重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 水肿
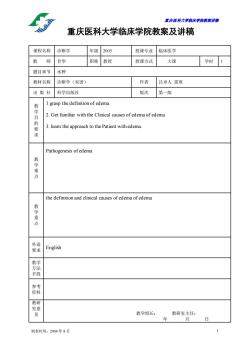
置庆医科大学脑床半院裁来讲满 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称诊断学 年级2005 授课专业临床医学 教师甘华 职称教授 授课方式 大课 学时1 题目章节水肿 教材名称诊断学(双语) 作者吕卓人雷寒 出版社科学出版社 版次第一版 1.grasp the definition of edema 目 2.Get familiar with the Clinical causes of edema of edema 3.leamn the approach to the Patient with edema. Pathogenesis ofedema 学难点 the definition and clinical causes of edema of edema 教学重点 外语 要求 English 清 见 教学组长: 教研室主任: 日 制表时间:2004年8月 1
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 1 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称 诊断学 年级 2005 授课专业 临床医学 教 师 甘华 职称 教授 授课方式 大课 学时 1 题目章节 水肿 教材名称 诊断学(双语) 作者 吕卓人 雷寒 出 版 社 科学出版社 版次 第一版 教 学 目 的 要 求 1.grasp the definition of edema. 2. Get familiar with the Clinical causes of edema of edema 3. learn the approach to the Patient with edema. 教 学 难 点 Pathogenesis of edema 教 学 重 点 the definition and clinical causes of edema of edema 外语 要求 English 教学 方法 手段 参考 资料 教研 室意 见 教学组长: 教研室主任: 年 月 日
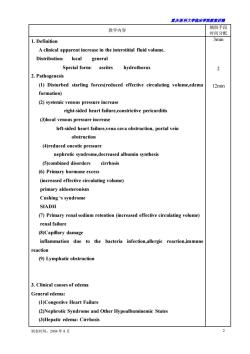
置庆医科大学床半院藏讲满 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 1.Definition 3min A clinical apparent increase in the interstitial fluid volume Distribution:local general Special form: ascites hydrothorax 2.Pathogenesis (1)Disturbed starling forces(reduced effective circulating volume,edema 12min formation) (2)systemic venous pressure increase right-sided heart failure,constrictive pericarditis (3)local venous pressure increase left-sided heart failure,vena cava obstruction,portal vein obstruction (4)reduced oncotic pressure nephrotic syndrome,decreased albumin synthesis (5)combined disorders cirrhosis (6)Primary hormone excess (increased effective circulating volume) primary aldosteronism Cushing's syndrome SIADH (7)Primary renal sodium retention(increased effective circulating volume) renal failure (8)Capillary damage inflammation due to the bacteria infection,allergic reaction immun reaction (9)Lymphatic obstruction 3.Clinical causes of edema General edema: (1)Congestive Heart Failure (2)Nephrotic Syndrome and Other Hypoalbuminemic States (3)Hepatic edema:Cirrhosis 制表时间:2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 2 教学内容 辅助手段 时间分配 1. Definition A clinical apparent increase in the interstitial fluid volume. Distribution: local general Special form: ascites hydrothorax 2. Pathogenesis (1) Disturbed starling forces(reduced effective circulating volume,edema formation) (2) systemic venous pressure increase right-sided heart failure,constrictive pericarditis (3)local venous pressure increase left-sided heart failure,vena cava obstruction, portal vein obstruction (4)reduced oncotic pressure nephrotic syndrome,decreased albumin synthesis (5)combined disorders cirrhosis (6) Primary hormone excess (increased effective circulating volume) primary aldosteronism Cushing ‘s syndrome SIADH (7) Primary renal sodium retention (increased effective circulating volume) renal failure (8)Capillary damage inflammation due to the bacteria infection,allergic reaction,immune reaction (9) Lymphatic obstruction 3. Clinical causes of edema General edema: (1)Congestive Heart Failure (2)Nephrotic Syndrome and Other Hypoalbuminemic States (3)Hepatic edema: Cirrhosis 3min 2 12min

重庆医科大学临床半院责未讲满 (④)Nutritional edema (5)Pharmaco edema,myxedema 15min (6)Idiopathic Edema: Localized edema: Obstruction of venous(and lymphatic)drainage of a limb Miscellaneous:located pretibial region,periorbital region .hypothyroidism(myxedema) ·Drug-induced edema Exogenous hyperadremocortism Estrogen vasodilators 4.Accompanied symtoms (1)With hepatomegaly (2)With gross proteinuria (3)With dyspnea (4)Related with menstrual cycle 5.Approach to the Patient (1)Localized or generalized? (2)Hydrothorax or ascites? 仔)Sites,.Timc 5min (4)accompanied symptom 5min 制表时间:2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 3 (4)Nutritional edema (5)Pharmaco edema, myxedema, (6)Idiopathic Edema: Localized edema: Obstruction of venous (and lymphatic) drainage of a limb Miscellaneous:located pretibial region,periorbital region • hypothyroidism(myxedema) • Drug-induced edema Exogenous hyperadremocortism Estrogen vasodilators 4. Accompanied symtoms (1)With hepatomegaly (2)With gross proteinuria (3)With dyspnea (4)Related with menstrual cycle 5. Approach to the Patient (1)Localized or generalized? (2)Hydrothorax or ascites? (3)Sites, Time (4)accompanied symptom 15min 5min 5min

重庆医科大半脑床半院载未讲满 1.Definition of edema. 2.Pathogenesis 3.Clinical causes of edema 4. Accompanied symtoms 5.Approach to the Patien 小结 1.What are the clinic cause of edema? 思考 制表时间:2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 4 小结 1.Definition of edema. 2.Pathogenesis 3.Clinical causes of edema 4.Accompanied symtoms 5.Approach to the Patient 思考 题及 预习 1.What are the clinic cause of edema?
