重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 心脏检查
置庆医科大学脑床学院讲满 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称诊断学 年级2005 授课专业临床医学 教师雷寒 职称教授 授课方式口大课示教学时5 题目章节心脏检查 教材名称诊断学(双语) 作者吕卓人雷寒 出版社 科学出版社 版次 第一版 掌握心脏检查的内容和方法,常见体征改变的鉴别和临床意义。 求 心脏听诊的内容,鉴别和临床意义。 The r rub may be the contents of auscultation 点 教学重点 心脏扣诊和心脏听诊。 The emphasis may be put on the percussion and auscultation of heart. 父 English 多媒体教学 Multi-edia teaching method 花 制表时间:2004年8月
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 1 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称 诊断学 年级 2005 授课专业 临床医学 教 师 雷寒 职称 教授 授课方式 □ 大课 示教 学时 5 题目章节 心脏检查 教材名称 诊断学(双语) 作者 吕卓人 雷寒 出 版 社 科学出版社 版次 第一版 教 学 目 的 要 求 掌握心脏检查的内容和方法,常见体征改变的鉴别和临床意义。 To grasp the contents and way of heart examination and be able to identify the common positive signs and the underlying clinical significances. 教 学 难 点 心脏听诊的内容,鉴别和临床意义。 The rub may be the contents of auscultation. 教 学 重 点 心脏扣诊和心脏听诊。 The emphasis may be put on the percussion and auscultation of heart. 外语 要求 English 教学 方法 手段 多媒体教学 Multi-media teaching method. 参考 资料 教研 室意 见

露庆医科大学临床半蕊裁案讲满 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 The examination of heart 15min Inspection 1.The shape of the thorax The anomalies of the thorax will affect the heart.The prominence of the precordium;The character of the respiration. 2 The apical impulse is generally fet at the fifth intercostal space in the midclavicular line.The normal apical impulse occupies a small area approximately the size of a quarter(2.5-3.0 cm in diameter).The different position,the alteration of near organs and cardiomegaly will change the way of apical impulse.Inward impulse may present at adhesive pericarditis or the sever The third and fourth left ICS pulsation beside the sterum may be the sign of hypertrophy of the right ventricle:Subxiphoid impulses:to differentiate the righ ventricular impulse from the transmitted abdominal aortic pulsations;Pulsations over the second left intercostal space Palpation To verify what has been seen by inspection and discover more. 15min 1.Precordial pulsationor Sustained left ventricular thrust has been noted to be associated with an increase in left ventricular mass and volume and is the indicator of hypertrophied ventricle 2 Thrill:a feeling of subtle palpation,which may represent the pathological changes in the heart. Pericardial friction feeling 三.Percussion The aim of cardiac percussion it to define its size,shape and the position within the 10min thorax.The key is to find the dullness boundaries set by the heart and its big blood vessels. Method:finger-on-finger percussion. Sequence:left sideright side,outside>inside,belowup.The percussion of the left boundary start at the point 2 to3 cm outside the apical pulse.The right boundary starts from the upper intercostal of the superior liver boundary (generally the fourth right ICS).It is the heart boundary When the resonant note changes into the dul note. 制表时间:2004年8月
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 2 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 The examination of heart 一.Inspection 1. The shape of the thorax The anomalies of the thorax will affect the heart. The prominence of the precordium; The character of the respiration. 2. The apical impulse is generally felt at the fifth intercostal space in the midclavicular line. The normal apical impulse occupies a small area approximately the size of a quarter(2.5–3.0 cm in diameter). The different position, the alteration of near organs and cardiomegaly will change the way of apical impulse. Inward impulse may present at adhesive pericarditis or the sever hypertrophy of the right ventricle. 3. Other chest-wall pulsation The third and fourth left ICS pulsation beside the sternum may be the sign of hypertrophy of the right ventricle;Subxiphoid impulses: to differentiate the right ventricular impulse from the transmitted abdominal aortic pulsations; Pulsations over the second left intercostal space. 二.Palpation To verify what has been seen by inspection and discover more. 1. Precordial pulsationor Sustained left ventricular thrust has been noted to be associated with an increase in left ventricular mass and volume and is the indicator of hypertrophied ventricle. 2. Thrill: a feeling of subtle palpation, which may represent the pathological changes in the heart. 3. Pericardial friction feeling 三.Percussion The aim of cardiac percussion it to define its size, shape and the position within the thorax. The key is to find the dullness boundaries set by the heart and its big blood vessels. Method: finger-on-finger percussion. Sequence:left side→right side,outside→inside,below→up. The percussion of the left boundary start at the point 2 to 3 cm outside the apical pulse. The right boundary starts from the upper intercostal of the superior liver boundary (generally the fourth right ICS)。It is the heart boundary When the resonant note changes into the dull note. 15min 15min 10min
