《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)29 treatment for angina pectoris

vasodilators & the treatment of angina pectoris
vasodilators & the treatment of angina pectoris

what is angina pectoris?symptom ofAngina pectoris is a common(CAD)byarterydiseasecausedcoronarytransient episodes of myocardial ischemia andanoxia.Pathophysiology of anginaAngina pectoris results from an imbalancebetween oxygen supply-demand relationship inischemic regions ofthemyocardium
what is angina pectoris? Angina pectoris is a common symptom of coronary artery disease (CAD) caused by transient episodes of myocardial ischemia and anoxia. Pathophysiology of angina Angina pectoris results from an imbalance between oxygen supply-demand relationship in ischemic regions of the myocardium

Key factors for oxygen demand includes:myocardial wall tensionintraventricular pressureventricular volumewall thicknessheart ratecontractility
Key factors for oxygen demand includes: myocardial wall tension intraventricular pressure ventricular volume wall thickness heart rate contractility

For oxygen supply includes:coronarybloodflowbloodpressureduration of diastolecoronary vascular bed resistance
For oxygen supply includes: coronary blood flow blood pressure duration of diastole coronary vascular bed resistance
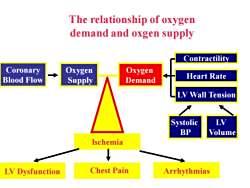
The relationship of oxygendemand and oxgen supplyContractilityCoronaryOxygenOxygenHeartRateBlood FlowSupplyDemandLVWall TensionLVSystolicBPVolumeIschemiaChest PainArrhythmiasLV Dysfunction
The relationship of oxygen demand and oxgen supply Coronary Blood Flow Oxygen Supply Oxygen Demand Systolic BP LV Volume Contractility Heart Rate LV Wall Tension Arrhythmias Ischemia LV Dysfunction Chest Pain

Classification of angina pectoris patterns1. Stable angina (classical angina)the primary cause of angina pectoris is an imbalance between theoxygen requirement of the heart and the oxygen supplied to it viathe coronary vessels(such as stenosis of coronary arteries)2. Unstable angina (crescendo angina)unstable angina is caused by episodes of increased epicardialcoronary artery tone or small platelet clots occurring in thevicinity of an atherosclerotic plaque.3. Variant angina (prinzmetal's angina)variant angina is caused by spontaneous coronary spasm, eitherat work or at rest, rather than by increases in myocardial oxygenrequirements
Classification of angina pectoris patterns 1. Stable angina (classical angina) the primary cause of angina pectoris is an imbalance between the oxygen requirement of the heart and the oxygen supplied to it via the coronary vessels(such as stenosis of coronary arteries ). 2. Unstable angina (crescendo angina) unstable angina is caused by episodes of increased epicardial coronary artery tone or small platelet clots occurring in the vicinity of an atherosclerotic plaque. 3. Variant angina (prinzmetal’s angina) variant angina is caused by spontaneous coronary spasm, either at work or at rest, rather than by increases in myocardial oxygen requirements

The conditions can cause unstable anginaCoronary atherosclerosis2Coronary artery spasm3Transient platelet aggregationCoronary thrombosis5Endothelia injury causing the accumulation ofvasocontraction substances6Coronary vasocontraction following adrenergicstimulation
The conditions can cause unstable angina 1 Coronary atherosclerosis 2 Coronary artery spasm 3 Transient platelet aggregation 4 Coronary thrombosis 5 Endothelia injury causing the accumulation of vasocontraction substances 6 Coronary vasocontraction following adrenergic stimulation

Variant angina occurs at rest, at the sametime each day, and is usually due tocoronary artery spasm.: It is characterized by an elevated STsegment on the ECG during chest pain, andmay be accompanied by ventriculararrhythmias
• Variant angina occurs at rest, at the same time each day, and is usually due to coronary artery spasm. • It is characterized by an elevated ST segment on the ECG during chest pain, and may be accompanied by ventricular arrhythmias

Any way to relieve the chest pain?Any idea to ‘cure'the chest pain?
Any way to relieve the chest pain? Any idea to ‘cure’ the chest pain?

Awaywhichcankeepabalancebetweenoxygen supply-demand may ameliorateangina--relievethe pain.You can reduce oxygen demand or increaseoxygen supply or both to relieve the pain
• A way which can keep a balance between oxygen supply-demand may ameliorate angina-relieve the pain. • You can reduce oxygen demand or increase oxygen supply or both to relieve the pain
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)27 treatment for CHF2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)28 Agents Used in Hyperlipidemia.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)12 central nervous system stimulants.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)17 Antiparkin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)13 anesthesia.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)18 neuroleptic drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)19 opioid analgesics and antagonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)05 the autonomic nervous system.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)10 adrenergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)06 cholinergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)07 adrenergic antagonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)12 antidepression.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十八章 抗菌药物概论.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十九章 β-内酰胺类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十一章 氨基苷类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十章 大环内酯类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十三章 人工合成类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十四章 肾上腺皮质激素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十三章 作用于血液及造血器官药物.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十六章 甲状腺激素和抗甲状腺药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)20 anti-inflammation drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)23 diuretic.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)25 treatment for arrthymia2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)35 insullin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)34 adrenocortical hormones.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)36 thyroid drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43b Sulfonamides and other Synthetic Antimicrobial Drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43a Quinolones and Urinary Tract Antiseptics.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)41 Aminoglycosides.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)42 Tetracyclines, Chloramphenicol.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)38 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)40 Macrolides, Lincomycin, Clindamycin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)39 Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis.ppt
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学大纲 Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics.doc
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学资源(教案,2012版).doc
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学资源(讲稿,2014版).doc
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷6(答案).doc
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5(答案).doc
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷6(试题).doc
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5(试题).doc
