《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)13 anesthesia

CompanynameAnesthetic drugs
Company name Anesthetic drugs

Key termsAnesthesiaIs a loss of feeling or sensation.There are two types of anesthesia: local anesthesia andgeneral anesthesiaLocal anesthesiaIs the provision of a pain-free state in a aspecific area(or region).The patient is fully awake but does not feel pain in thearea tha has been anesthetizeGeneral anesthesiaIs the provision of a pain-free state for the entire bodyThe patient loses consciousness and feels no pain.Company Logo
Company Logo Key terms Anesthesia Is a loss of feeling or sensation. There are two types of anesthesia: local anesthesia and general anesthesia. Local anesthesia Is the provision of a pain-free state in a aspecific area (or region). The patient is fully awake but does not feel pain in the area tha has been anesthetize. General anesthesia Is the provision of a pain-free state for the entire body. The patient loses consciousness and feels no pain
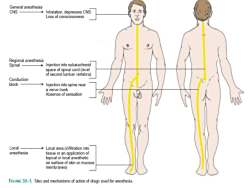
GeneralanesthesiaCNSInhalation,depressesCNs+LossofconsciousnessRegional anesthesiaInjectionintosubarachnoidSpinalspaceof spinal cord (levelofsecondlumbarvertebra)Conductionblock+Injection intospinenearanervetrunkRAbsenceofsensationLocalLocalarea(infiltrationintoanesthesiatissueoranapplicationoftopicalorlocalanestheticonsurfaceofskinormucousmembranes)FicuRE35-1.Sitesandmechanismsofactionofdrugsusedforanesthesia
Company Logo

PREANESTHETICDRUGSPurpose of Preanesthetic Drugs? Narcotic or antianxiety drug-to decrease anxietyand apprehension immediately before surgery.? Cholinergic blocking drugto decrease secretions ofthe upper respiratory tract. invoid pneumonia oratelectasis· Antiemetic-to lessen the incidence of nausea andvomiting during the immediate postoperativerecovery periodCompany Logo
Company Logo PREANESTHETIC DRUGS Purpose of Preanesthetic Drugs • Narcotic or antianxiety drug—to decrease anxiety and apprehension immediately before surgery. • Cholinergic blocking drug—to decrease secretions of the upper respiratory tract. invoid pneumonia or atelectasis. • Antiemetic—to lessen the incidence of nausea and vomiting during the immediate postoperative recovery period

EXAMPLESOFPREANESTHETICTABLE35-2DRUGSGENERIC NAMETRADENAMENarcoticsdroperidolInapsinefentanylSublimaze,genericmeperidinehydrochlorideDemerol,genericDuramorph,genericmorphinesulfateBarbituratespentobarbitalNembutalSodium,genericsecobarbitalgenericCholinergic-BlockingDrugsgenericatropinesulfateRobinul,genericglycopyrrolatescopolaminegenericAntianxietyDrugsWithAntiemeticPropertieshydroxyzineAtarax,Vistaril,genericAntianxietyDrugschlordiazepoxideLibrium,genericValium,genericdiazepamVersedmidazolam-ogo
Company Logo

GENERALANESTHESIAThe administration of general anesthesiarequires the use of one or more drugs. Thechoice of anesthetic drug depends on manyfactors, including·The general physical condition of the patient · The area, organ, or system being operated on · The anticipated length of the surgicalprocedureCompany Logo
Company Logo The administration of general anesthesia requires the use of one or more drugs. The choice of anesthetic drug depends on many factors, including: • The general physical condition of the patient • The area, organ, or system being operated on • The anticipated length of the surgical procedure GENERAL ANESTHESIA

Methohexital and ThiopentalThese drugs have a rapid onset and a short duration ofaction. They depress the central nervous system (CNS)to produce hypnosis and anesthesia but do not produceanalgesia. Recovery after a small dose is rapidClinic use· Induction of anesthesia? Short surgical procedures with minimal painfulstimuli? In conjunction with or as a supplement to otheranesthetics? Control of convulsive states (thiopental)Company Logo
Company Logo Clinic use • Induction of anesthesia • Short surgical procedures with minimal painful stimuli • In conjunction with or as a supplement to other anesthetics • Control of convulsive states (thiopental) Methohexital and Thiopental These drugs have a rapid onset and a short duration of action. They depress the central nervous system (CNS) to produce hypnosis and anesthesia but do not produce analgesia. Recovery after a small dose is rapid

口Etomidate Etomidate (Amidate),a nonbarbiturate,isusedforinduction of anesthesia.Etomidate also may beusedtosupplementotheranesthetics,suchasnitrousoxide,forshortsurgical procedures.Itisahypnoticwithoutanalgesic activity口PropofolPropofol (Diprivan)is usedfor induction andmaintenance of anesthesia.It also may be usedforsedation during diagnostic procedures andprocedures that use a local anesthetic.This drugalso is usedforcontinuous sedation ofintubated orrespiratory-controlled patients in intensive careunits.Company Logo
Company Logo Etomidate Etomidate (Amidate), a nonbarbiturate, is used for induction of anesthesia. Etomidate also may be used to supplement other anesthetics, such as nitrous oxide, for short surgical procedures. It is a hypnotic without analgesic activity. Propofol Propofol (Diprivan) is used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It also may be used for sedation during diagnostic procedures and procedures that use a local anesthetic. This drug also is used for continuous sedation of intubated or respiratory-controlled patients in intensive care units