重庆医科大半床半院载未讲满 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 The elements of each intercostals in both border of the heart. Left boundaryⅡ Pulmonary 20min artery : Left auricle IV,V Left ventricle Right boundary II Ascending aorta M.IV.V Right atrium The normal heart boundary in adult Right(cm) Intercostals Left(cm) 2~3 2-3 3.54.5 56 9 Left midclavicular line to mid-sternum line:810cm Clinical significance (1)Factors of the heart itself.Enlargement or expansion of the heart or big vessels (2)Extra-cardiac factors. Such as a massive hydrothorax,a massive infiltration and consolidation of the lung etc.Massive ascites.a huge abdominal tumor will push the diaphragm upward putting the heart in transverse position. (3)Hydropericardium:The dullness varies with the position(enlarged dullness of 1s and 2ndICS on lying flat) 四.Auscultation The aim of cardiac auscultation is to hear the normal and pathological hea 20min sounds.Cardiac auscultation has an important position in the examination of the heart.The character of the cardiac sounds is frequently more significant than the presence or absence of murmurs. The patient may assume a sitting or supine position,when necessary,the patient may change his position from supine to lying on his left side.The physician will auscultate the patient in different condition according to the practical changes.We should perform it in a quiet surroundings and concentrate on the activity. To find a well-designed stethoscope is important for proper auscultation The bell of the stethoscope picks up low frequencies while the diaphragm picks up the high frequencies. 制表时间:2004年8月
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 3 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 The elements of each intercostals in both border of the heart. Left boundary Ⅱ Pulmonary artery Ⅲ: Left auricle Ⅳ,Ⅴ Left ventricle Right boundary Ⅱ Ascending aorta Ⅲ,Ⅳ,Ⅴ Right atrium The normal heart boundary in adult Right(cm) Intercostals Left(cm) 2~3 2~3 3~4 Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ 2~3 3.5~4.5 5~6 7~9 Left midclavicular line to mid-sternum line: 8~10cm Clinical significance (1) Factors of the heart itself. Enlargement or expansion of the heart or big vessels. (2) Extra-cardiac factors. Such as a massive hydrothorax, a massive infiltration and consolidation of the lung etc. Massive ascites, a huge abdominal tumor will push the diaphragm upward putting the heart in transverse position. (3) Hydropericardium : The dullness varies with the position(enlarged dullness of 1st and 2nd ICS on lying flat) 四.Auscultation The aim of cardiac auscultation is to hear the normal and pathological hear sounds. Cardiac auscultation has an important position in the examination of the heart. The character of the cardiac sounds is frequently more significant than the presence or absence of murmurs. The patient may assume a sitting or supine position, when necessary, the patient may change his position from supine to lying on his left side. The physician will auscultate the patient in different condition according to the practical changes. We should perform it in a quiet surroundings and concentrate on the activity. To find a well-designed stethoscope is important for proper auscultation. The bell of the stethoscope picks up low frequencies while the diaphragm picks up the high frequencies. 20min 20min

君庆医科大学临床半院表来讲满 1.Topographic valve areas The valve auscultatory areas are closely linked to the trend of blood flow.Th five traditional auscultation areas are as follows. Mitral area:the apical pulsation part: Pulmonary area:the left2nICS beside the stemum. Aortic area:the right 2 IC beside the stemum The second Aortic area:the left third ICS beside the sternum: The tricuspid area:the eft fourth and fifthICS beside the stemum: Any of the auscultation areas shouldn't be omitted. 2.The contents of the auscultation. 