重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 呼吸系统症状和体征
营庆医科大学脑床半院藏案讲满 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称诊断学 年级2005 授课专业临床医学 教师陈虹 职称副教授授课方式 大课 学时2 题目章节呼吸系统常见症状和体征 教材名称《诊断学(双语)》 作者吕卓人雷寒 出版社科学出版社 版次第一版 Toget familiar with consolidation and its examining method 目的 sion and s examining method h signs and their examining pulmonary emphysema and pneumothorax Clinic manifestation of pneumothorax 难 The different signs of emphysema,pneumothorax and pleura effusion 1 The definitions of COPD 教学重点 Clinic manifestation of pleura effusion 3 The signs of pulmonary emphysema,pneumothorax,and pleura effusion 整领 English 教学 方法 Power point,pictures and forms 手段 1.kumark&clark clinical medicine 2.Davidson imtemal medicine 制表时间:2005年8月 1
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2005 年 8 月 1 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称 诊断学 年级 2005 授课专业 临床医学 教 师 陈虹 职称 副教授 授课方式 大课 学时 2 题目章节 呼吸系统常见症状和体征 教材名称 《诊断学(双语)》 作者 吕卓人 雷寒 出 版 社 科学出版社 版次 第一版 教 学 目 的 要 求 To get familiar with consolidation and its examining method To master the signs of pleural effusion and its examining method To be familiar with signs and their examining pulmonary emphysema and pneumothorax. 教 学 难 点 1 Clinic manifestation of pneumothorax 2 The different signs of emphysema, pneumothorax and pleura effusion 教 学 重 点 1 The definitions of COPD 2 Clinic manifestation of pleura effusion 3 The signs of pulmonary emphysema, pneumothorax, and pleura effusion 外语 要求 English 教学 方法 手段 Power point, pictures and forms 参考 资料 1.kumark& clark clinical medicine 2. Davidson imternal medicine 教研 室意 见

重庆医科大半脑床半院载未讲满 讲稿 时间分配 Symptoms and signs of some respiratory diseases 1.Lobar Pneumonia 10分钟 Lobar pneumonia is defined as an infection of lung parenchyma with a obar distribution of consolidation. Its pathological changes could be divided into three stages,which include ongestion,consolidation and resolution. Symptoms Young adults with motivation,sudden onset. Chills,high fever,chest pain,cough,rusty sputum. signs Face of acute ill and fever,dyspnea,herpes labialis Inspection:decrease of respiratory movement Palpation:increase of vocal fremitus,trachea in middle position Percussion:dullness Auscultation:bronchial breath sound,pleural friction rub,rales 2.Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease(COPD) 10分钟 COPD has been defined as a disease characterized by the presence of airflow limitation,which is partially reversible and generally progressive. The exact cause of COPD still remains unclear,but mostly is associated with abnormally pulmonary inflammatory response to the harmful gases or articles. Symptoms Chronic productivecough. whitish mucoid frothy sputum,yellowish sputum when complicated with infection. short of breath or dyspnea,wheezing,dyspnea with exertion. signs Inspection:barrel chest,decrease of respiratory movement Palpation:decrease of vocal fremitus. Percussion:bilateral hyperresonance 制表时间:2005年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2005 年 8 月 2 讲 稿 时间分配 Symptoms and signs of some respiratory diseases 1. Lobar Pneumonia Lobar pneumonia is defined as an infection of lung parenchyma with a lobar distribution of consolidation. Its pathological changes could be divided into three stages, which include congestion, consolidation and resolution. Symptoms Young adults with motivation, sudden onset. Chills, high fever, chest pain, cough, rusty sputum. signs Face of acute ill and fever, dyspnea, herpes labialis Inspection: decrease of respiratory movement Palpation: increase of vocal fremitus, trachea in middle position Percussion: dullness Auscultation: bronchial breath sound, pleural friction rub, rales. 2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) COPD has been defined as a disease characterized by the presence of airflow limitation, which is partially reversible and generally progressive. The exact cause of COPD still remains unclear, but mostly is associated with abnormally pulmonary inflammatory response to the harmful gases or particles. Symptoms Chronic productive cough, whitish mucoid frothy sputum, yellowish sputum when complicated with infection. short of breath or dyspnea, wheezing, dyspnea with exertion. signs Inspection: barrel chest, decrease of respiratory movement Palpation: decrease of vocal fremitus. Percussion: bilateral hyperresonance 10 分钟 10 分钟
