《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes
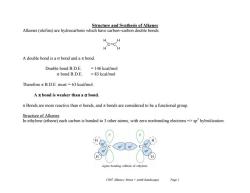
Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Alkenes(olefins)are hydrocarbons which have carbon-carbon double bonds H H =C H- H A double bond is a o bond and a nt bond. Double bond B.D.E. =146 kcal/mol o bond B.D.E. =83 kcal/mol Therefore n B.D.E.must =63 kcal/mol. A n bond is weaker than a o bond. Bonds are more reactive than o bonds,and r bonds are considered to be a functional group. Structure of Alkenes In ethylene(ethene)each carbon is bonded to 3 other atoms,with zero nonbonding electrons=>sp'hybridization. sigma bonding orbitals of ethylene Ch07 Alkenes:Struct +synth (landscape) Page I
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 1 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Alkenes (olefins) are hydrocarbons which have carbon–carbon double bonds. A double bond is a bond and a bond. Double bond B.D.E. = 146 kcal/mol bond B.D.E. = 83 kcal/mol Therefore B.D.E. must = 63 kcal/mol. A bond is weaker than a bond. Bonds are more reactive than bonds, and bonds are considered to be a functional group. Structure of Alkenes In ethylene (ethene) each carbon is bonded to 3 other atoms, with zero nonbonding electrons => sp2 hybridization
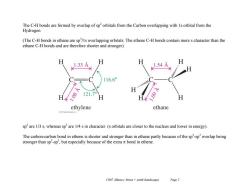
The C-H bonds are formed by overlap of sp'orbitals from the Carbon overlapping with 1s orbital from the Hydrogen. (The C-H bonds in ethane are sp/ls overlapping orbitals.The ethene C-H bonds contain more s character than the ethane C-H bonds and are therefore shorter and stronger). 1.33A H H 1.54A 116.6° 121.7 H ethylene ethane sp'are 1/3 s,whereas sp'are 1/4 s in character.(s orbitals are closer to the nucleus and lower in energy). The carbon-carbon bond in ethene is shorter and stronger than in ethane partly because of the sp'-sp overlap being stronger than sp'-sp',but especially because of the extra it bond in ethene. Ch07 Alkenes:Struct synth (landscape) Page 2
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 2 The C-H bonds are formed by overlap of sp2 orbitals from the Carbon overlapping with 1s orbital from the Hydrogen. (The C-H bonds in ethane are sp3 /1s overlapping orbitals. The ethene C-H bonds contain more s character than the ethane C-H bonds and are therefore shorter and stronger). sp 2 are 1/3 s, whereas sp3 are 1/4 s in character. (s orbitals are closer to the nucleus and lower in energy). The carbon-carbon bond in ethene is shorter and stronger than in ethane partly because of the sp 2 -sp 2 overlap being stronger than sp3 -sp 3 , but especially because of the extra bond in ethene
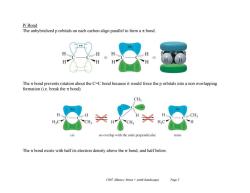
Pi Bond The unhybridized p orbitals on each carbon align parallel to form a nt bond. The n bond prevents rotation about the C-C bond because it would force the p orbitals into a non overlapping formation (i.e.break the nt bond). CH H CH3 CH CH no overlap with the ends perpendicular ran The nt bond exists with half its electron density above the o bond,and half below. Ch07 Alkenes:Struct +synth (landscape) Page3
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 3 Pi Bond The unhybridized p orbitals on each carbon align parallel to form a bond. The bond prevents rotation about the C=C bond because it would force the p orbitals into a non overlapping formation (i.e. break the bond). The bond exists with half its electron density above the bond, and half below