40min Heart rate:one minute is needed to acquire the heart rate,which is judged by the first sound.Normal range is 60 to 100 times/min in traditional criteria However the recent studies have showed the upper limit may be the 95 times/min and the lower limit may be 51 times/min.the median is 67 to 73 times/min.Tachycardia and bradycardia need can be judged easily. Cardia rhythm:Sinus arrhythmia and premature beat and atrial fibrillation are the most common places when it comes to the irregular beat rhythm.We need be familiar with them. The three characters of atrial are as follows,absolute irregular heart beat, variable SI intensity and pulse deficit. Heart sound.Four kinds of heart sound are defined. First heartsound,S1 It occurs at the onset of ventricular contraction and is made of man components,which overlap each other.These components are "atrial," “mitral,”“tricuspid,”and“aortic”.Because the major and the mos important component of S1 is M1,the S1 is usually heard loudest at the apex and the lower left stemal border around the fourth left intercostals space. The sound is usually low pitched and longer in duration compared to the sharper,shorter,and higher-frequency second heart sound (S2).It can be timed to occur at the onset of a carotid pulse or the apical impulse and is a useful way of distinguishng it from.It can be mimicked by the yllabe “Lubbb”as opposed to the sharper S2,which sounds like“dub.' 制表时间:2004年8月 4
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 4 1. Topographic valve areas. The valve auscultatory areas are closely linked to the trend of blood flow. The five traditional auscultation areas are as follows. Mitral area: the apical pulsation part; Pulmonary area: the left 2nd ICS beside the sternum.; Aortic area: the right 2 nd ICS beside the sternum; The second Aortic area: the left third ICS beside the sternum; The tricuspid area: the left fourth and fifth ICS beside the sternum; Any of the auscultation areas shouldn’t be omitted. 2. The contents of the auscultation. ✓ Heart rate; one minute is needed to acquire the heart rate, which is judged by the first sound。Normal range is 60 to 100 times/min in traditional criteria. However the recent studies have showed the upper limit may be the 95 times/min and the lower limit may be 51 times/min. the median is 67 to 73 times/min. Tachycardia and bradycardia need can be judged easily. ✓ Cardia rhythm: Sinus arrhythmia and premature beat and atrial fibrillation are the most common places when it comes to the irregular beat rhythm. We need be familiar with them. The three characters of atrial are as follows, absolute irregular heart beat, variable S1 intensity and pulse deficit. ✓ Heart sound. Four kinds of heart sound are defined. First heart sound, S1 It occurs at the onset of ventricular contraction and is made of many components, which overlap each other. These components are “atrial,” “mitral,” “tricuspid,” and “aortic”. Because the major and the most important component of S1 is M1, the S1 is usually heard loudest at the apex and the lower left sternal border around the fourth left intercostals space. The sound is usually low pitched and longer in duration compared to the sharper, shorter, and higher-frequency second heart sound (S2). It can be timed to occur at the onset of a carotid pulse or the apical impulse and is a useful way of distinguishing it from S2. It can be mimicked by the syllable “Lubbb”as opposed to the sharper S2, which sounds like “dub.” 40min

置庆医科大学床半院未讲满 教学内容 Second heart sound,S2 The second heart sound occurs at the end of the ejection phase of systole.It is related to the closure of the semilunar valves.Since there are two semilunar valves,aortic and pulmonary,there are also two components for the 2 namely the aortic component(A2)and the pulmonary component (P2).The S is usually sharper,crisper,and shorter in duration compared to S1. The A2 component is normally heard over the true aortic area,which is the sash area (the area extending from the second right intercostal space at the sternal border to the apex).P2,on the other hand,is heard over the second and the third left intercostals spaces near the sternal border.Therefore,the splitting of the normal S2 is best appreciated at the second and third left intercosta space.Young people:P2>A2;Middle age man:P2=A2;Old age man:A2>P2 Third heart sound,S3: The early phase of the ventricular filling is characterized by sudden vigorous expansion associated with rapid inflow of blood.The peak of this filling period may be accompanied by a sound,which is termed the third heart sound,or S3 in children and in pregnant women. the S3 is a low-frequency sound or a thud similar to the sound caused by a small lead ball falling on a cushioned floor.It is obviously best audible over the apex area Fourth heart sound,S4 The atrium