露庆医科大半脑床半院藏来讲满 Auscultation:decrease of breath soundsand diffused rhonchiand rales 3.bronchial asthma Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airway in10 which many cells and cellular components play a role.in particular mast cells. eosinophils,T-lymphocytes,neutrophils,epithelial cells and so forth.This chronic inflammation causes airway hyperresponsiveness and recurent episodes of wheezing.breathlessness,chest tightness,and cough,particularly at night and/or in the early momning.These symptoms are usually associated with widespread but variable airway limitation that is reversible either spontaneously or with treatment. Symptoms Childhood or adolescence onset,recurrent attacks and seasonality. Contact of allergen,allergic rhinitis Chest tightness,expiratory dyspnea with wheezing Remission spontaneously or with treatment. Signs Inspection:expiratory dyspnea,forced sitting position,accessory respiratory muscle use,sweating.cyanosis,chest hyperinflation. Palpation:decrease of respiratory movement and fremitus Percussion:hyperresonant note Auscultation:diffused rhonchi 4.pleural effusion Pleural effusion is defined as the abnormal accumulation of fluid within 15分钟 the pleural space.It may be caused by an either excess fluid production or decreased absorption,which are associated with increased pleural capillaries hydrostatic pressure or decreased oncotic pressure or increased pleural capillaries permeability. The character of pleural fluid can be divided into exudates and transudate. Symptoms The symptoms are not obvious when the fluid is less than 300ml Dry cough,pleuritic chest pain,the pain will be palliated when the fluid ncrease short breath and chest tightness when the fluid is over 500ml 制表时间:2005年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2005 年 8 月 3 Auscultation: decrease of breath sounds and diffused rhonchi and rales 3.bronchial asthma Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airway in which many cells and cellular components play a role, in particular mast cells, eosinophils, T-lymphocytes, neutrophils, epithelial cells and so forth. This chronic inflammation causes airway hyperresponsiveness and recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and cough, particularly at night and/or in the early morning. These symptoms are usually associated with widespread but variable airway limitation that is reversible either spontaneously or with treatment. Symptoms Childhood or adolescence onset, recurrent attacks and seasonality. Contact of allergen, allergic rhinitis Chest tightness, expiratory dyspnea with wheezing Remission spontaneously or with treatment. Signs Inspection: expiratory dyspnea, forced sitting position, accessory respiratory muscle use, sweating, cyanosis, chest hyperinflation. Palpation: decrease of respiratory movement and fremitus. Percussion: hyperresonant note Auscultation: diffused rhonchi. 4.pleural effusion Pleural effusion is defined as the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the pleural space. It may be caused by an either excess fluid production or decreased absorption, which are associated with increased pleural capillaries hydrostatic pressure or decreased oncotic pressure or increased pleural capillaries permeability. The character of pleural fluid can be divided into exudates and transudate. Symptoms The symptoms are not obvious when the fluid is less than 300ml Dry cough, pleuritic chest pain, the pain will be palliated when the fluid increase short breath and chest tightness when the fluid is over 500ml 10 分钟 15 分钟

重庆医科大半脑床半院载未讲满 dyspnea and cyanosis when the fluid is large symptoms of the basic disease Signs Usually there is no signs if the fluid is<500ml Middle to large fluid Inspection:restriction of the respiratory movement on the affected side, bulging intercostals margins Palpation:Shift of apex beat and trachea to the uninvolved side Absent tactile fremitus over effusion Percussion:dullness on the effusion area Auscultation:Decreased or absent breath sounds over the effusion. Bronchial breath sounds could be heard above the pleural effusion. Pleural rub could be heard in dry or fibrinous pleurisy. 