《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)19 opioid analgesics and antagonists

opioid analgesics and antagonistOpioids are usually understand to include all ofthe natural and semisynthetic alkaloidderivatives from opiumMorphine is the prototypical opioid agonistAll drugs in this category act by binding to opioidreceptors in the CNS to produce effects that mimic theaction of endogenous opioid peptides
opioid analgesics and antagonist Opioids are usually understand to include all of the natural and semisynthetic alkaloid derivatives from opium. Morphine is the prototypical opioid agonist All drugs in this category act by binding to opioid receptors in the CNS to produce effects that mimic the action of endogenous opioid peptides

The classification of the painAcute pain:which does not outlast the initiatingpainful stimulus, include Burns,myocardialinfarctionChronic pain: outlasts the initiating stimulussuch as cancer ,arthritis and neuropathic painSuch drugs eliminate pain by either decreasingthe underlying cause of the pain or decreasingthe transmission of nociceptive impulses andpain perception
The classification of the pain Acute pain:which does not outlast the initiating painful stimulus, include Burns, myocardial infarction Chronic pain: outlasts the initiating stimulus such as cancer ,arthritis and neuropathic pain Such drugs eliminate pain by either decreasing the underlying cause of the pain or decreasing the transmission of nociceptive impulses and pain perception

I. Basic pharmacology of the opioid analgesicsClassification :full agonistsmorphineOpioid drugdezocinepartialagonistsnaloxoneantagonists
I. Basic pharmacology of the opioid analgesics Classification : full agonists morphine Opioid drug partial agonists dezocine antagonists naloxone

EndogenousOpioidsThe endogenous opioids are naturally occurringpeptides include:enkephalins, β -endorphin and dynorphinsenkephalins were first discovered in the brainwhich means from the head.The endogenous opioids modulate most of thecritical functions of the body, includinghormonal fluctuations, thermoregulation
Endogenous Opioids The endogenous opioids are naturally occurring peptides include: enkephalins, β -endorphin and dynorphins enkephalins were first discovered in the brain which means from the head. The endogenous opioids modulate most of the critical functions of the body, including hormonal fluctuations, thermoregulation

mediation of stress and anxiety, production ofanalgesia, and development ofopioid toleranceand dependence. The endogenousopioidsmaintain homeostasis, amplify signals fromthe periphery to the brain, and serveasneuromodulatorsof the body's responsetoexternal stimuli. As such, the endogenousofopioids are critical to themaintenancehealth and a sense of well-being
mediation of stress and anxiety, production of analgesia, and development of opioid tolerance and dependence. The endogenous opioids maintain homeostasis, amplify signals from the periphery to the brain, and serve as neuromodulatorsof the body’s response to external stimuli. As such, the endogenous opioids are critical to the maintenance of health and a sense of well-being

PharmacodynamicssA:mechanism of actionOpioid agonists produce analgesia by binding tospecific receptors in brain and spinal cord regions1.Receptor types (μ, 8 ,and k )μreceptor: μ,μl2Oreceptor: 0,2k receptor: KKK
Pharmacodynamics: A:mechanism of action Opioid agonists produce analgesia by binding to specific receptors in brain and spinal cord regions 1.Receptor types (μ,δ,and κ ) μreceptor: μ1 μ2 δreceptor: δ1 δ2 κ receptor: κ1 κ2 κ3

2.Relation of physiologic effects to receptor typeμ, R: mediate the analgesic and euphoric effectsof the opioids and physical dependence on themμ,R: mediate the bradycardiac and respiratorydepressanteffectsR: mediate spinal analgesic effects and have beenimplicated in the modulation of tolerance toμ-opioidsk R: mediate spinal analgesia, miosis, sedation, anddiuresis
2.Relation of physiologic effects to receptor type μ1 R: mediate the analgesic and euphoric effects of the opioids and physical dependence on them μ2R: mediate the bradycardiac and respiratory depressant effects δR: mediate spinal analgesic effects and have been implicated in the modulation of tolerance to μ-opioids κ R: mediate spinal analgesia, miosis, sedation, and diuresis
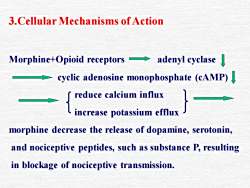
3.Cellular Mechanisms of Actionadenyl cyclaseMorphine+Opioid receptorscyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)reduce calcium influxincrease potassium effluxmorphine decrease the release of dopamine, serotonin,and nociceptive peptides, such as substance P, resultingin blockage of nociceptive transmission
3.Cellular Mechanisms of Action Morphine+Opioid receptors adenyl cyclase cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) reduce calcium influx increase potassium efflux morphine decrease the release of dopamine, serotonin, and nociceptive peptides, such as substance P, resulting in blockage of nociceptive transmission

4.Tolerance and Physical DependenceThe biochemicalmechanisms are unclearwithTolerancefrequentlyrepeatedofdosesadministrationoftherapeuticmorphine or its surrogates,there is a gradualloss in effectiveness.to reproduce the originalresponse,a larger dose must be administrated
4.Tolerance and Physical Dependence The biochemical mechanisms are unclear. Tolerance : with frequently repeated administrationof therapeutic doses of morphine or its surrogates,there is a gradual loss in effectiveness.to reproduce the original response,a larger dose must be administrated

Physical Dependence :the cessation of opioiddrug administrationleads to an observableabstinence syndrome.signs of withdrawalinclude chills, fever,diarrhea,sweating,vomiting,yawning,Thedizziness, andhypertension.nausea,onset of symptoms occurs 6 to 12 hours aftercontinues for severalthe last drug dose anddays
Physical Dependence : the cessation of opioid drug administration leads to an observable abstinence syndrome. signs of withdrawal include chills, fever, sweating, yawning, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, dizziness, and hypertension. The onset of symptoms occurs 6 to 12 hours after the last drug dose and continues for several days
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)05 the autonomic nervous system.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)10 adrenergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)06 cholinergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)07 adrenergic antagonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)12 antidepression.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十八章 抗菌药物概论.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十九章 β-内酰胺类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十一章 氨基苷类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十章 大环内酯类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十三章 人工合成类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十四章 肾上腺皮质激素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十三章 作用于血液及造血器官药物.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十六章 甲状腺激素和抗甲状腺药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十五章 胰岛素及口服降血糖药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十五章 抗心律失常药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十三章 利尿药及脱水药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十九章 抗高血压药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十六章 治疗慢性充血性心力衰竭的药物.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十七章 抗心肌缺血药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(中枢神经系统药物)第十五章 镇静催眠药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)18 neuroleptic drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)13 anesthesia.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)17 Antiparkin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)12 central nervous system stimulants.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)28 Agents Used in Hyperlipidemia.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)27 treatment for CHF2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)29 treatment for angina pectoris.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)20 anti-inflammation drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)23 diuretic.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)25 treatment for arrthymia2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)35 insullin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)34 adrenocortical hormones.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)36 thyroid drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43b Sulfonamides and other Synthetic Antimicrobial Drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43a Quinolones and Urinary Tract Antiseptics.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)41 Aminoglycosides.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)42 Tetracyclines, Chloramphenicol.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)38 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)40 Macrolides, Lincomycin, Clindamycin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)39 Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis.ppt