normally contracts at the end of diastole and gives an extra stretch to the ventricles.When the ventricular compliance is significantly reduced then this evokes a more vigorous contraction from the atrium,which forms the vibration.The sound is sometimes referred to as atrial gallop. Differentiate the Sland S2. The changes of heart sound and its clinical significance 40min (1)thenchanges of intensity of S1 and S2. S1 intensity depends on the degree of acceleration achieved by the contracting myofibrils at the time of mitral valve closure.Pressure rise (dP/dt)in the ventricle plays an important part.Increased atrial pressure will enhance the pressure rise (dP/dt),which may be obvious in mitral stenosis,incomplete atrial relaxation.Noncardiac factors such as body shape or chest wall deformities or the presence of pulmonary disease will functiontoo Severe mitral regurgitation will decrease the intensity of S1. 制表时间:2004年8月
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 5 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 Second heart sound, S2: The second heart sound occurs at the end of the ejection phase of systole. It is related to the closure of the semilunar valves. Since there are two semilunar valves, aortic and pulmonary, there are also two components for the S2, namely the aortic component (A2) and the pulmonary component (P2). The S2 is usually sharper, crisper, and shorter in duration compared to S1. The A2 component is normally heard over the true aortic area, which is the sash area (the area extending from the second right intercostal space at the sternal border to the apex). P2, on the other hand, is heard over the second and the third left intercostals spaces near the sternal border. Therefore, the splitting of the normal S2 is best appreciated at the second and third left intercostal space. Young people:P2>A2; Middle age man: P2=A2; Old age man: A2>P2 Third heart sound, S3: The early phase of the ventricular filling is characterized by sudden vigorous expansion associated with rapid inflow of blood. The peak of this filling period may be accompanied by a sound, which is termed the third heart sound, or S3. This occurs in children and in pregnant women. the S3 is a low-frequency sound or a thud similar to the sound caused by a small lead ball falling on a cushioned floor. It is obviously best audible over the apex area Fourth heart sound, S4 The atrium normally contracts at the end of diastole and gives an extra stretch to the ventricles. When the ventricular compliance is significantly reduced, then this evokes a more vigorous contraction from the atrium, which forms the vibration. The sound is sometimes referred to as atrial gallop. Differentiate the S1and S2. The changes of heart sound and its clinical significance. (1) then changes of intensity of S1 and S2. S1 intensity depends on the degree of acceleration achieved by the contracting myofibrils at the time of mitral valve closure. Pressure rise (dP/dt) in the ventricle plays an important part. Increased atrial pressure will enhance the pressure rise (dP/dt) , which may be obvious in mitral stenosis, incomplete atrial relaxation. Noncardiac factors such as body shape or chest wall deformities or the presence of pulmonary disease will function too. Severe mitral regurgitation will decrease the intensity of S1. 40min

·置庆医科大学临床半鹿藏来讲满 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 Variations in S1 intensity from cycle to cycle may refer to the following. Atrial fibrillation,where the diastolic filling periods keep changing constantly causing various degrees of Starling effect and variations in left atrial pressure at the time of mitral valve closure. A-V dissociation.The shorter PR intervals will have louder s1 whereas the longer PR will have softer S1.This phenomenon can occur in complete A-V block,patients with electronic pacemakers,and also in ventricular rhythms The intensity of S2 mainly depends on the aortic and pulmonary pressure and the contractility of the right ventricle (2)Quality changes of heart sound. Serious myocardial lesions such as myocardial infraction cause the SI to loose its original characteristics and it simulates S2.The auscultatory phenomenon is like that of the sound tick-tack of a clock;such cardiac rhythm is then called fetal heart rhythm. (3)Splitting ofheart sound The chief components of normal heart sound may be more obviously dissynchronised causing one heart sound to split into two or three audible sounds. The splitting of the S1:right bundle branch block or the severe pulmonary pressure. The splitting of the S2:The P2 is delayed on inspiration for two reasons:the increased volume on the right side and the fall in the pulmonary resistance on inspiration.The former will result in an increase in the right ventricular ejection time.The latter will allow easier forward flow,resulting in slower tendency for reversal.On expiration,the above is reversed.However A2 is affected to a very small degree. physiologic splitting:occur in adolescent when inspiring. 