5.pneumothorax 15分钟 Air in the pleural space Can be classified as follows according to the causative factors: spontaneous pneumothorax:COPD,pulmonary tuberculosis artificial pneumothorax traumatic pneumothorax Classified clinically as follows according to the pleural hole: closed pneumothorax open pneumothorax tension pneumothorax Symptoms motivation(strenuous exertion) Sudden onset with unilateral pleuritic pain and dyspnea.The degree of dyspnea varies according to the size of the pneumothorax and the lung's nealthy condition Small closed pneumothorax with a good basic lung function,the initia dyspnea is slight and will improve after a few hours Large tension pneumothorax will produce sever dyspnea and ever espiratory or circulatory failure 制表时间:2005年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2005 年 8 月 4 dyspnea and cyanosis when the fluid is large. symptoms of the basic disease. Signs Usually there is no signs if the fluid is <500ml Middle to large fluid Inspection: restriction of the respiratory movement on the affected side, bulging intercostals margins Palpation: Shift of apex beat and trachea to the uninvolved side. Absent tactile fremitus over effusion Percussion: dullness on the effusion area Auscultation:Decreased or absent breath sounds over the effusion. Bronchial breath sounds could be heard above the pleural effusion. Pleural rub could be heard in dry or fibrinous pleurisy. 5.pneumothorax Air in the pleural space Can be classified as follows according to the causative factors: spontaneous pneumothorax: COPD, pulmonary tuberculosis artificial pneumothorax traumatic pneumothorax Classified clinically as follows according to the pleural hole: closed pneumothorax open pneumothorax tension pneumothorax. Symptoms motivation (strenuous exertion) Sudden onset with unilateral pleuritic pain and dyspnea. The degree of dyspnea varies according to the size of the pneumothorax and the lung’s healthy condition Small closed pneumothorax with a good basic lung function, the initial dyspnea is slight and will improve after a few hours. Large tension pneumothorax will produce sever dyspnea and even respiratory or circulatory failure 15 分钟
君庆医科大学脑床半院表来讲测 Sign No obvious signs if pneumothorax is small Large pneumothorax: Inspection:the affected thoracic is full and the respiratory movement is restricted. Palpation:tracheal and apex beat deviation,vocal fremitus diminished or disappeared Percus ion:hyper-resonance on percussion Auscultation:diminution of breath sounds. 6.Atelectasis Loss of alveolar volume,usually occurred in respiratory disease 15分钟 Obstructive atelectasis. foreign body,neoplasm,sputum plug.endobronchial tuberculosis Non-obstructive atelectasis: Compressive,e.g.pneumothorax,pleural effusion Symptoms: varies according to the extent and degree of atelectasis. dyspnea,cough,toxic symptom associated with secondary infection. Signs: Inspection:retraction of the involved side and the respiratory movement is estricted. Palpation:heart and tracheal shift to the affected side,vocal fremitus is decreased,but increased in compressed atelectasis Percussion:dullness on percussion. Auscultation:diminution of breath sounds on the involved side,bronchial breath sounds could be heard on the compressive atelectasis. 7.Summary Differential diagnosis of common pulmonary and pleural diseases: 5分钟 制表时间:2005年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2005 年 8 月 5 Sign No obvious signs if pneumothorax is small Large pneumothorax: Inspection: the affected thoracic is full and the respiratory movement is restricted. Palpation: tracheal and apex beat deviation, vocal fremitus diminished or disappeared. Percussion: hyper-resonance on percussion Auscultation: diminution of breath sounds. 6. Atelectasis Loss of alveolar volume, usually occurred in respiratory disease. Obstructive atelectasis: foreign body, neoplasm, sputum plug, endobronchial tuberculosis Non-obstructive atelectasis : Compressive , e.g. pneumothorax, pleural effusion Symptoms: varies according to the extent and degree of atelectasis. dyspnea, cough, toxic symptom associated with secondary infection. Signs: Inspection: retraction of the involved side and the respiratory movement is restricted. Palpation: heart and tracheal shift to the affected side, vocal fremitus is decreased, but increased in compressed atelectasis Percussion: dullness on percussion. Auscultation: diminution of breath sounds on the involved side, bronchial breath sounds could be heard on the compressive atelectasis. 7.Summary Differential diagnosis of common pulmonary and pleural diseases: 15 分钟 5 分钟
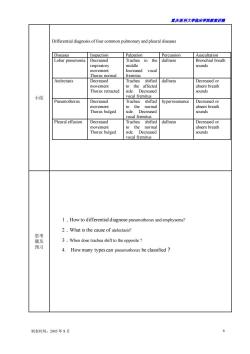
