重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 循环系统主要症状与体征
重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称 诊断学年级 2005 授课专业临床医学 教师秦俭职称副教授授课方式 大课学时2 题目章节 循环系统常见疾病的主要症状和体征 教材名称诊断学 作者吕卓人雷寒 出版社 科学出版社 版次 第一版 教 学 掌握二尖籍狭窄及关闭不全的体征。To master the signs of mitral stenosis and regurgitation 2、掌握主动脉瓣关闭不全的体征。To master the signs of aortic regurgitation: 3、掌握心包积液的体征。To master the signs of pericardial effusion: 的要求 、心力衰竭的体征。To master the signs of heart failure. 二尖瓣狭窄的心浊音界改变及听诊特点。Changes of cardiac dullness of mitral stenosisan he char 难 动关闭不全的病理生理。Patholoy 点 B、周围血管体征。Peripherial vascular 教 二尖瓣狭窄及关闭不全的体征。(ignsof mitral stenosis and regurgitation) b、主动脉瓣关闭不全的体征。(Signs of ortic regurgitation) 学重点 B、心包积液的体征。(Signs of pericardial effusion) 4、心力衰竭的体征。(Signs of heart failure.) 外语要求 English 教学方法手段 参考资料 Mdicine 教研室意见
重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称 诊断学 年级 2005 授课专业 临床医学 教 师 秦俭 职称 副教授 授课方式 大 课 学时 2 题目章节 循环系统常见疾病的主要症状和体征 教材名称 诊断学 作者 吕卓人 雷寒 出 版 社 科学出版社 版次 第一版 教 学 目 的 要 求 1、掌握二尖瓣狭窄及关闭不全的体征。To master the signs of mitral stenosis and regurgitation; 2、掌握主动脉瓣关闭不全的体征。To master the signs of aortic regurgitation; 3、掌握心包积液的体征。To master the signs of pericardial effusion; 4、心力衰竭的体征。To master the signs of heart failure. 教 学 难 点 1、 二尖瓣狭窄的心浊音界改变及听诊特点。Changes of cardiac dullness of mitral stenosis and the characteristics of auscultation; 2、 主动脉瓣关闭不全的病理生理。Pathology of aortic regurgitation; 3、周围血管体征。Peripherial vascular signs. 教 学 重 点 1、二尖瓣狭窄及关闭不全的体征。(Signs of mitral stenosis and regurgitation) 2、主动脉瓣关闭不全的体征。(Signs of aortic regurgitation) 3、心包积液的体征。(Signs of pericardial effusion) 4、心力衰竭的体征。(Signs of heart failure.) 外语要求 English 教学方法手段 参考资料 Chinese Medicine Practical Internal Medicine 教研室意见
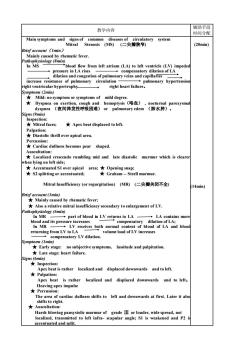
教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 Main symptoms and signs of common diseases of circulatory system Mitral Stenosis(MS)(二尖瓣狭窄) (20min) Brief account (Imin) matic fever. rom lett (A)tori (LV)mpd A rises increase resistance of pulmonary circulation pulmonary hypertension right ventricular hypertrophy right heart failure. no symptom or sympto oms of mild degree Dyspne 夜间阵发性呼吸困难) tral faces; Apex beat displaced to left. Diastolic thrill over apical area. Percussion: *Cardiac dullness becomes pear shaped. murmur which is cleare Accentuated S1 over apical area;Opening snap; *S2 splitting or accentuated; ★Graham-一Steell murmur. Mitral Insufficiency (or regurgitation)(MR) (二尖瓣关闭不全) (14min) Brief account (Imin) Mainly caused by rhematic fever; Also a relative mitral insufficiency secondary to enlargement of LV. part of blood in LV returns to LA- 一→LA contains more compensatory dilation of LA; returning from LV toL receives both of LA and blood compensatory LV dilation. po) nosubjective symptoms,lassitude and palpitation failu ★Inspection: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left. ther localized and displaced dowmwards and to le The area of cardiac dullness shifts to left and downwards at first.Later it also Harsh blowine p nsystolic murmur of localized.transmitted to left infra- a2 accentuated and split
教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 Main symptoms and signs of common diseases of circulatory system Mitral Stenosis (MS) (二尖瓣狭窄) Brief account(1min) Mainly caused by rhematic fever. Pathophysiology (8min) In MS blood flow from left atrium (LA) to left ventricle (LV) impeded pressure in LA rises compensatory dilation of LA dilation and congestion of pulmonary veins and capillaries increase resistance of pulmonary circulation pulmonary hypertension right ventricular hypertrophy right heart failure。 Symptoms (2min) ★ Mild: no symptom or symptoms of mild degree. ★ Dyspnea on exertion, cough and hemoptysis(咯血) , nocturnal paroxysmal dyspnea (夜间阵发性呼吸困难) or pulmonary edem (肺水肿)。 