《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Organic Reactions

Organic reactions Kinds of Reactions Mechanisms(polar,non-polar) Bond Dissociation Energy Reaction Profiles
Organic Reactions Kinds of Reactions Mechanisms (polar, non-polar) Bond Dissociation Energy Reaction Profiles
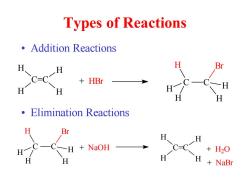
Types of Reactions ·Addition Reactions H C=C H H Elimination Reactions Br H +NaOH +H2O H +NaBr
Types of Reactions • Addition Reactions • Elimination Reactions C=C H H H H + HBr C C H H Br H H H C=C H H H H C C + NaOH H H Br H H H + H2 O + NaBr
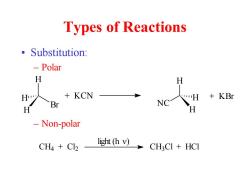
Types of Reactions 。Substitution: -Polar H H +KCN +KBr Br NC H H Non-polar light (h v) CH4 Cl2 CHCI HCI
Types of Reactions • Substitution: – Polar – Non-polar H Br H H + KCN H NC H H + KBr CH4 + Cl2 CH3 Cl + HCl light (h )
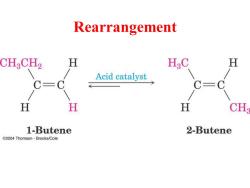
Rearrangement CH3CH2 H H:C H Acid catalyst C=C H H H CH 1-Butene 2-Butene e2004 Thomson-Brooks/Cole
Rearrangement
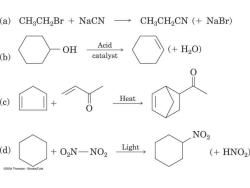
(a) CHgCH2Br NaCN CHaCH2CN (NaBr) OH Acid (+H20) (b) catalyst (c) Heat NO2 d) +02N-NO2 Light (HNO2 @2004 Thomson-Brooks/Cole

Definitions Mechanism:Complete step-by-step of exactly which bonds break and which bonds form and in what order. 。 Thermodynamics:The study of the energy changes that occur in chemical transformations. This allows for comparison of stability of reactants and products. Kinetics:The study of reaction rates,determining which products are formed most rapidly.One can predict how the rate will change with changing conditions
Definitions • Mechanism: Complete step-by-step of exactly which bonds break and which bonds form and in what order. • Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that occur in chemical transformations. This allows for comparison of stability of reactants and products. • Kinetics: The study of reaction rates, determining which products are formed most rapidly. One can predict how the rate will change with changing conditions
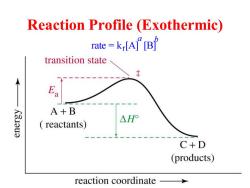
Reaction Profile (Exothermic) rate=krA”B transition state A+B K3.Iu3 △H reactants) C+D (products) reaction coordinate
Reaction Profile (Exothermic) rate = kr [A] [B] a b
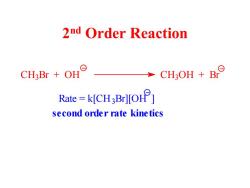
2nd Order Reaction CH3Br OH CH3OH B Rate=kICH3Br][O] second order rate kinetics
2 nd Order Reaction C H3 Br + OH C H3 OH + Br Rate = k[CH3 Br][OH ] second order rate kinetics
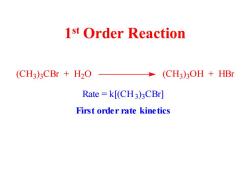
1st Order Reaction (CH3)3CBr H2O (CH3)3OH +HBr Rate=k[(CH3)3CBr] First order rate kinetics
1 st Order Reaction (CH3) 3 CBr + H2 O (CH3) 3 OH + HBr Rate = k[(CH3) 3 CBr] First order rate kinetics

Bond Breaking: Non-polar and Polar →A·+·B Homolytic bond breaking (radical) (one electron stays with each fragment A:B →A++:B Heterolytic bond breaking(polar) (two electrons stay with one fragment) 2004 Thomson-Brooks/Cole
Bond Breaking: Non-polar and Polar
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Nomenclature of Saturated Hydrocarbons.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Infrared(IR)spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Functional Groups.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Ethers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Enols and Enolates.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Conjugated Dienes and U.V. Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Conformational Analysis.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Carboxylic Acids Nitriles.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Benzene and Aromaticity(2011).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkynes McMurry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkyl Halides from Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkenes Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alkenes Overview.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Alcohols-structure and synthesis 2.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules.pptx
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Proton NMR Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, William A. Price, Ph.D. PPT, La Salle University, L.G.WADE, JR., 8th Edition)Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 01 Structure And Bonding(主讲:王俊儒).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 02 Alkanes and cycloalkane.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 03 functional groups.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 04 stereochemistry.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 05 Nucleophiles and Electrophiles.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 06 reactions and mechanisms.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 07 Acids and Bases.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 08 Alkenes and Alkynes.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 09 Aromatic chemistry.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 10 Aldehydes and ketones.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2009)Chapter 11 Carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:王俊儒).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of OM.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 03 Brief Introduction and Nomenclature of OC.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 04 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes(打印版).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学 Organic chemistry》课程教学课件(2010)Chapter 05 The Study of Chemical Reactions(打印版).pdf