2general splitting:pulmonary hypertension,RBBB,inspiring. fixed splitting:atrium septal defect,not influenced by breathing 4reversed splitting:LBBB,aortic stenosis,occur in expiring. More information is showed in figure 1. extra cardiac sound (1)gallop rhythm: 制表时间:2004年8月 6
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 6 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 Variations in S1 intensity from cycle to cycle may refer to the following. Atrial fibrillation, where the diastolic filling periods keep changing constantly, causing various degrees of Starling effect and variations in left atrial pressure at the time of mitral valve closure. A-V dissociation, The shorter PR intervals will have louder S1, whereas the longer PR will have softer S1. This phenomenon can occur in complete A-V block, patients with electronic pacemakers, and also in ventricular rhythms。 The intensity of S2 mainly depends on the aortic and pulmonary pressure and the contractility of the right ventricle. (2) Quality changes of heart sound. Serious myocardial lesions such as myocardial infraction cause the S1 to loose its original characteristics and it simulates S2. The auscultatory phenomenon is like that of the sound tick-tack of a clock; such cardiac rhythm is then called fetal heart rhythm. (3) Splitting of heart sound The chief components of normal heart sound may be more obviously dissynchronised causing one heart sound to split into two or three audible sounds. The splitting of the S1: right bundle branch block or the severe pulmonary pressure. The splitting of the S2: The P2 is delayed on inspiration for two reasons: the increased volume on the right side and the fall in the pulmonary resistance on inspiration. The former will result in an increase in the right ventricular ejection time. The latter will allow easier forward flow, resulting in slower tendency for reversal. On expiration, the above is reversed. However A2 is affected to a very small degree. ① physiologic splitting:occur in adolescent when inspiring. ② general splitting:pulmonary hypertension, RBBB, inspiring. ③ fixed splitting:atrium septal defect, not influenced by breathing. ④ reversed splitting: LBBB, aortic stenosis, occur in expiring. More information is showed in figure 1. ✓ extra cardiac sound (1) gallop rhythm:

重庆医科大半脑床半院载未讲满 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 In patients with significant left ventricular dysfunction of whatever etiology the left ventricular diastolic pressure will rise because of decreased ventricular compliance.The increased left atrial v wave pressure will aid in the development of greater energy acquired by the moving column of blood during the rapid filling phase,which will cause the vibration of the impaired ventricles.Thus the setup is there for the production of s3 in these states. A gallop rhythm is subdivided into atrial gallop.ventrical gallop and summation gallop.It is obvious near the apex.Left side gallop account for most of them.it is a low-frequency sound,it must be searched for with the bel of the stethoscope.The patient should be turned to the left lateral position and the apical impulse located,and the area of the palpable apex beat must be auscultated (2)opening snap when the valves are stiffened and fused at the commissures. resulting in some degree of stenosis,as seen in rheumatic mitral stenosis,then one may hear a sound associated with the opening of the mitral valve.The sound is often snapping and sharp in quality and hence termed the opening snap.The OS is generally maximally loud somewhere between the lower left stemal border and the apex. (3)pericardial knock.In chronic constrictive pericarditis,the thickened and fibrosed,sometimes even alcified pericardium surrounds the ventricles like steel armor.The rapid inflows will be abruptly decelerated by the decreased compliance of the ventricles caused by the abnormal pericardium producing the S3.The sound may also be somewhat sharper and easily be heard in the left side of the sternum. (4)tumor plop:In atrial myxoma,one may hear an S3-like sound termed the tumor plop.The sound is actually produced when the tumor plops into the ventrice in diastole. (5)early systolic ejection sound it occurs in obviously dilated pulmonary (aortic)artery or distinct elevated pulmonary (aortic)artery pressure.The ejection make the vibration of the artery. (6)Mid-systolic and late systolic ejection sounds 制表时间:2004年8月