Signs(9min) Inspection: ★ Mitral faces; ★ Apex beat displaced to left. Palpation: ★ Diastolic thrill over apical area. Percussion: ★ Cardiac dullness becomes pear shaped. Auscultation: ★ Localized crescendo rumbling mid and late diastolic murmur which is clearer when lying on left side; ★ Accentuated S1 over apical area; ★ Opening snap; ★ S2 splitting or accentuated; ★ Graham - Steell murmur. Mitral Insufficiency (or regurgitation) (MR) (二尖瓣关闭不全) Brief account (1min) ★ Mainly caused by rhematic fever; ★ Also a relative mitral insufficiency secondary to enlargement of LV. Pathophysiology (6min) In MR part of blood in LV returns to LA LA contains more blood and its pressure increases compensatory dilation of LA; In MR LV receives both normal content of blood of LA and blood returning from LV to LA volume load of LV increases compensatory LV dilation. Symptoms (1min) ★ Early stage: no subjective symptoms, lassitude and palpitation. ★ Late stage: heart failure. Signs(6min) ★ Inspection: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left. ★ Palpation: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left; Heaving apex impulse ★ Percussion: The area of cardiac dullness shifts to left and downwards at first. Later it also shifts to right. ★ Auscultation: Harsh blowing pansystolic murmur of grade Ⅲ or louder, wide spread, not localized, transmitted to left infra- scapular angle; S1 is weakened and P2 is accentuated and split. (20min) (14min)
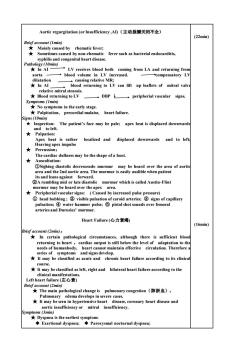
Aortic regurgitation(or Insufficiency,A(主动脉瓣关闭不全) (22min) Brief account(Imin) *Mainly caused by rhematic fever; Sometimes caused by non-rhematic fever such as bacterial endocarditis, al heart disease ★nAI LV receives blood both coming from LA and returning from blood volume in LV increased. compensatory LV relative mitral stenosis ★Blood returning to LV DBP peripherial vascular signs. *Inspection:The patient's face may be pale;apex beat is displaced downwards and toleft. eatis rather localized and Heaving apex impulse displaced downwards and to left ★Percussion: The cardiac dullness may be the shape of a boot. ★ he hear murmur which is called Austin-Flin ★ ncreased pulse pressure) ①head bobbing:②visible pulsation of ca ries: :tehamu:or capitlary arteries and Duroziez'murmur. Heart Failure(心力衰竭) (16min) Brief account (2min): *In certain pathological circumstances,although there is sufficient blood returning to heart,cardiac output is still below the level of adaptation to th dy,heart a course. It may be classified as left,right and bilateral heart failure according to the ice左装表 ★The main pathological change is pulmonary congestion(肺淤血), e,coronary heart disease and eney or fficiency *Dyspnea is the earliest symptom: ◆Exertional d小yspnea;◆Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea;
Aortic regurgitation (or Insufficiency ,AI)(主动脉瓣关闭不全) Brief account (1min) ★ Mainly caused by rhematic fever; ★ Sometimes caused by non-rhematic fever such as bacterial endocarditis, syphilis and congenital heart disease. Pathology (10min) ★ In AI LV receives blood both coming from LA and returning from aorta blood volume in LV increased. compensatory LV dilatation causing relative MR; ★ In AI blood returning to LV can lift up leaflets of mitral valve relative mitral stenosis. ★ Blood returning to LV DBP ↓ peripherial vascular signs. Symptoms (1min) ★ No symptoms in the early stage. ★ Palpitation, precordial malaise, heart failure. Signs(10min) ★ Inspection: The patient’s face may be pale; apex beat is displaced downwards and to left. ★ Palpation: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left; Heaving apex impulse ★ Percussion: The cardiac dullness may be the shape of a boot. ★ Auscultation: ①Sighing diastolic decrescendo murmur may be heard over the area of aortic area and the 2nd aortic area. The murmur is easily audible when patient its and leans against forward. ②A rumbling mid or late diastolic murmur which is called Austin-Flint murmur may be heard over the apex area. ★ Peripherial vascular signs: ( Caused by increased pulse pressure) ① head bobbing ; ② visible pulsation of caroid arteries; ③ signs of capillary pulsation; ④ water hammer pulse; ⑤ pistol shot sounds over femoral arteries and Duroziez’ murmur. Heart Failure (心力衰竭) Brief account (2min): ★ In certain pathological circumstances, although there is sufficient blood returning to heart ,cardiac output is still below the level of adaptation to the needs of humanbody, heart cannot maintain effective circulation. Therefore a series of symptoms and signs develop. ★ It may be classified as acute and chronic heart failure according to its clinical course. ★ It may be classified as left, right and bilateral heart failure according to the clinical manifestations. Left heart failure (左心衰) Brief account (2min) ★ The main pathological change is pulmonary congestion(肺淤血), Pulmonary edema develops in severe cases. ★ It may be seen in hypertensive heart disease, coronary heart disease and aortic insufficiency or mitral insufficiency. Symptoms (3min) ★ Dyspnea is the earliest symptom: ◆ Exertional dyspnea; ◆ Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea; (22min) (16min)
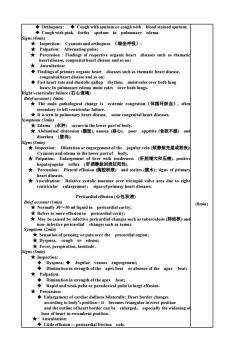
Orthopnea;Cough with sputum or cough with blood stained sputum; Cough with pink forthy sputum in pulmonary edema. ,(端坐呼吸) ★Per ussion Findings tive organic heart diseases such as rhema heart disease.congenital heart disease and so on: ★Auscultation: Findings of primary organic heart diseases such as rhematic heart disease, moist rales over both lung ver both lungs. Right ventricular failure(右心衰竭) some congenital heart diseases. ★Edema(水)occursin the lower part of body. ★Abdominal distension(腹张),nausea(恶心),poor appetite(食欲不振)and diarrhea(腹泻) 5g ection:dilatation or eng ment of the jugular vein(颈静脉充盈或怒张) ★Palpation:Enlargement of liver with tenderness(肝脏增大和压痛,positive Pleural effusion(腔积液)and ascites(腹水)片signs of primary Relative systolie。 mur over tricuspid valve area due to righ ventricular enlargement:s signs of prin ary heart diseases Pericardial effusion(心包积液 Bnm款omg-0mlauianperikardialcaine (8min) Refers to more effusion in pericardial cavity; ★May be caused by infeetive pericardial changes such as tuberculosis(肺结核)and non-infective pericardial changes such as tumor. S( ma Fever,perspiration,lassitude Signs(5min) ★Inspection: ution in strength of the apex beat or absence of the apex beat; ★ heat apulse in large effusion F零Enirecalotearhcdnlaesbinlenlr:heanborircdane according to body's position-it becomes triangular in erect position and the outline of heart border can be enlarged,especially the wideningo base of heart in recumbent position
◆ Orthopnea; ◆ Cough with sputum or cough with blood stained sputum; ◆ Cough with pink forthy sputum in pulmonary edema. Signs(4min) ★ Inspection: Cyanosis and orthopnea (端坐呼吸); ★ Palpation: Alternating pulse; ★ Percussion : Findings of respective organic heart diseases such as rhematic heart disease, congenital heart disease and so on; ★ Auscultation: ◆ Findings of primary organic heart diseases such as rhematic heart disease, congenital heart disease and so on; ◆ Fast heart rate and diastolic gallop rhythm; moist rales over both lung bases; In pulmonary edema moist rales over both lungs. Right ventricular failure (右心衰竭) Brief account ( 1min) ★ The main pathological change is systemic congestion(体循环淤血), often secondary to left ventricular failure. ★ It is seen in pulmonary heart