds are derived from living organisms -Over 99%of 37 million known compounds contain carbon
Organic chemistry ▪ All organic compounds contain the element carbon ▪ 4A element ▪ Shares four electrons ▪ Forms four strong covalent bonds ▪ Bonds to other carbons to create chains and rings ▪ Not all carbon compounds are derived from living organisms ▪ Over 99% of 37 million known compounds contain carbon Carbon
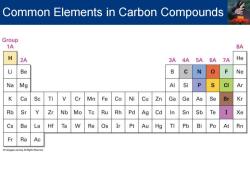
Common Elements in Carbon Compounds Group 1A 8A H 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A He Li Be B N Ne Na Mg AI Si P CI Ar K Ca Sc Ti Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Xe Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg TI Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ra Ac
Common Elements in Carbon Compounds
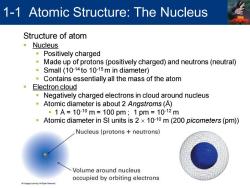
1-1 Atomic Structure:The Nucleus Structure of atom ·Nucleus ·Positively charged Made up of protons(positively charged)and neutrons(neutral) 意 Small (10-14to 10-15m in diameter) Contains essentially all the mass of the atom Electron cloud Negatively charged electrons in cloud around nucleus Atomic diameter is about 2 Angstroms(A) 。1A=1010m=100pm;1pm=1012m Atomic diameter in SI units is 2 x 10-10 m(200 picometers(pm)) Nucleus(protons neutrons) Volume around nucleus occupied by orbiting electrons
Structure of atom ▪ Nucleus ▪ Positively charged ▪ Made up of protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) ▪ Small (10-14 to 10-15 m in diameter) ▪ Contains essentially all the mass of the atom ▪ Electron cloud ▪ Negatively charged electrons in cloud around nucleus ▪ Atomic diameter is about 2 Angstroms (Å) ▪ 1 Å = 10-10 m = 100 pm ; 1 pm = 10-12 m ▪ Atomic diameter in SI units is 2 10-10 m (200 picometers (pm)) 1-1 Atomic Structure: The Nucleus

Atomic Structure:The Nucleus Atomic number (Z) Number of protons in the atom's nucleus All atoms of a given element have the same atomic number Mass number (A) Number of protons plus neutrons in the atom's nucleus Isotopes Atoms of the same element (same Z)that have different Numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers(different A) Atomic mass (atomic weight) -Weighted average mass in atomic mass units (amu)of an element's naturally occurring isotopes
Atomic number (Z) ▪ Number of protons in the atom's nucleus ▪ All atoms of a given element have the same atomic number Mass number (A) ▪ Number of protons plus neutrons in the atom’s nucleus Isotopes ▪ Atoms of the same element (same Z) that have different Numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers (different A) Atomic mass (atomic weight) ▪ Weighted average mass in atomic mass units (amu) of an element’s naturally occurring isotopes Atomic Structure: The Nucleus

1-2 Atomic Structure:Orbitals Quantum Mechanical Model Behavior of a specific electron in an atom described by mathematical expression called a wave equation Wave equation is similar to mathematical expression used to describe motion of waves in fluids -Solution of wave equation is called a wave function -Wave function is an orbital Orbital denoted by Greek letter psi, Plot of 2 describes volume of space around nucleus that the electron is most likely to occupy Electron cloud has no sharp boundary
Quantum Mechanical Model ▪ Behavior of a specific electron in an atom described by mathematical expression called a wave equation ▪ Wave equation is similar to mathematical expression used to describe motion of waves in fluids ▪ Solution of wave equation is called a wave function ▪ Wave function is an orbital ▪ Orbital denoted by Greek letter psi, ▪ Plot of 2 describes volume of space around nucleus that the electron is most likely to occupy ▪ Electron cloud has no sharp boundary 1-2 Atomic Structure: Orbitals
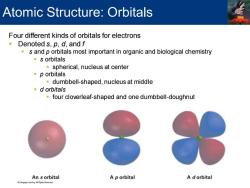
Atomic Structure:Orbitals Four different kinds of orbitals for electrons Denoted s,p,d,and f s and p orbitals most important in organic and biological chemistry s orbitals spherical,nucleus at center p orbitals dumbbell-shaped,nucleus at middle d orbitals four cloverleaf-shaped and one dumbbell-doughnut An s orbital A p orbital A dorbital
Four different kinds of orbitals for electrons ▪ Denoted s, p, d, and f ▪ s and p orbitals most important in organic and biological chemistry ▪ s orbitals ▪ spherical, nucleus at center ▪ p orbitals ▪ dumbbell-shaped, nucleus at middle ▪ d orbitals ▪ four cloverleaf-shaped and one dumbbell-doughnut Atomic Structure: Orbitals
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 22 Condensations and Alpha Substitutions of Carbonyl Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 21 Part 1 - Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 04 Organic Compounds - Cycloalkanes and Their Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 07 Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 11 Structure Determination - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 10 Structure Determination - Mass Spectrometry, Infrared Spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 12 Organohalides - Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols; Ethers and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 17 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution and Condensation Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 18 Amines and Heterocycles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 19 Biomolecules - Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 20 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 21 Biomolecules - Carbohydrates.ppt
