《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives
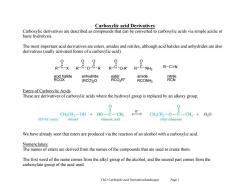
Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are esters,amides and nitriles,although acid halides and anhydrides are also derivatives(really activated forms of a carboxylic acid). 0 R-C-X R-C-O-C-R R-C-O-R' R-C-NH2 R-C=N Rooxalide anhydride (RCO)O 882R amide RCONH2 R心9 Esters of Carboxylic Acids These are derivatives of carboxylic acids where the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group. H CHCH一OH+HO C-CH CHCH,-0-C-CH+HO IUPAC name: ethanol ethanoic acid cthyl ethanoate We have already seen that esters are produced via the reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid. Nomenclature The names of esters are derived from the names of the compounds that are used to create them. The first word of the name comes from the alkyl group of the alcohol,and the second part comes from the carboxylate group of the acid used. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page I
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 1 Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are esters, amides and nitriles, although acid halides and anhydrides are also derivatives (really activated forms of a carboxylic acid). Esters of Carboxylic Acids These are derivatives of carboxylic acids where the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group. We have already seen that esters are produced via the reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid. Nomenclature The names of esters are derived from the names of the compounds that are used to create them. The first word of the name comes from the alkyl group of the alcohol, and the second part comes from the carboxylate group of the acid used. R C X O R C O O R C O-R' O R C NH2 O C O R R C N acid halide RCOX anhydride (RCO)2O ester RCO2R" amide RCONH2 nitrile RCN
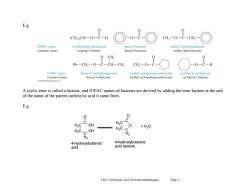
E.g. (CH)2CH-O一C-H CH,-OC-CH2 IUPAC name: 1-methylethyl methanoate phenyl benzoate methyl 2-phenylethanoate common name isopropyl formate phenyl benzoate methyl phenylacetate 0 CH Ph一CH2一O一C一CH一CH CH一O -0-C-H IUPAC name: benzyl 2-methylpropanoate methyl cyclopentanecarboxylate cyclohexyl methanoate common name: benzyl isobutyrate methyl cyclopentanecarboxylate cyclohexyl formate A cyclic ester is called a lactone,and IUPAC names of lactones are derived by adding the term lactone at the end of the name of the parent carboxylic acid it came from. E.g. Hc-C OH HC-C H2C-C +H2O H2C. C-OH 4-hydroxybutanoic 4-hydroxybutanoic acid acid lactone Ch21 Carboxylie acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 2
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 2 E.g. A cyclic ester is called a lactone, and IUPAC names of lactones are derived by adding the term lactone at the end of the name of the parent carboxylic acid it came from. E.g. H2C H2C C H2 OH OH C O H2C H2C C H2 O C O + H2O 4-hydroxybutanoic acid 4-hydroxybutanoic acid lactone
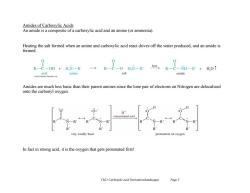
Amides of Carboxylic Acids An amide is a composite of a carboxylic acid and an amine (or ammonia). Heating the salt formed when an amine and carboxylic acid react drives off the water produced,and an amide is formed. 0 R-C-OH H,N-R C一OHN-R hetR-C-NH一R+H,OT amine salt amide Amides are much less basic than their parent amines since the lone pair of electrons on Nitrogen are delocalized onto the carbonyl oxygen. H+ concentrated acid very weakly basic protonation on oxyger In fact in strong acid,it is the oxygen that gets protonated first! Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 3
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 3 Amides of Carboxylic Acids An amide is a composite of a carboxylic acid and an amine (or ammonia). Heating the salt formed when an amine and carboxylic acid react drives off the water produced, and an amide is formed. Amides are much less basic than their parent amines since the lone pair of electrons on Nitrogen are delocalized onto the carbonyl oxygen. In fact in strong acid, it is the oxygen that gets protonated first!