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 7 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 In patients with significant left ventricular dysfunction of whatever etiology, the left ventricular diastolic pressure will rise because of decreased ventricular compliance, The increased left atrial v wave pressure will aid in the development of greater energy acquired by the moving column of blood during the rapid filling phase, which will cause the vibration of the impaired ventricles. Thus the setup is there for the production of S3 in these states. A gallop rhythm is subdivided into atrial gallop, ventrical gallop and summation gallop. It is obvious near the apex. Left side gallop account for most of them. it is a low-frequency sound, it must be searched for with the bell of the stethoscope. The patient should be turned to the left lateral position and the apical impulse located, and the area of the palpable apex beat must be auscultated (2) opening snap when the valves are stiffened and fused at the commissures, resulting in some degree of stenosis, as seen in rheumatic mitral stenosis, then one may hear a sound associated with the opening of the mitral valve. The sound is often snapping and sharp in quality and hence termed the opening snap. The OS is generally maximally loud somewhere between the lower left sternal border and the apex. (3) pericardial knock. In chronic constrictive pericarditis, the thickened and fibrosed, sometimes even alcified pericardium surrounds the ventricles like steel armor. The rapid inflows will be abruptly decelerated by the decreased compliance of the ventricles caused by the abnormal pericardium producing the S3。The sound may also be somewhat sharper and easily be heard in the left side of the sternum. (4) tumor plop: In atrial myxoma, one may hear an S3-like sound termed the tumor plop. The sound is actually produced when the tumor plops into the ventricle in diastole. (5) early systolic ejection sound it occurs in obviously dilated pulmonary (aortic) artery or distinct elevated pulmonary (aortic) artery pressure. The ejection make the vibration of the artery. (6)Mid-systolic and late systolic ejection sounds
·量庆医科大学脑床半院教来讲满 It is equal to the mitral-prolapse-click syndrome or click syndrome,which is caused by the tense valve during systole. (7)extra sound by the artficial facilities. Artificial valve.When the artificial valves open or close,they will bump the setup contacted then it will give rise to the extra sound. Artificial pacemaker:the electrility sometimes will stimulate the tissues near the electrod lead and give rise to the extra sound before the S1. √Mumurs 40min Normal blood flow is described as laminar flow.The flow at the point of constriction is no longer laminar and is turbulent.The turbulent flow will be seen to have many different randomly distributed directions.The amount and extent of turbulence may vary according to the underlying abnormality and its severity.Thus,turbulent flow is an important cause of cardiovascula murmurs.It occurs in following common conditions:acceleration of blood flow.stenosisi of ventricular orifice.incomplete closure of valves causes reguritation of blood,abnormal shuntwithn the cardica chambers,floatting flake,abnormal dilatation of the cardiac cavity. Chief points of analysing a murmur (1)location of maximum intesity:it may represent the lesion location (2)time of appearance.It can be classfied into systolic murmur,diastolic murmur continuous mumur,dual period murmur.Early phase,middle phase and later phase are further be described when it comes to a certain murmur Genenarlly speaking.diastolic and continuous murmurs are pathologic murmurs,while systolic murmur may be pathologicor physiologic one. (3)quality and pitch of the murmur.Such as blowing in character(or soft or harsh),rumbling,sighing,mechanical,musical. (4)the intensity of a murmur:the systolic murmur is generally divided into six degrees.When a murmur is not immediately audible,the moment one begins to auscultate and has to tune in to detect the presence of the murmur by eliminating mentally the room noise,then the grade of the murmur is grade Grade I murmurs are not generally appreciated by the beginners in auscultation.Grade II murmur does not require this tuning in process.It is immediately audible the moment one begins to listen.Grade III murmur is the loudest murmur audible,but is not associated with a palpable thrill.When a murmur is audible and associated with a thrill,it must be between grades IV and VI.Grade IV murmur requires full contact of the chest wall with the chest 制表时间:2004年8月