disease, some congenital heart diseases. Symptoms (1min) ★ Edema (水肿) occurs in the lower part of body. ★ Abdominal distension (腹胀), nausea (恶心), poor appetite (食欲不振) and diarrhea (腹泻). Signs(3min) ★ Inspection: Dilatation or engorgement of the jugular vein (颈静脉充盈或怒张); Cyanosis and edema in the lower part of body. ★ Palpation: Enlargement of liver with tenderness (肝脏增大和压痛), positive hepatojugular reflux (肝颈静脉回流征阳性). ★ Percussion: Pleural effusion (胸腔积液) and ascites (腹水); signs of primary heart diseases. ★ Auscultation: Relative systolic murmur over tricuspid valve area due to right ventricular enlargement ; signs of primary heart diseases. Pericardial effusion (心包积液) Brief account (1min) ★ Normally 30~50 ml liquid in pericardial cavity; ★ Refers to more effusion in pericardial cavity; ★ May be caused by infective pericardial changes such as tuberculosis (肺结核) and non- infective pericardial changes such as tumor. Symptoms (2min) ★ Sensation of pressing or pain over the precordial region; ★ Dyspnea, cough or edema; ★ Fever, perspiration, lassitude . Signs(5min) ★ Inspection: ◆ Dyspnea; ◆ Jugular venous engorgement; ◆ Diminution in strength of the apex beat or absence of the apex beat; ★ Palpation: ◆ Diminution in strength of the apex beat; ◆ Rapid and weak pulse or paradoxical pulse in large effusion. ★ Percussion: ◆ Enlargement of cardiac dullness bilaterally; Heart border changes according to body’s position- it becomes triangular in erect position and the outline of heart border can be enlarged, especially the widening of base of heart in recumbent position. ★ Auscultation: ◆ Little effusion- pericardial friction rub; (8min)
Large effusion-fast heart rate diminution of intensity of hear nds(rem te heart sounds) Enlargement of liver with tenderness,positive Mitral Stenosis(MS)(仁尖瓣狭窄) Signs Diastolic thrill over apical area. Percussion: Cardiac dullness becomes pear shaped. murmur which is clearer when lving on left side: Accentuated S1 over apical area; ★Opening snap; S2 splitting or accentuated; ★Graham l murmur Mitral Insufficiency(or regurgitation)MR)(二尖瓣关闭不全) israter localized and displaced dowwards andtolef ★Palpation: 小结 Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left Heaving apex impulse Thercu shifts to riht cardiac dullness shifts to left and downwards at first.Later itals ★Auscultation: Harsh blowing pansystolic murmur of grade I or louder,wide spread,not to left infra-scapular angle;SI is weakened and P2 Aortic regurgitation(or Insufficieney,A)(主动脉瓣关闭不全) The patien's face may be pale ape beat displaced do ★Palpation: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left ★ Heaving apex impulse The cardiac dullness may be the shape of a boot. ★Auscultation:: Sighing diastolic decrescendo murmur may be heard over the area of aortic area and the 2nd aortic area.is easily audible when patient stolic murmur which is called Austin-Flint
◆ Large effusion- fast heart rate, diminution of intensity of heart sounds( remote heart sounds), ◆ Large effusion- Enlargement of liver with tenderness, positive hepatojugular reflux. 小结 Mitral Stenosis (MS) (二尖瓣狭窄) Signs Inspection: ★ Mitral faces; ★ Apex beat displaced to left. Palpation: ★ Diastolic thrill over apical area. Percussion: ★ Cardiac dullness becomes pear shaped. Auscultation: ★ Localized crescendo rumbling mid and late diastolic murmur which is clearer when lying on left side; ★ Accentuated S1 over apical area; ★ Opening snap; ★ S2 splitting or accentuated; ★ Graham - Steell murmur. Mitral Insufficiency (or regurgitation) (MR) (二尖瓣关闭不全) Signs ★ Inspection: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left. ★ Palpation: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left; Heaving apex impulse ★ Percussion: The area of cardiac