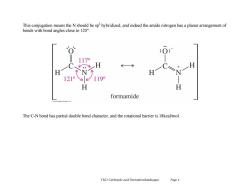
This conjugation means the N should be sp'hybridized,and indeed the amide nitrogen has a planar arrangement of bonds with bond angles close to 120. 117 .,H H 121° 119° H formamide The C-N bond has partial double bond character,and the rotational barrier is 18kcal/mol. Ch21 Carboxylie acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 4
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 4 This conjugation means the N should be sp2 hybridized, and indeed the amide nitrogen has a planar arrangement of bonds with bond angles close to 120°. The C-N bond has partial double bond character, and the rotational barrier is 18kcal/mol
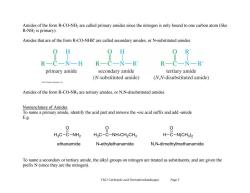
Amides of the form R-CO-NH2 are called primary amides since the nitrogen is only bound to one carbon atom(like R-NH2 is primary). Amides that are of the form R-CO-NHR'are called secondary amides.or N-substituted amides. H R-C-N-R RC-NR primary amide secondary amide tertiary amide (N-substituted amide) (N.N-disubstituted amide) 13Pen En re Amides of the form R-CO-NR2 are tertiary amides,or N,N-disubstituted amides Nomenclature of Amides To name a primary amide,identify the acid part and remove the-oic acid suffix and add-amide E.g. 0 H3C-C-NH2 HgC-C-NH-CH2CH3 H-C-N(CH3)2 ethanamide N-ethylethanamide N.,N-dimethylmethanamide To name a secondary or tertiary amide,the alkyl groups on nitrogen are treated as substituents,and are given the prefix N(since they are the nitrogen). Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 5
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 5 Amides of the form R-CO-NH2 are called primary amides since the nitrogen is only bound to one carbon atom (like R-NH2 is primary). Amides that are of the form R-CO-NHR' are called secondary amides, or N-substituted amides. Amides of the form R-CO-NR2 are tertiary amides, or N,N-disubstituted amides. Nomenclature of Amides To name a primary amide, identify the acid part and remove the -oic acid suffix and add -amide E.g. To name a secondary or tertiary amide, the alkyl groups on nitrogen are treated as substituents, and are given the prefix N (since they are the nitrogen)

Cyclic amides are known as Lactams Lactams are produced from amino acids,where the amino and the carboxylic acid groups react together to form an amide linkage. 0 heat OH N-H 4-aminobutanoic acid 4-aminobutanoic acid lactam They are named by adding the word lactam to the correct IUPAC name of the parent acid. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 6
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 6 Cyclic amides are known as Lactams. Lactams are produced from amino acids, where the amino and the carboxylic acid groups react together to form an amide linkage. 4-aminobutanoic acid 4-aminobutanoic acid lactam They are named by adding the word lactam to the correct IUPAC name of the parent acid. H2N C OH O N C O H +H2O heat
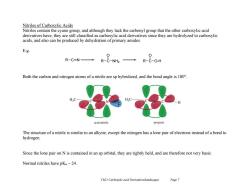
Nitriles of Carboxylic Acids Nitriles contain the cyano group,and although they lack the carbonyl group that the other carboxylic acid derivatives have,they are still classified as carboxylic acid derivatives since they are hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids,and also can be produced by dehydration of primary amides. E.g. 0 R-CN→ R-C-NH2 →R-&-OH Both the carbon and nitrogen atoms of a nitrile are sp hybridized,and the bond angle is 180. H.C acetonitrile propyne The structure of a nitrile is similar to an alkyne,except the nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons instead of a bond to hydrogen. Since the lone pair on N is contained in an sp orbital,they are tightly held,and are therefore not very basic. Normal nitriles have pKb~24. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 7
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 7 Nitriles of Carboxylic Acids Nitriles contain the cyano group, and although they lack the carbonyl group that the other carboxylic acid derivatives have, they are still classified as carboxylic acid derivatives since they are hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids, and also can be produced by dehydration of primary amides. E.g. Both the carbon and nitrogen atoms of a nitrile are sp hybridized, and the bond angle is 180°. The structure of a nitrile is similar to an alkyne, except the nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons instead of a bond to hydrogen. Since the lone pair on N is contained in an sp orbital, they are tightly held, and are therefore not very basic. Normal nitriles have pKb ~ 24. R C N R C O NH2 R C O O-H

Nomenclature IUPAC requires nitriles to be named based on the alkane name,with the suffix -nitrile added. E.g. OCH3 H3C-C=N HgC-C-CH2CH2CH2-C=N ethanenitrile H 5-methoxyhexanenitrile Acid Halides Acid(or acyl)halides are activated derivatives of carboxylic acids,and are often used to prepare the other carboxylic acid derivatives. The most common examples of this class are acid chlorides,but acid fluorides,bromides and iodides do exist(but are rarely used). R halogen R R C -Br an acid halide acid chloride acid bromide (acyl halide) (acyl chloride) (acyl bromide) The halogen atom inductively withdraws electron density away from the already electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 8