Elements of Unsaturation Alkanes are said to be saturated since they have they maximum number of bonds to hydrogen. An alkene is unsaturated. Any t system or a ring system reduces the maximum number of hydrogens a molecule can have. An element of unsaturation relates to 2 missing hydrogens from the saturated formula(C.H2+2). Consider alkane,alkenes,alkynes and cycles: CH,一CH2一CH CH,一CH=CH propane,C.H propene,C.H saturated one element of unsaturation CH2 CH2-CH2 CH,一C=C一H cyclopropane,C.H propyne,CH one element of unsaturation two elements of unsaturation Ch07 Alkenes:Struct synth (landscape) Page4
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 4 Elements of Unsaturation Alkanes are said to be saturated since they have they maximum number of bonds to hydrogen. An alkene is unsaturated. Any system or a ring system reduces the maximum number of hydrogens a molecule can have. An element of unsaturation relates to 2 missing hydrogens from the saturated formula (CnH2n+2). Consider alkane, alkenes, alkynes and cycles:

(Heteroatom complications Heteroatoms are considered anything other than C or H. Halogens These simply substitute for hydrogens in the molecular formula. Therefore just like C2H6 is saturated,so is C2HF2. Oxygen CH3-CH3 is saturated(C2H) CH-O-CH is also saturated(C2HO) An oxygen can be added without requiring any additional hydrogens,so ignore the number of oxygens when calculating elements of Unsaturation. Nitrogen Nitrogen is trivalent,and when it replaces a C in a chain it requires only one hydrogen (-NH-vs.-CH2-),so nitrogens count as half a carbon Thus C.HoN is equivalent to CasHo.(i.e.one element of Unsaturation).) Ch07 Alkenes:Struct synth (landscape) Page 5
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 5 (Heteroatom complications Heteroatoms are considered anything other than C or H. Halogens These simply substitute for hydrogens in the molecular formula. Therefore just like C2H6 is saturated, so is C2H4F2. Oxygen CH3-CH3 is saturated (C2H6) CH3-O-CH3 is also saturated (C2H6O) An oxygen can be added without requiring any additional hydrogens, so ignore the number of oxygens when calculating elements of Unsaturation. Nitrogen Nitrogen is trivalent, and when it replaces a C in a chain it requires only one hydrogen (-NH- vs. -CH2- ), so nitrogens count as half a carbon. Thus C4H9N is equivalent to C4.5H9. (i.e. one element of Unsaturation).)

Nomenclature of Alkenes Simple alkenes are named like alkanes (root from the longest carbon chain),but the-ane suffix is replaced by-ene. CH,-CH CH,=CH一CH IUPAC names: ethene propene cyclohexene Common names: ethylene propylene 每03 son Eaurtin ire When the chain is longer than 3 carbons,number the atoms such that the double bond is given the lowest number (i.e.start at the end nearest the double bond). CH2=CH-CH,-CH: CH,-CH-CH,-CH,-CH old IUPAC names: 1-butene 1-pentene new IUPAC names: but-l-ene pent-l-ene 3 CH,一CH=CH一CH3CH3一CH=CH一CH2一CH old IUPAC names: 2-butene 2-pentene new IUPAC names: but-2-ene pent-2-ene Ch07 Alkenes:Struct synth (landscape) Page 6
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 6 Nomenclature of Alkenes Simple alkenes are named like alkanes (root from the longest carbon chain), but the –ane suffix is replaced by-ene. When the chain is longer than 3 carbons, number the atoms such that the double bond is given the lowest number (i.e. start at the end nearest the double bond)

Compounds with 2 double bonds are called dienes,3 double bonds are trienes,etc. CH2=CH一CH一CH CH:-CH-CH-CH-CH-CH-CH, old IUPAC names 1.3-butadiene 1.3.5-heptatriene 1.3.5.7-cyclooctatetraene new IUPAC names: buta-1,3-diene hepta-1.3.5-triene cycloocta-1,3.5.7-tetraene For branches,each alkyl group is given a number,but the double bond is still given preference when numbering the chain. 2 CH;-CH-C-CH3 CH;-CH-CH-CH2 CH:-CH-C-CHz-CH2-CH-CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH 2-methyl-2-butene 3-mcthyl-1-butene 3.6-dimethyl-2-heptene 2-methylbut-2-ene 3-methylbut-1-ene 3.6-dimethylhept-2-ene CH CH3 1-methylcyclopentene 2-ethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene 7-bromo-1.3.5-cycloheptatriene 3-propyl-1-heptene 1-methylcyclopentene 2-ethylcyclohexa-1,3-diene 7-bromocyclohepta-1,3,5-triene 3-propylhept-1-ene 2013 Pearson Education.ind Ch07 Alkenes:Struct synth (landscape) Page 7
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 7 Compounds with 2 double bonds are called dienes, 3 double bonds are trienes, etc. For branches, each alkyl group is given a number, but the double bond is still given preference when numbering the chain

