南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 5 Microbial Nutrition and Culture Medium

Chapter 5 Microbial Nutrition and Culture medium
Chapter 5 Microbial Nutrition and Culture medium

Nutrition Nutrition is a process by which chemical substances called nutrients are required from the environment and used for the cellular activities of metabolism and growth. Nutrient:the substance could be used by microbes for metabolism or reproduction of cells
Nutrition : Nutrition is a process by which chemical substances called nutrients are required from the environment and used for the cellular activities of metabolism and growth. Nutrient:the substance could be used by microbes for metabolism or reproduction of cells
Nutrient provide the structural substance,energy, metabolic regulate substance and appropriate physiological environment. Some microbes could use nonmaterial energy-light
Nutrient provide the structural substance , energy, metabolic regulate substance and appropriate physiological environment. Some microbes could use nonmaterial energy-light

Section 1 Six kinds of essential nutrient for microbes I.cellular chemical constitutes It's much alike in the life in the element The main elements areC、H、O、N(90%-g7%to total dry cell weight),Cis about 50%,the others are inorganic nutrient.C/N is 5:1 usually
I. cellular chemical constitutes It’s much alike in the life in the element . The main elements are C、H、O、N (90%-97% to total dry cell weight), C is about 50%, the others are inorganic nutrient. C/N is 5:1 usually. Section 1 Six kinds of essential nutrient for microbes

element ☑Macronutrient:C、H、O、N、P、S ☑others element:K、Na、Ca、Mg、Fe、Mn、 Cu、Co、Zn、Mo,etal ■Existence form: ■☑organic:protein、sugar、lipoid、 nucleic acid、vitamin、decomposition substance,metabolic medial products u☑inorganic salt ash ■☑Vater-.=-70%~90%to wet cell weight
element ØMacronutrient :C、H、O、N、P、 S Øothers element:K、Na、Ca、Mg、Fe、Mn、 Cu、Co、Zn、Mo, et al Existence form: Ø organic:protein、sugar、lipoid、 nucleic acid、vitamin、decomposition substance、metabolic medial products Ø inorganic salt ash Ø Water-70% ~ 90% to wet cell weight
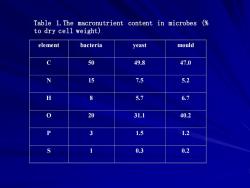
Table 1.The macronutrient content in microbes ( to dry cell weight) element bacteria yeast mould 50 49.8 47.0 15 7.5 5.2 8 5.7 6.7 20 31.1 40.2 3 1.5 1.2 0.3 0.2
element bacteria yeast mould C 50 49.8 47.0 N 15 7.5 5.2 H 8 5.7 6.7 O 20 31.1 40.2 P 3 1.5 1.2 S 1 0.3 0.2 Table 1.The macronutrient content in microbes (% to dry cell weight)

Microbes is omnivorous. The substance utilized by generic species could be utilized by microbes too. The substance couldn't be utilized by generic species could be utilized by microbes. Some kinds of substance harmful to generic species also could be utilized by microbes
The substance utilized by generic species could be utilized by microbes too. The substance couldn’t be utilized by generic species could be utilized by microbes. Some kinds of substance harmful to generic species also could be utilized by microbes. Microbes is omnivorous

ll.Main nutrient and the function ■Carbon source ■Nitrogen source ■Energy source Growth factor ☐Inorganic salt Water
II. Main nutrient and the function Carbon source Nitrogen source Energy source Growth factor Inorganic salt Water

Functions: vconstitute the cells of the microbes uvprovide the energy needed in the physiological activity to microbes uvthe source to form the microbial metabolic products uNutrient is the substance base for microbial metabolism and living activity. If lose this base,the life will die
Functions: vconstitute the cells of the microbes vprovide the energy needed in the physiological activity to microbes vthe source to form the microbial metabolic products Nutrient is the substance base for microbial metabolism and living activity. If lose this base, the life will die

1.Carbon sources The nutrient provide the carbon element for microbies Organic carbon sources:protein,nucleic acid,starch,glucose,et al Inorganic acid:CO2,Na,CO3,CaCO3 et al Heterotrophic microbe:is an organism must obtain its carbon in an organic form. Autotrophic microbe:is an organism that uses CO2,an inorganic gas,as its carbon source
Heterotrophic microbe: is an organism must obtain its carbon in an organic form. Autotrophic microbe: is an organism that uses CO2 , an inorganic gas, as its carbon source. 1.Carbon sources The nutrient provide the carbon element for microbies ❑Organic carbon sources: protein, nucleic acid, starch, glucose, et al ❑Inorganic acid: CO2 , Na2CO3 , CaCO3 et al
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 4 The Viruses.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 3 Eukaryotic Microorganism.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 2 Prokaryotic Microorganism.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 1 Introduction of Microbiology.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第九章 微生物的生态(microbiological ecology).ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第八章 微生物遗传学.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第七章 微生物生长.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第六章 微生物代谢调节.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第五章 微生物的营养与培养基.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第四章 病毒.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第三章 真核微生物.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第二章 原核微生物.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第一章 绪论 Microbiology.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版)第十章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 微生物生态和废水的生物处理.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 微生物菌种的选育.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 环境因子对微生物生长和代谢的影响.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 微生物的代谢与调节及其人工控制.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 微生物的营养与生长.ppt
- 江南大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论 Microbiology(主讲:樊游).ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 6 Microbial Metabolism.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 7 Microbial Growth.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chapter 9 Microbial Ecology.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验十 细菌的凝集反应.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验十一 水的微生物学检查.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验一 细菌的单染色及油镜的使用.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验二 革兰氏染色及细菌特殊结构观察.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验三 霉菌、放线菌形态观察及微生物菌落观察.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验四 微生物的显微镜直接计数法和大小的测定.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验五 培养基的制备、器具包扎和灭菌.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验六 微生物的接种技术及分离纯化.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验七 环境因素对微生物的影响.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验八 微生物的生理生化反应.ppt
- 南京师范大学:《微生物学》课程PPT教学课件(实验指导)实验九 噬菌体的分离.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(参考资料)微生物基本术语(英汉对照词汇).pdf
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 DNA的结构.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 有机体、染色体和基因.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 DNA复制(DNA Replication).ppt