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 8 Nomenclature IUPAC requires nitriles to be named based on the alkane name, with the suffix -nitrile added. E.g. Acid Halides Acid (or acyl) halides are activated derivatives of carboxylic acids, and are often used to prepare the other carboxylic acid derivatives. The most common examples of this class are acid chlorides, but acid fluorides, bromides and iodides do exist (but are rarely used). The halogen atom inductively withdraws electron density away from the already electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group. H3C C N ethanenitrile 5-methoxyhexanenitrile H3C C OCH3 H CH2CH2CH2 C N
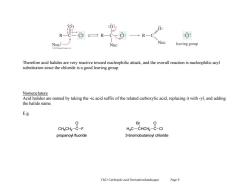
R一C R-Ca :C Nuc: Nuc Nuc leaving group Therefore acid halides are very reactive toward nucleophilic attack,and the overall reaction is nucleophilic acyl substitution since the chloride is a good leaving group. Nomenclature Acid halides are named by taking the-ic acid suffix of the related carboxylic acid,replacing it with-yl,and adding the halide name. E.g. 0 Br CHgCH2-C-F H C-CHCH-C-CI propanoyl fluoride 3-bromobutanoyl chloride Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 9
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 9 Therefore acid halides are very reactive toward nucleophilic attack, and the overall reaction is nucleophilic acyl substitution since the chloride is a good leaving group. Nomenclature Acid halides are named by taking the -ic acid suffix of the related carboxylic acid, replacing it with -yl, and adding the halide name. E.g. CH3CH2 C O F CHCH2 C O Cl Br H3C propanoyl fluoride 3-bromobutanoyl chloride
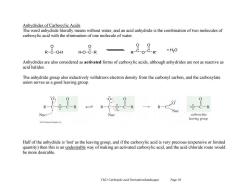
Anhydrides of Carboxylic Acids The word anhydride literally means without water,and an acid anhydride is the combination of two molecules of carboxylic acid with the elimination of one molecule of water 0 0 R-C-O-H H-O-C-R R C-O-C-R' +H2O Anhydrides are also considered as activated forms of carboxylic acids,although anhydrides are not as reactive as acid halides The anhydride group also inductively withdraws electron density from the carbonyl carbon,and the carboxylate anion serves as a good leaving group. RCO Q-C-R R-C :0-C-R Nuc: carboxylate leaving group Half of the anhydride is'lost'as the leaving group,and if the carboxylic acid is very precious(expensive or limited quantity)then this is an undesirable way of making an activated carboxylic acid,and the acid chloride route would be more desirable. Ch21 Carboxylie acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 10
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 10 Anhydrides of Carboxylic Acids The word anhydride literally means without water, and an acid anhydride is the combination of two molecules of carboxylic acid with the elimination of one molecule of water. Anhydrides are also considered as activated forms of carboxylic acids, although anhydrides are not as reactive as acid halides. The anhydride group also inductively withdraws electron density from the carbonyl carbon, and the carboxylate anion serves as a good leaving group. Half of the anhydride is 'lost' as the leaving group, and if the carboxylic acid is very precious (expensive or limited quantity) then this is an undesirable way of making an activated carboxylic acid, and the acid chloride route would be more desirable. R C O O-H C R O H-O R C O O C O R' + H2O
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 19 Amines.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 14 Ethers and Epoxides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance(NMR)Spectroscopy.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 10 Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 09 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 04 Rates & Kinetics.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 03 Alkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(Organic Chemistry, Alex Jonathan Roche lecture notes Rutgers The State University NJ, wade 8th)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)CHM 201 Introduction and Review - Structure and Bonding.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alcohols-structure and synthesis 2.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkenes Overview.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkenes Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkyl Halides from Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkynes McMurry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Benzene and Aromaticity(2011).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Carboxylic Acids Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Conformational Analysis.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Conjugated Dienes and U.V. Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Enols and Enolates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Ethers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Functional Groups.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Infrared(IR)spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Mass Spectrometry.ppt