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 8 It is equal to the mitral-prolapse-click syndrome or click syndrome, which is caused by the tense valve during systole. (7)extra sound by the artficial facilities. Artificial valve. When the artificial valves open or close, they will bump the setup contacted then it will give rise to the extra sound. Artificial pacemaker: the electrility sometimes will stimulate the tissues near the electrod lead and give rise to the extra sound before the S1. ✓ Mumurs Normal blood flow is described as laminar flow. The flow at the point of constriction is no longer laminar and is turbulent. The turbulent flow will be seen to have many different randomly distributed directions. The amount and extent of turbulence may vary according to the underlying abnormality and its severity. Thus, turbulent flow is an important cause of cardiovascular murmurs. It occurs in following common conditions: acceleration of blood flow, stenosisi of ventricular orifice, incomplete closure of valves causes reguritation of blood, abnormal shuntwithn the cardica chambers, floatting flake, abnormal dilatation of the cardiac cavity. Chief points of analysing a murmur (1) location of maximum intesity:it may represent the lesion location. (2) time of appearance. It can be classfied into systolic murmur, diastolic murmur,continuous murmur, dual period murmur. Early phase, middle phase and later phase are further be described when it comes to a certain murmur. Genenarlly speaking, diastolic and continuous murmurs are pathologic murmurs, while systolic murmur may be pathologic or physiologic one. (3) quality and pitch of the murmur. Such as blowing in character(or soft or harsh), rumbling, sighing, mechanical, musical. (4) the intensity of a murmur:the systolic murmur is generally divided into six degrees. When a murmur is not immediately audible, the moment one begins to auscultate and has to tune in to detect the presence of the murmur by eliminating mentally the room noise, then the grade of the murmur is grade I. Grade I murmurs are not generally appreciated by the beginners in auscultation. Grade II murmur does not require this tuning in process. It is immediately audible the moment one begins to listen. Grade III murmur is the loudest murmur audible, but is not associated with a palpable thrill. When a murmur is audible and associated with a thrill, it must be between grades IV and VI. Grade IV murmur requires full contact of the chest wall with the chest 40min

露庆医科大半脑床半鹿袁未讲满 piece of the stethoscope for its detection.Grade V murmur requires only partial contact,like the edge of the chest piece,for its detection.Grade V murmur.on the other hand.is audible even when the chest piece is held slightly but completely off the chest. (5)configuration of the murmur.It refers to the alteration patter of the internsity of a murmur during one cardiac cycle.The following are the commonplaces.crescendo,decrescendo.crescendo-decrescendo.continuous. (6)direction of transmission.There are some rules about the transmission of a murmur.Mitral valve regurgitation:left axilla and posteriorly:aortic valve stenosis:carotids mitral valve stenosis:located. (7)the effect of posture,respiration,and exercise on the murmur Clinical indication Genenarlly speaking,diastolic and continuous murmurs are pathologic murmurs,while systolic murmur may be pathologic or physiologic one. Though pathologic and physiologic one can be differentiated from several points,the basic cardiac condition is the most important factor. The location of the murmur indicate the location of lesion.The timing and qulity will indicate the lesion quality of the valves. The presence of palpable thrill accompanying need be emphasized,which can identify the pathologic lesion.Innocent murmur need be identifid Pericardial friction sound It can be reageded as the confirmatory signs of a heart diseas.Pericardial friction sound may occur in rheumatic or tuberculous or purulent pericarditis It may also occur in myocardial infarction,severe uremia,or connective tissu disease.The cadence is like chou-chou-chou and is most obvious in the left third and fourth ICS near the stemal. 制表时间:2004年8月