MidazolamMidazolam Versed),a short-acting benzodiazepine CNSdepressant,is used as a preanesthetic drugto relieveanxiety:forinduction of anesthesia,for conscioussedation beforeminorprocedures,suchas endoscopicprocedures;andto supplementnitrous oxide andoxygenfor short surgical procedures.Whenthedrug is used forinduction anesthesia,thepatient graduallylosesconsciousness duringaperiodof 1to2minutesSevoflurane口Sevoflurane (Ultane)is an inhalational analgesic.It is口usedforinduction andmaintenance ofgeneralanesthesia in adult and pediatric patients for inpatientand outpatient surgical procedures.Company Logo
Company Logo Midazolam Midazolam (Versed), a short-acting benzodiazepine CNS depressant, is used as a preanesthetic drug to relieve anxiety; for induction of anesthesia; for conscious sedation before minor procedures, such as endoscopic procedures; and to supplement nitrous oxide and oxygen for short surgical procedures. When the drug is used for induction anesthesia, the patient gradually loses consciousness during a period of 1 to 2 minutes. Sevoflurane Sevoflurane (Ultane) is an inhalational analgesic. It is used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia in adult and pediatric patients for inpatient and outpatient surgical procedures

KetamineKetamine(Ketalar)isarapid-actinggeneralanesthetic.Itproduces ananestheticstatecharacterizedbyprofoundanalgesia,cardiovascularandrespiratorystimulation,normalorenhancedskeletalmuscletone,andoccasionallymildrespiratorydepression.Ketamineisusedfordiagnosticandsurgicalproceduresthat donotreguirerelaxationofskeletalmuscles,forinductionofanesthesiabeforetheadministrationofotheranestheticdrugs,and as asupplementto otheranestheticdrugs.Cyclopropane口Ananestheticgas,cyclopropanehasarapidonsetofaction口and maybeusedforinductionandmaintenanceofanesthesia.Skeletalmusclerelaxationisproducedwithfullanestheticdoses.Cyclopropaneissuppliedinorangecylinders.Disadvantagesofcyclopropanearedifficultyindetectingtheplanesofanesthesia,occasionallaryngospasmcardiacarrhythmias,andpostanesthesianausea,vomiting,andheadache.Cyclopropaneandoxygenmixtures areexplosive,whichlimitstheuseofthisgasanestheticCompanyLogo
Company Logo Ketamine Ketamine (Ketalar) is a rapid-acting general anesthetic. It produces an anesthetic state characterized by profound analgesia, cardiovascular and respiratory stimulation, normal or enhanced skeletal muscle tone, and occasionally mild respiratory depression. Ketamine is used for diagnostic and surgical procedures that do not require relaxation of skeletal muscles, for induction of anesthesia before the administration of other anesthetic drugs, and as a supplement to other anesthetic drugs. Cyclopropane An anesthetic gas, cyclopropane has a rapid onset of action and may be used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. Skeletal muscle relaxation is produced with full anesthetic doses. Cyclopropane is supplied in orange cylinders. Disadvantages of cyclopropane are difficulty in detecting the planes of anesthesia, occasional laryngospasm, cardiac arrhythmias, and postanesthesia nausea, vomiting, and headache. Cyclopropane and oxygen mixtures are explosive, which limits the use of this gas anesthetic
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)18 neuroleptic drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)19 opioid analgesics and antagonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)05 the autonomic nervous system.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)10 adrenergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)06 cholinergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)07 adrenergic antagonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)12 antidepression.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十八章 抗菌药物概论.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十九章 β-内酰胺类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十一章 氨基苷类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十章 大环内酯类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十三章 人工合成类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十四章 肾上腺皮质激素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十三章 作用于血液及造血器官药物.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十六章 甲状腺激素和抗甲状腺药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十五章 胰岛素及口服降血糖药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十五章 抗心律失常药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十三章 利尿药及脱水药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十九章 抗高血压药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十六章 治疗慢性充血性心力衰竭的药物.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)17 Antiparkin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)12 central nervous system stimulants.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)28 Agents Used in Hyperlipidemia.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)27 treatment for CHF2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)29 treatment for angina pectoris.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)20 anti-inflammation drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)23 diuretic.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)25 treatment for arrthymia2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)35 insullin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)34 adrenocortical hormones.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)36 thyroid drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43b Sulfonamides and other Synthetic Antimicrobial Drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43a Quinolones and Urinary Tract Antiseptics.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)41 Aminoglycosides.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)42 Tetracyclines, Chloramphenicol.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)38 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)40 Macrolides, Lincomycin, Clindamycin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)39 Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis.ppt
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学大纲 Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics.doc
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学资源(教案,2012版).doc