dullness shifts to left and downwards at first. Later it also shifts to right. ★ Auscultation: Harsh blowing pansystolic murmur of grade Ⅲ or louder, wide spread, not localized, transmitted to left infra- scapular angle; S1 is weakened and P2 is accentuated and split. Aortic regurgitation (or Insufficiency ,AI)(主动脉瓣关闭不全) Signs ★ Inspection: The patient’s face may be pale; apex beat is displaced downwards and to left. ★ Palpation: Apex beat is rather localized and displaced downwards and to left; Heaving apex impulse ★ Percussion: The cardiac dullness may be the shape of a boot. ★ Auscultation: ①Sighing diastolic decrescendo murmur may be heard over the area of aortic area and the 2nd aortic area. The murmur is easily audible when patient sits and leans against forward. ②A rumbling mid or late diastolic murmur which is called Austin-Flint
area. ★ reased pulse pressure) Heart Failure(心力衰竭) Left heart failure(左心度) Signs ★Inspection:Cyanosis and orthopnea(W坐呼吸); Alternating pulse; Percu ★A Findings of primary organic heart diseases such as rhematic heart disease congenital heart disease and so on: Fast heart rate and diastolic gallop rhythm;moist rales over both lung moist rales over both lungs. ★Inspection::Dilatation or engorgement of the jugularvein(颈静脉充盈或怒张) Cyanosis and edema in the low r part of body. 女Palpation f liv ter es(肝脏增大和压痛,positiv 所颈游 and ascites(腹水)片signs of prima Auscultation:Relative systolic murmur over tricuspid valve area due to right ventricular enlargement;signs of primary heart diseases. Pericardial effusion(心包积液) ◆Dyspnea:◆Jugular venous eng rgement: Diminution in strength of the apex beat orabsence of the apex beat; ★Palpation: Diminution in strength of the apex beat; Rapid and weak pulse or paradoxical pulse in large effusion. nlarge ent of cardiac dul Heart border changes and the outline of heart border can be enla base of heart in recumbent position. 女Auscultation: Large effusion eart rate, diminution of intensity of heart sounds ment of liver with tenderness,positive hepatojugular reflux. What are the signs of 思考
murmur may be heard over the apex area. ★ Peripherial vascular signs: ( Caused by increased pulse pressure) ① head bobbing ; ② visible pulsation of caroid arteries; ③ signs of capillary pulsation; ④ water hammer pulse; ⑤ pistol shot sounds over femoral arteries and Duroziez’ murmur. Heart Failure (心力衰竭) Left heart failure (左心衰) Signs ★ Inspection: Cyanosis and orthopnea (端坐呼吸); ★ Palpation: Alternating pulse; ★ Percussion : Findings of respective organic heart diseases such as rhematic heart disease, congenital heart disease and so on; ★ Auscultation: ◆ Findings of primary organic heart diseases such as rhematic heart disease, congenital heart disease and so on; ◆ Fast heart rate and diastolic gallop rhythm; moist rales over both lung bases; In pulmonary edema moist rales over both lungs. Right ventricular failure (右心衰竭) Signs ★ Inspection: Dilatation or engorgement of the jugular vein (颈静脉充盈或怒张); Cyanosis and edema in the lower part of body. ★ Palpation: Enlargement of liver with tenderness (肝脏增大和压痛), positive hepatojugular reflux (肝颈静脉回流征阳性). ★ Percussion: Pleural effusion (胸腔积液) and ascites (腹水); signs of primary heart diseases. ★ Auscultation: Relative systolic murmur over tricuspid valve area due to right ventricular enlargement ; signs of primary heart diseases. Pericardial effusion (心包积液) Signs ★ Inspection: ◆ Dyspnea; ◆ Jugular venous engorgement; ◆ Diminution in strength of the apex beat or absence of the apex beat; ★ Palpation: ◆ Diminution in strength of the apex beat; ◆ Rapid and weak pulse or paradoxical pulse in large effusion. ★ Percussion: ◆ Enlargement of cardiac dullness bilaterally; Heart border changes according to body’s position- it becomes triangular in erect position and the outline of heart border can be enlarged, especially the widening of base of heart in recumbent position. ★ Auscultation: ◆ Little effusion- pericardial friction rub; ◆ Large effusion- fast heart rate, diminution of intensity of heart sounds ( remote heart sounds), ◆ Large effusion- Enlargement of liver with tenderness, positive hepatojugular reflux. 