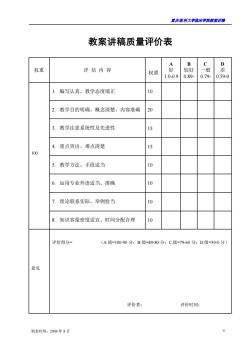
君庆医科大学临床半院表来讲满 教案讲稿质量评价表 D 权重 评估内容 权重 较好 一般 10-0.9 0.89. 0.79 0.59.0 编写认真、教学态度端正 2. 教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 20 3. 教学注意系统性及先进性 15 重点突出、难点清楚 15 % 教学方法、手段适当 10 6.运用专业外语适当、准确 10 理论联系实际、举例恰当 10 8.知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 10 评价得分= (A级=100-90分:B级=89-80分:C级=79-60分:D级=59-0分) 意见 评价者: 评价时间: 制表时间:2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 5 教案讲稿质量评价表 权重 评 估 内 容 权重 A 好 1.0-0.9 B 较好 0.89- C 一般 0.79- D 差 0.59-0 100 1. 编写认真、教学态度端正 10 2. 教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 20 3. 教学注意系统性及先进性 15 4. 重点突出、难点清楚 15 5. 教学方法、手段适当 10 6. 运用专业外语适当、准确 10 7. 理论联系实际、举例恰当 10 8. 知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 10 意见 评价得分= (A 级=100-90 分;B 级=89-80 分;C 级=79-60 分;D 级=59-0 分) 评价者: 评价时间:
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 绪论与问诊.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 腹部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 病历与诊断.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 呕血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 便血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八讲 脑脊液常规及生殖系统检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七讲 大便常规、免疫学检查及心肌标志物检查.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六讲 肾功能检查(主讲:唐敏).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四讲 血栓与出血检查(主讲:胥文春).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三讲 骨髓细胞学检查、血型与输血.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一讲 总论及血液一般检查(上).ppt
- 上海科学技术出版社:《实验诊断学——彩色图谱》书籍PDF电子版(主编:张丽霞、陈金宝).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程复习题集(无答案).doc
- 《实验诊断学》课程实验指导书 laboatoty diagnosis(共九章,含练习及答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(教案)第8讲 CSF生殖系统.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(教案)第7讲 大便 免疫 心肌.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(教案)第6讲 肾功能.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(教案)第2讲 血液(下).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程实验教学大纲(供临床医学专业本科用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《实验诊断学》课程理论教学大纲(供五年制临床医学、儿科医学、预防医学、麻醉医学、影像医学专业本科使用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 黄疸.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 腹痛.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 腹泻.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 心电图.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 心脏检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 呼吸系统症状和体征.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 循环系统主要症状与体征.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 超声心动图检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 血管检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 发热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 胸部检查.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 呼吸困难.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 咳嗽、咳痰.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《诊断学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 咯血.doc
- 医学临床本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis.doc
- 医学临床本科《影像诊断学》课程教学大纲 medical imaging(包含MRI部分).doc
- 医学影像本科《MRI诊断学》课程教学大纲(Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学资源(讲稿,共五章).doc
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 MRI总论.ppt
- 石河子大学:《MRI诊断学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 呼吸系统 3.1 3.2 正常及异常.ppt
