河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第十章 生物膜 Mechanism of Enzyme Action

Chapter 10 Mechanism of Enzyme Action Although the catalytic properties of enzymes may seem almost magical,it is simply chemistry-the breaking and making of bonds-that gives enzymes their prowess. This chapter will explore the unique features of this chemistry
Chapter 10 Mechanism of Enzyme Action Although the catalytic properties of enzymes may seem almost magical, it is simply chemistry—the breaking and making of bonds—that gives enzymes their prowess. This chapter will explore the unique features of this chemistry
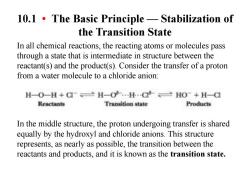
10.1.The Basic Principle-Stabilization of the Transition State In all chemical reactions,the reacting atoms or molecules pass through a state that is intermediate in structure between the reactant(s)and the product(s).Consider the transfer of a proton from a water molecule to a chloride anion: H-O-H+CH-H.C>HO-+H-C Reactants Transition state Products In the middle structure,the proton undergoing transfer is shared equally by the hydroxyl and chloride anions.This structure represents,as nearly as possible,the transition between the reactants and products,and it is known as the transition state
10.1 • The Basic Principle — Stabilization of the Transition State In all chemical reactions, the reacting atoms or molecules pass through a state that is intermediate in structure between the reactant(s) and the product(s). Consider the transfer of a proton from a water molecule to a chloride anion: In the middle structure, the proton undergoing transfer is shared equally by the hydroxyl and chloride anions. This structure represents, as nearly as possible, the transition between the reactants and products, and it is known as the transition state

Enzymes catalyze by stabilizing transition states Free energy G of a chemical reaction can be plotted over time Favorable reactions have a Transition state,s positive difference (AG)in free △Gt(uncatalyzed energy between the substrate and catalyzed) product ò Substrate The free energy of activation for AG the transition state limits the for the reaction progress of the reaction Enzymes act by reducing the free Product energy of the transition state Reaction progress
Enzymes catalyze by stabilizing transition states • Free energy G of a chemical reaction can be plotted over time • Favorable reactions have a positive difference (DG) in free energy between the substrate and product • The free energy of activation for the transition state limits the progress of the reaction • Enzymes act by reducing the free energy of the transition state

Importance of intermediate states (L8-4) Transition state ( 4 uncat -AGt -ES一EP at S P Reaction coordinate
Importance of intermediate states (L8-4)
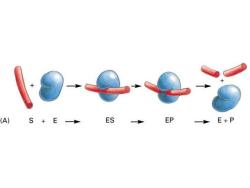
(A) S+E ES EP E+P

(A)HYDROLYSIS OF AN AMIDE BOND ● -N-H+ H tetrahedral water intermediate (B)TRANSITION-STATE ANALOG FOR AMIDE HYDROLYSIS HN HN NH NH O NO2 OH O analog amide Figure 3-47.Molecular Biology of the Cell,4th Edition
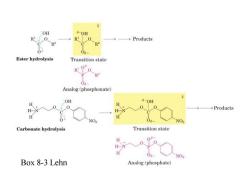
OH 6-0H R 0 R 0 →Products 0 08 Ester hydrolysis Transition state 06 R 0 R Analog (phosphonate) OH 8-0H H H-N H一】 →Products H NO NO Carbonate hydrolysis Transition state H 06 H-N H NO Box 8-3 Lehn Analog (phosphate)
Box 8-3 Lehn
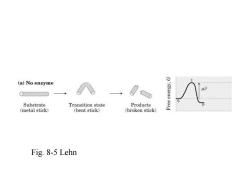
(a)No enzyme Substrate Transition state Products (metal stick) (bent stick) (broken stick) Fig.8-5 Lehn
Fig. 8-5 Lehn
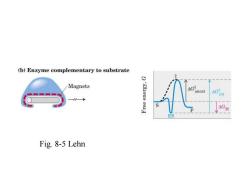
(b)Enzyme complementary to substrate Magnets Gancat → ES Fig.8-5 Lehn
Fig. 8-5 Lehn

(c)Enzyme complementary to transition state G neat Reaction coordinate Fig.8-5 Lehn
Fig. 8-5 Lehn
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第九章 代谢调节 Specificity Is the Result of Molecular Recognition.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第五章 脂类代谢 Lipid.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第四章 糖类代谢 Carbohydrates.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第三章 酶 Protein Structures.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第一章 核酸化学 Chemistry Is the Logic of Biological Phenomena.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十六 用阳离子交换树脂摄取氯化钠.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十四 还原糖和总糖含量的测定.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十三 蛋白质的两性性质及等电点的测定.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十二 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十一 蛋白质脱盐.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十 脲酶Km值测定.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验九 酶的基本性质.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验七 小麦萌发前后淀粉酶活力的比较.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验六 蛋白质含量测定(考马斯亮蓝G-250法).doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验五 蛋白质的水解和氨基酸的纸层析法分离.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验四 甲醛滴定法测定氨基氮.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验三 酵母RNA的提制(浓盐法).doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 菜花(花椰莱)中核酸的分离和鉴定.doc
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 醋酸纤维薄膜电泳分离核苷酸.doc
- 河南师范大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 可逆电池.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)绪论 Biochemistry(主讲:陈新建).ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第一章 核酸化学.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第二章 蛋白质.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第三章 酶 Enzyme.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第四章 糖类代谢.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第六章 含氮化合物的代谢.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第七章 核酸的生物合成.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第八章 蛋白质的生物合成.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第九章 物质代谢的调控.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第十章 生物膜.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)生物化学绪论.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 蛋白质化学.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 酶学.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 糖类代谢.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 含氮化合物代谢.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 核酸的生物合成.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第八章 蛋白质的生物合成(1/2).ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第八章 蛋白质的生物合成(2/2).ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第九章 代谢调节.ppt
- 青岛农业大学(莱阳农学院):《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(主讲:杨爱萍).ppt