露庆医科大半脑床半院教未讲满 ifferential diagnosis of four common pulmonary and pleural diseases Palpation Percussion Auscultation Lobar pneumonia Decreased Trachea in the dullness Bronchial breath middle sounds vocal Thorax normal fremitus Atelectasis Decreased Irachea shifted dullness 小结 vocal fremitus Decreased hyperresonance e Thorax bulged ide cal fremitus eural effusion the Thorax bulged side Decreased sounds vocal fremitus 1.How to differential diagnose pneumothorax and emphysema? 2.What is the cause of atelectasis? 3.When dose trachea shift to the opposite? 预习 4.How many typescan pneumothorax be classified 制表时间:2005年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2005 年 8 月 6 小结 Differential diagnosis of four common pulmonary and pleural diseases Diseases Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation Lobar pneumonia Decreased respiratory movement Thorax normal Trachea in the middle Increased vocal fremitus dullness Bronchial breath sounds Atelectasis Decreased movement Thorax retracted Trachea shifted to the affected side. Decreased vocal fremitus dullness Decreased or absent breath sounds Pneumothorax Decreased movement Thorax bulged Trachea shifted to the normal side. Decreased vocal fremitus hyperresonance Decreased or absent breath sounds Pleural effusion Decreased movement Thorax bulged Trachea shifted to the normal side. Decreased vocal fremitus dullness Decreased or absent breath sounds 思考 题及 预习 1.How to differential diagnose pneumothorax and emphysema? 2.What is the cause of atelectasis? 3.When dose trachea shift to the opposite ? 4. How many types can pneumothorax be classified?
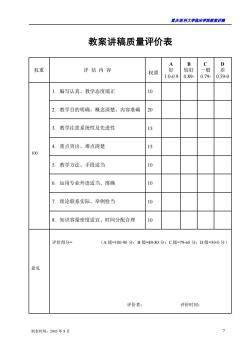
君庆医科大学临床半院表来讲满 教案讲稿质量评价表 D 权重 评估内容 权重 较好 一般 1.0-0.9 0.89 0.79 0.59-0 编写认真、教学态度端正 10 2. 教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 20 3. 教学注意系统性及先进性 15 4. 重点突出、难点清楚 15 100 教学方法、手段适当 0 6.运用专业外语适当、准确 10 理论联系实际、举例恰当 o 8.知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 评价得分 (A级=100-90分:B级=89-80分:C级=79-60分:D级=59-0分) 意见 评价者: 评价时间: 制表时间:2005年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2005 年 8 月 7 教案讲稿质量评价表 权重 评 估 内 容 权重 A 好 1.0-0.9 B 较好 0.89- C 一般 0.79- D 差 0.59-0 100 1. 编写认真、教学态度端正 10 2. 教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 20 3. 教学注意系统性及先进性 15 4. 重点突出、难点清楚 15 5. 教学方法、手段适当 10 6. 运用专业外语适当、准确 10 7. 理论联系实际、举例恰当 10 8. 知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 10 意见 评价得分= (A 级=100-90 分;B 级=89-80 分;C 级=79-60 分;D 级=59-0 分) 评价者: 评价时间:
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 心脏检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 心电图.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 腹泻.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 腹痛.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 黄疸.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 水肿.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 绪论与问诊.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 腹部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 病历与诊断.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 呕血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 便血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八讲 脑脊液常规及生殖系统检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七讲 大便常规、免疫学检查及心肌标志物检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六讲 肾功能检查(主讲:唐敏).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四讲 血栓与出血检查(主讲:胥文春).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三讲 骨髓细胞学检查、血型与输血.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一讲 总论及血液一般检查(上).ppt
- 上海科学技术出版社:《实验诊断学——彩色图谱》书籍PDF电子版(主编:张丽霞、陈金宝).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程复习题集(无答案).doc
- 《实验诊断学》课程实验指导书 laboatoty diagnosis(共九章,含练习及答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 循环系统主要症状与体征.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 超声心动图检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 血管检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 发热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 胸部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 呼吸困难.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 咳嗽、咳痰.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 咯血.doc
- 医学临床本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis.doc
- 医学临床本科《影像诊断学》课程教学大纲 medical imaging(包含MRI部分).doc
- 医学影像本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲(Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学资源(讲稿,共五章).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 MRI总论.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.1 3.2 正常及异常.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.3 支气管扩张及肺部炎症.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.4 肺结核.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.5 肺肿瘤.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.6 纵膈疾病.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 循环系统(冠脉及主动脉).ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 消化系统和腹膜腔 5.2 急腹症.ppt