思考 题及 预习 1、What are the signs of mitral stenosis? 2、What are the signs of mitral insufficiency? 3、What are the signs of aortic insufficiency? 4、What are the signs of heart failure? 5、What are the signs of pericardial effusion?
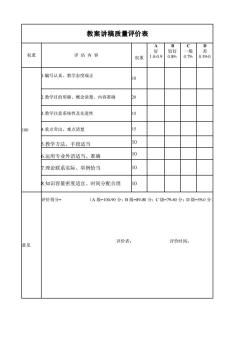
教案讲稿质量评价表 D 权重 评估内容 差 权重 0.59-0 编写认真、教学态度端正 10 2教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 3.教学注意系统性及先进性 % 4.重点突出、难点清楚 5.教学方法、手段适当 10 .运用专业外语适当、准确 7.理论联系实际、举例恰当 10 3知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 10 平价得分 (A级=10-90分:B级=89-80分:C级=79-60分:D级=59-0分 意见 评价者: 评价时间:
教案讲稿质量评价表 权重 评 估 内 容 权重 A 好 1.0-0.9 B 较好 0.89- C 一般 0.79- D 差 0.59-0 100 1.编写认真、教学态度端正 10 2.教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 20 3.教学注意系统性及先进性 15 4.重点突出、难点清楚 15 5.教学方法、手段适当 10 6.运用专业外语适当、准确 10 7.理论联系实际、举例恰当 10 8.知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 10 意见 评价得分= (A 级=100-90 分;B 级=89-80 分;C 级=79-60 分;D 级=59-0 分) 评价者: 评价时间:
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 呼吸系统症状和体征.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 心脏检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 心电图.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 腹泻.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 腹痛.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 黄疸.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 水肿.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 绪论与问诊.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 腹部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 病历与诊断.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 呕血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 便血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八讲 脑脊液常规及生殖系统检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七讲 大便常规、免疫学检查及心肌标志物检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六讲 肾功能检查(主讲:唐敏).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四讲 血栓与出血检查(主讲:胥文春).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三讲 骨髓细胞学检查、血型与输血.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一讲 总论及血液一般检查(上).ppt
- 上海科学技术出版社:《实验诊断学——彩色图谱》书籍PDF电子版(主编:张丽霞、陈金宝).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程复习题集(无答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 超声心动图检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 血管检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 发热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 胸部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 呼吸困难.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 咳嗽、咳痰.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 咯血.doc
- 医学临床本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis.doc
- 医学临床本科《影像诊断学》课程教学大纲 medical imaging(包含MRI部分).doc
- 医学影像本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲(Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学资源(讲稿,共五章).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 MRI总论.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.1 3.2 正常及异常.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.3 支气管扩张及肺部炎症.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.4 肺结核.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.5 肺肿瘤.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.6 纵膈疾病.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 循环系统(冠脉及主动脉).ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 消化系统和腹膜腔 5.2 急腹症.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 消化系统和腹膜腔 5.3 肝脏.ppt
