西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 05 Nucleophiles and Electrophiles

Section E Nucleophiles and Electrophiles Definition:Nucleophiles and electrophiles Active Intermediates: Anions Cations ;Charged Species; ■Radicals Neutral inorganic species
College of Science Section E Nucleophiles and Electrophiles Definition: Nucleophiles and electrophiles Active Intermediates: zAnions ; Cations ;Charged Species; Radicals Neutral inorganic species

E1:Nucleophiles s and electrophiles ■1 Nucleophiles electron-rich molecules and react with electrophiles Nucleophile ("nucleus-loving")=Lewis base(electron-pair donor) ooften negatively charged and used as Na+ or K+salt ●symbolized as:Nu. ■Nucleophilic center OThe specific atom or region of the molecule which is electron rich
College of Science E1: Nucleophiles and electrophiles 1 Nucleophiles zelectron-rich molecules and react with electrophiles zNucleophile (“nucleus-loving”) = Lewis base(electron-pair donor) zoften negatively charged and used as Na+ or K + salt zsymbolized as :Nu¯. Nucleophilic center zThe specific atom or region of the molecule which is electron rich
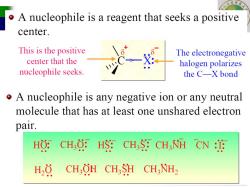
o A nucleophile is a reagent that seeks a positive center. This is the positive The electronegative center that the halogen polarizes nucleophile seeks. the C-X bond o A nucleophile is any negative ion or any neutral molecule that has at least one unshared electron pair. HO: CHO:HS:CH3S CH3NH CN :I H,0 CH,OH CH3SH CH3NH2
College of Science
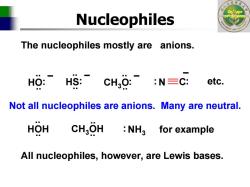
Nucleophiles The nucleophiles mostly are anions. HO:HS:: :N三C: etc. Not all nucleophiles are anions.Many are neutral. HOH CHgOH NH3 for example All nucleophiles,however,are Lewis bases
College of Science Nucleophiles The nucleophiles mostly are anions. – : : N C .. .. HS: .. – .. HO: – .. .. CH 3 O: – etc. Not all nucleophiles are anions. Many are neutral. .. .. HOH CH 3OH.. .. NH 3 : for example All nucleophiles, however, are Lewis bases

E1:Nucleophiles and electrophiles ■2 Electrophiles o electron-deficient molecules o can react with nucleophiles Electrophile ("electron-loving")=Lewis acid Electrophilic center othe specific atom or region of the molecule which is electron deficient ■symbolized as E+
College of Science E1: Nucleophiles and electrophiles 2 Electrophiles z electron-deficient molecules z can react with nucleophiles Electrophile (“electron-loving”) = Lewis acid Electrophilic center zthe specific atom or region of the molecule which is electron deficient symbolized as E +

E2 Charged Carbon species 1 Anions Negatively charged ions with lone pairs of electrons are nucleophiles.The atom bearing the negative charge is the nucleophilic center 2 Cations Positively charged ions are electrophiles. The atom bearing the positivecharge is the electrophilic center. .carbocations:sp2(trigonal) geometry,planar,positive charge carbanions:sp3(tetrahedral) geometry,strong base,negative charge a Carbocation a Carbon Radical a Carbanion
College E2、 Charged Carbon speciesof Science 1 Anions Negatively charged ions with lone pairs of electrons are nucleophiles. The atom bearing the negative charge is the nucleophilic center 2 Cations Positively charged ions are electrophiles. The atom bearing the positivecharge is the electrophilic center. •carbocations: sp2 (trigonal) geometry,planar, positive charge • carbanions: sp3 (tetrahedral) geometry, strong base, negative charge
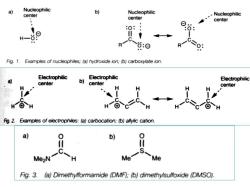
a Nucleophilic , Nucleophilic center .Nucleophilic center center 9 :⊙ Fig.1.Examples of nucleophiles;(a)hydroxide ion;(b)carboxylate ion. Electrophilic Electrophilic a) center b) Electrophilic center H Fig.2. Examples of electrophiles:(a)carbocation;(b)allylic cation. a 0 b) Me2N C-H Me- Me Fig.3.(a)Dimethylformamide (DMF):(b)dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)
College of Science

E3-1Nu:(亲核试剂与亲核性 Relative Nucleophilicity ■ 亲核性:在过渡态时对缺电子碳亲合能力(亲 近C+) ■碱性:与质子结合能力(亲近H+) 亲核能力: ■ RS>CN->I>NH3(NH2R )>RO (OH) >Br>PhO>CI》H20>F
College of Science E3-1 Nu: (亲核试剂与亲核性) Relative Nucleophilicity 亲核性:在过渡态时对缺电子碳亲合能力(亲 近C+) 碱性: 与质子结合能力(亲近H+) 亲核能力: RS->CN->I->NH3(NH2R )>RO- (OH-) >Br- >PhO- >Cl- 》H2O >F-

亲核试剂 亲核性是针对碳而言,其亲核性强弱往往受到 ■ 底物、溶剂甚至是浓度的影响。 ■比较亲核试剂的强弱在相同的底物和相同的反 应条件下比较: Nu CH3-Br Nu-CH3 Br Nu= H2O CH3CO2 NH3 CI OH CHO· CN HS relative reactivity 500 700 1,00016,00025,000100,000 125,000 Less reactive More reactive
College 亲核试剂 of Science 亲核性是针对碳而言,其亲核性强弱往往受到 底物、溶剂甚至是浓度的影响。 比较亲核试剂的强弱在相同的底物和相同的反 应条件下比较: Nu - Nu - CH 3 + Br - + CH 3 - Br Nu = H2O CH3CO2- NH3 Cl - OH - CH3O - I - CN - HS - relative reactivity 1 500 700 1,000 16,000 25,000 100,000 125,000 More reactive Less reactive

Nucleophilicity(亲核性) CH3CO2CI->F- Anions are more nucleophilic than neutral compounds ■The solvent matters!
College Nucleophilicity(亲核性 of Science ) CH 3CO 2 - Cl - > F - Anions are more nucleophilic than neutral compounds The solvent matters!
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 04 stereochemistry.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 03 functional groups.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 02 Alkanes and cycloalkane.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 01 Structure And Bonding(主讲:王俊儒).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Proton NMR Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Organic Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Nomenclature of Saturated Hydrocarbons.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Infrared(IR)spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Functional Groups.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Ethers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Enols and Enolates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Conjugated Dienes and U.V. Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Conformational Analysis.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Stereochemistry.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 06 reactions and mechanisms.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 07 Acids and Bases.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 08 Alkenes and Alkynes.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 09 Aromatic chemistry.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 10 Aldehydes and ketones.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 11 Carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:王俊儒).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of OM.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 03 Brief Introduction and Nomenclature of OC.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 04 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes(打印版).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 05 The Study of Chemical Reactions(打印版).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 06 Stereochemistry(打印版).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 07 Alkyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination(打印版).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2012)Chapter 04 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2012)Chapter 17 & 18 Aromatic chemistry.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2012)Chapter 05 The Study of Chemical Reactions.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2012)Chapter 06 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2012)Chapter 07 Alkyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2012)Chapter 08 & 09 Alkenes.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2012)Chapter 19 Ketones and Aldehydes.pdf