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 9 piece of the stethoscope for its detection. Grade V murmur requires only partial contact, like the edge of the chest piece, for its detection. Grade VI murmur, on the other hand, is audible even when the chest piece is held slightly but completely off the chest. (5) configuration of the murmur. It refers to the alteration pattern of the internsity of a murmur during one cardiac cycle. The following are the commonplaces, crescendo, decrescendo, crescendo-decrescendo, continuous. (6) direction of transmission. There are some rules about the transmission of a murmur. Mitral valve regurgitation: left axilla and posteriorly; aortic valve stenosis:carotids ;mitral valve stenosis:located. (7) the effect of posture, respiration, and exercise on the murmur. Clinical indication. Genenarlly speaking, diastolic and continuous murmurs are pathologic murmurs, while systolic murmur may be pathologic or physiologic one. Though pathologic and physiologic one can be differentiated from several points, the basic cardiac condition is the most important factor. The location of the murmur indicate the location of lesion. The timing and qulity will indicate the lesion quality of the valves. The presence of palpable thrill accompanying need be emphasized, which can identify the pathologic lesion. Innocent murmur need be identifid. ✓ Pericardial friction sound It can be reageded as the confirmatory signs of a heart diseas. Pericardial friction sound may occur in rheumatic or tuberculous or purulent pericarditis. It may also occur in myocardial infarction, severe uremia,or connective tissue disease. The cadence is like chou-chou-chou and is most obvious in the left third and fourth ICS near the sternal
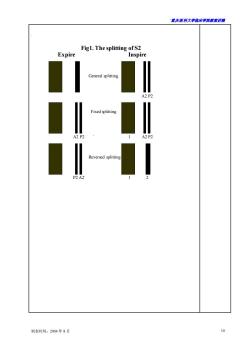
君庆医科大学脑床半院表来讲测 Fig1.The splitting of S2 Expire Inspire 制表时间:2004年8月 10
`重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 10 . Fig1. The splitting of S2 Expire Inspire General splitting A2 P2 Fixed splitting 1 A2 P2 ` 1 A2 P2 Reversed splitting 1 P2 A2` 1 2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 心电图.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 腹泻.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 腹痛.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 黄疸.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 水肿.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 绪论与问诊.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 腹部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 病历与诊断.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 呕血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 便血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八讲 脑脊液常规及生殖系统检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七讲 大便常规、免疫学检查及心肌标志物检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六讲 肾功能检查(主讲:唐敏).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四讲 血栓与出血检查(主讲:胥文春).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三讲 骨髓细胞学检查、血型与输血.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一讲 总论及血液一般检查(上).ppt
- 上海科学技术出版社:《实验诊断学——彩色图谱》书籍PDF电子版(主编:张丽霞、陈金宝).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程复习题集(无答案).doc
- 《实验诊断学》课程实验指导书 laboatoty diagnosis(共九章,含练习及答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(教案)第8讲 CSF生殖系统.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 呼吸系统症状和体征.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 循环系统主要症状与体征.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 超声心动图检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 血管检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 发热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 胸部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 呼吸困难.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 咳嗽、咳痰.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 咯血.doc
- 医学临床本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis.doc
- 医学临床本科《影像诊断学》课程教学大纲 medical imaging(包含MRI部分).doc
- 医学影像本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲(Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学资源(讲稿,共五章).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 MRI总论.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.1 3.2 正常及异常.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.3 支气管扩张及肺部炎症.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.4 肺结核.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.5 肺肿瘤.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.6 纵膈疾病.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 循环系统(冠脉及主动脉).ppt
