南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 3 Eukaryotic Microorganism

Chapter 3 Eukaryotic Microorganism
Chapter 3 Eukaryotic Microorganism

Definition Eukaryotic microorganisms have the nuclear membrane coating a cell nucleus,carry out mitosis,and have mitochondria in the cytoplasm. They mainly include yeast (unicelluar fungi), filamentous fungi,microalgae and protozoa. Thus,the eukaryotic microorganisms is not a natural monophyletic taxon.The Fungi is one of the most significant kingdoms in these Eukaryotic microorganisms which have more species
Eukaryotic microorganisms have the nuclear membrane coating a cell nucleus, carry out mitosis, and have mitochondria in the cytoplasm. They mainly include yeast (unicelluar fungi), filamentous fungi, microalgae and protozoa. Thus, the eukaryotic microorganisms is not a natural monophyletic taxon. The Fungi is one of the most significant kingdoms in these Eukaryotic microorganisms which have more species. Definition

Eukaryotic Microorganisms Molds Mushrooms Fungi Yeasts Microalgae Algae Protozoa
Molds Mushrooms Fungi Yeasts Microalgae Algae Protozoa Eukaryotic Microorganisms

The kingdom Fungi is a natural taxon.Members in this kingdom involve very tiny yeast and larger mushroom.In the biologist's viewpoint,this term fungus indicates those organisms that have true nucleus,produce spores by asexual or sexual reproduction,absorb the nourishment material, have no chloroplast. As the development of biosystematics including fungal systematics,some organisms that were thought to been belong to the Fungi in the past have been classificated into other kingdoms now,For example,Oomycetes and Hyphochytidiomycetes is put into the kingdom Chromista or Straminipila,Myxomycetes and Plasmodiophoremycetes into the Protozoa
The kingdom Fungi is a natural taxon. Members in this kingdom involve very tiny yeast and larger mushroom. In the biologist’s viewpoint, this term fungus indicates those organisms that have true nucleus, produce spores by asexual or sexual reproduction, absorb the nourishment material, have no chloroplast. As the development of biosystematics including fungal systematics, some organisms that were thought to been belong to the Fungi in the past have been classificated into other kingdoms now, For example, Oomycetes and Hyphochytidiomycetes is put into the kingdom Chromista or Straminipila, Myxomycetes and Plasmodiophoremycetes into the Protozoa

Major characters of fungi ①with a real nucleus 2having no chloroplast and photosynthesis 3vegetative bodies are usually developing filamentous and branched structure as well as unicell 4 typically forming asexual and sexual reproductive spores containing chitin in the cell wall 6heterotrophy by absorption more living adaptively in the land
Major characters of fungi ①with a real nucleus ②having no chloroplast and photosynthesis ③vegetative bodies are usually developing filamentous and branched structure as well as unicell ④ typically forming asexual and sexual reproductive spores ⑤containing chitin in the cell wall ⑥heterotrophy by absorption ⑦more living adaptively in the land
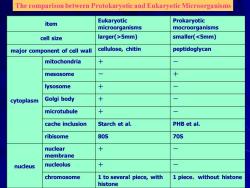
The comparison between Protokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microorganisms item Eukaryotic Prokaryotic microorganisms mocroorganisms cell size larger(>5mm) smaller(<5mm) major component of cell wall cellulose,chitin peptidoglycan mitochondria mesosome + lysosome + cytoplasm Golgi body + microtubule + cache inclusion Starch et al. PHB et al. ribisome 80S 70S nuclear membrane nucleus nucleolus chromosome 1 to several piece,with 1 piece,without histone histone
The comparison between Protokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microorganisms item Eukaryotic microorganisms Prokaryotic mocroorganisms cell size larger(>5mm) smaller(<5mm) major component of cell wall cellulose, chitin peptidoglycan cytoplasm mitochondria + - mesosome - + lysosome + - Golgi body + - microtubule + - cache inclusion Starch et al. PHB et al. ribisome 80S 70S nucleus nuclear membrane + - nucleolus + - chromosome 1 to several piece, with histone 1 piece,without histone

CelI Structure of Eukaryotic Microorganism Cell Wall yeast:mannan and glucan fungi:chitin Flagellum 9+2 type Cytomembrane sterol
Cell Structure of Eukaryotic Microorganism Cell Wall yeast: mannan and glucan fungi:chitin Flagellum Cytomembrane 9+2 type sterol

Cytoplasma and Cell Nucleous lysosome microbody lomasome hydrogenosome vacuole microfilum mitochondria
lysosome microbody lomasome hydrogenosome Cytoplasma and Cell Nucleous vacuole microfilum mitochondria

Section 1 Filamentous fungi-Molds Fungi also are extensive to distribute in moist place and are very important to mankind,the current benefit is again harmful.At the vegetative stage,the fungi mainly exit in a form of hypha.Mold is the popularized name of filamentous fungi.There are filamentous fungi nearly throughout the world
Section 1 Filamentous fungi——Molds Fungi also are extensive to distribute in moist place and are very important to mankind, the current benefit is again harmful. At the vegetative stage, the fungi mainly exit in a form of hypha. Mold is the popularized name of filamentous fungi. There are filamentous fungi nearly throughout the world

Vegetative bodies Septate hyphae and Mycelium non-septate hyphae Cited from"Taxonomic illustration of the fungal genus"edited by Zhou Maofan (1983)
Cited from “Taxonomic illustration of the fungal genus” edited by Zhou Maofan(1983) Mycelium Septate hyphae and non-septate hyphae Vegetative bodies
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 2 Prokaryotic Microorganism.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 1 Introduction of Microbiology.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第九章 微生物的生态(microbiological ecology).ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第八章 微生物遗传学.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第七章 微生物生长.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第六章 微生物代谢调节.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第五章 微生物的营养与培养基.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第四章 病毒.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第三章 真核微生物.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第二章 原核微生物.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第一章 绪论 Microbiology.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第十章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 微生物生态和废水的生物处理.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 微生物菌种的选育.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 环境因子对微生物生长和代谢的影响.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 微生物的代谢与调节及其人工控制.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 微生物的营养与生长.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论 Microbiology(主讲:樊游).ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)实验十三 酒曲或其他样品中某类特定微生物的 分离纯化(设计).doc
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)实验十 二 质粒DNA的小量制备、电泳检测及细菌转化.doc
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 4 The Viruses.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 5 Microbial Nutrition and Culture Medium.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 6 Microbial Metabolism.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 7 Microbial Growth.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 9 Microbial Ecology.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验十 细菌的凝集反应.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验十一 水的微生物学检查.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验一 细菌的单染色及油镜的使用.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验二 革兰氏染色及细菌特殊结构观察.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验三 霉菌、放线菌形态观察及微生物菌落观察.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验四 微生物的显微镜直接计数法和大小的测定.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验五 培养基的制备、器具包扎和灭菌.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验六 微生物的接种技术及分离纯化.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验七 环境因素对微生物的影响.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验八 微生物的生理生化反应.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验九 噬菌体的分离.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(参考资料)微生物基本术语(英汉对照词汇).pdf
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 DNA的结构.ppt