When alkenes are substituents,they are termed alkenyl groups,and may be named systematically CH2 多-Hc-&=cH methylene 2-propenyl group group (allyl group) Geometric isomers The rigidity of a it bond gives rise to geometric isomers. When similar groups(not H's)are bound to the same side of the double bond the alkene is said to be cis. When similar groups are bound to opposite side of the double bond it is said to be trans. H H H CH2CH3 CH2CH3 trans-pent-2-ene cis-pent-2-ene Cycloalkenes must have or more carbons before they are large enough to incorporate a trans double bond. cyclohexene trans-cyclodecene Therefore cycloalkenes are deemed to be cis unless specified otherwise. Ch07 Alkenes:Struct synth (landscape) Page 8
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 8 When alkenes are substituents, they are termed alkenyl groups, and may be named systematically. Geometric isomers The rigidity of a bond gives rise to geometric isomers. When similar groups (not H’s) are bound to the same side of the double bond the alkene is said to be cis. When similar groups are bound to opposite side of the double bond it is said to be trans. Cycloalkenes must have 8 or more carbons before they are large enough to incorporate a trans double bond. Therefore cycloalkenes are deemed to be cis unless specified otherwise. CH2 H2C H C CH2 methylene group 2-propenyl group (allyl group) cyclohexene trans-cyclodecene
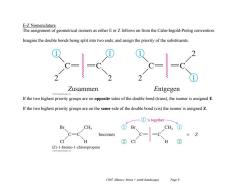
E-Z Nomenclature The assignment of geometrical isomers as either E or Z follows on from the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention Imagine the double bonds being split into two ends,and assign the priority of the substituents Zusammen Entgegen If the two highest priority groups are on opposite sides of the double bond(trans),the isomer is assigned E. If the two highest priority groups are on the same side of the double bond(cis)the isomer is assigned Z. ①'s together Br CH; ①D Br CH C=C becomes Z CI ② ② (Z)-1-bromo-1-chloropropene Ch07 Alkenes:Struct +synth (landscape) Page 9
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 9 E-Z Nomenclature The assignment of geometrical isomers as either E or Z follows on from the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention. Imagine the double bonds being split into two ends, and assign the priority of the substituents. If the two highest priority groups are on opposite sides of the double bond (trans), the isomer is assigned E. If the two highest priority groups are on the same side of the double bond (cis) the isomer is assigned Z

If there is more than one double bond,then the stereochemistry around each double bond must be specified. Br 3 2 A 6 8 (32,5E)-3-bromoocta-3,5-diene Ch07 Alkenes:Struct synth (landscape) Page 10
Ch07 Alkenes; Struct + synth (landscape) Page 10 If there is more than one double bond, then the stereochemistry around each double bond must be specified
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 04 Rates & Kinetics.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 03 Alkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 27 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 26 Orbitals and Organic Chemistry - Pericyclic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 25 Secondary Metabolites - An Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 24 Biomolecules - Nucleic Acids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 23 Biomolecules - Lipids and Their Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 22 Carbohydrate Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 21 Biomolecules - Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 20 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 19 Biomolecules - Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 18 Amines and Heterocycles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 17 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution and Condensation Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3th Edition, John McMurry, 2016)Chapter 14 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Additions Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 09 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 10 Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance(NMR)Spectroscopy.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 14 Ethers and Epoxides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 19 Amines.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)CHM 201 Introduction and Review - Structure and Bonding.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alcohols-structure and synthesis 2.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkenes Overview.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkenes Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkyl Halides from Alcohols.ppt
