《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)18 neuroleptic drugs

Antipsychotic DrugsBasic concepts of psychotic disordersPsychotic disorders are characterized by a mental statethat is out of touch with reality, involving a varietyof abnormalities of perception, thought, and ideasPsychotic illnesses :1. Schizophrenia2. Schizoaffective disorder3. Delusional disorders4.Somedepressiveandmanicillnesses
Basic concepts of psychotic disorders Psychotic disorders are characterized by a mental state that is out of touch with reality, involving a variety of abnormalities of perception, thought, and ideas. Psychotic illnesses : 1. Schizophrenia 2. Schizoaffective disorder 3. Delusional disorders 4. Some depressive and manic illnesses Antipsychotic Drugs

SchizophreniaSymptoms and signsSchizophrenia is a psychotic illness characterized bymultiple symptoms affecting thought, perception.emotion,and volitionSymptoms fall into two groups (positive and negative)Positive symptoms1)Delusions2) Hallucinations3) Thought alienation and disordered thought
Schizophrenia Symptoms and signs Schizophrenia is a psychotic illness characterized by multiple symptoms affecting thought, perception, emotion, and volition. Symptoms fall into two groups (positive and negative) Positive symptoms 1) Delusions 2) Hallucinations 3) Thought alienation and disordered thought

Negative symptoms1) Poverly of speech2) Flattening of affect3) Social withdrawal4) Anhedonia5) Avolition/apathy, involving reduced drive, energy,and interest6) Attention deficit, manifested by inattentiveness atworkoroninterview
Negative symptoms 1) Poverly of speech 2) Flattening of affect 3) Social withdrawal 4) Anhedonia 5) Avolition/apathy, involving reduced drive, energy, and interest 6) Attention deficit, manifested by inattentiveness at work or on interview

GeneralIntroductionThe Dopamine theory for SchizophreniaExcessive dopaminergic activity underlies the disorder:1. Mostblockdrugsantipsychotic stronglypostsynaptic D2 receptors in the central nervous system,especially in the mesolimbic-frontal system;2. Drugs that increase dopaminergic activity, such aslevodopa (a precursor), amphetamine (releases ofdopamine), or apomorphine (a direct dopaminereceptor agonist) aggravate schizophrenia or produce itin some patients;
Excessive dopaminergic activity underlies the disorder: 1. Most antipsychotic drugs strongly block postsynaptic D2 receptors in the central nervous system, especially in the mesolimbic-frontal system; 2. Drugs that increase dopaminergic activity, such as levodopa (a precursor), amphetamine (releases of dopamine), or apomorphine (a direct dopamine receptor agonist) aggravate schizophrenia or produce it in some patients; General Introduction The Dopamine theory for Schizophrenia

3.Dopamine receptor density has been found.postmortem, to be increased in the brains ofschizophrenics;4. Positron emission tomography (PET) has shownincreased dopamine receptor density in both treatedand untreated schizophrenics;5.Successful treatment of schizophrenic patients hasbeen reported to change the amount of homovanillicacid (HVA), a metabolite of dopamine, in thecerebrospinal fluid,plasma and urine
3.Dopamine receptor density has been found, postmortem, to be increased in the brains of schizophrenics; 4. Positron emission tomography (PET) has shown increased dopamine receptor density in both treated and untreated schizophrenics; 5.Successful treatment of schizophrenic patients has been reported to change the amount of homovanillic acid (HVA), a metabolite of dopamine, in the cerebrospinal fluid, plasma and urine

Classical antipsychotic drugs can mainly improvesymptoms, such as hallucination, delusion and thoughtdisorder but they almost have no effect on negativesymptoms, such as poverty of thinking process, apathy,will,abilityofloweredsocialde-creasedcommunication5-HT dysfunction could be involved in schizophrenia.Many effective antipsychotic drugs in addition toblocking dopamine receptors also act 5-HT, receptorantagonists. 5-HT has a modulatory effect on dopaminepathways, so the two theories are not incompatible
Classical antipsychotic drugs can mainly improve symptoms, such as hallucination, delusion and thought disorder but they almost have no effect on negative symptoms, such as poverty of thinking process, apathy, de-creased will, lowered ability of social communication. 5-HT dysfunction could be involved in schizophrenia. Many effective antipsychotic drugs in addition to blocking dopamine receptors also act 5-HT2 receptor antagonists. 5-HT has a modulatory effect on dopamine pathways, so the two theories are not incompatible

DopaminergicSystemsFive important dopaminergic system and pathways1.Mesolimbic-mesocortical pathwaywhich projects from cell bodies near nucleus substantianigra to the limbic system and neocortex.This system has connection with emotions2.Nigrostriatal pathwayIt consists of neurons that project from the substantia nigrato the caudate and putamenit is involved in the coordination of voluntary movement
Five important dopaminergic system and pathways. 1.Mesolimbic-mesocortical pathway which projects from cell bodies near nucleus substantia nigra to the limbic system and neocortex. This system has connection with emotions. 2.Nigrostriatal pathway It consists of neurons that project from the substantia nigra to the caudate and putamen. it is involved in the coordination of voluntary movement. Dopaminergic Systems

3. Tuberoinfundibular systemIt connects arcuate nuclei and periventricular neurons tothe hypothalamus and posterior pituitaryDopamine released by these neurons physiologicallyinhibits prolactin secretion4. Medullary-periventricular pathwayIt consists of neurons in the motor nucleus of the vagusThis system may be involved in eating behavior5.Incertohypothalamic pathwayIt forms connections with the hypothalamus and to thelateral septal nucleiIts functions are not yet defined
3. Tuberoinfundibular system It connects arcuate nuclei and periventricular neurons to the hypothalamus and posterior pituitary. Dopamine released by these neurons physiologically inhibits prolactin secretion. 4. Medullary-periventricular pathway It consists of neurons in the motor nucleus of the vagus. This system may be involved in eating behavior. 5.Incertohypothalamic pathway It forms connections with the hypothalamus and to the lateral septal nuclei. Its functions are not yet defined
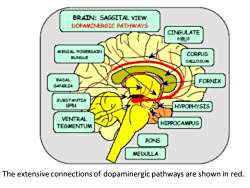
BRAIN:SAGGITALVIEWDOPAMTNERGICPATHWAYSCINGULATEYRUSMEUIALFOREBRAINCORPUSBUNDLECALLOSUMBASALFORNIXGANGLTASUBSTANTIANPRAHVPOPHYSISVENTRALHIPPOCAMPUSTEGMENTUMPONSMEDULLAThe extensive connections of dopaminergic pathways are shown in red
The extensive connections of dopaminergic pathways are shown in red

Dopamine ReceptorsFive types of dopamine receptors1.D, receptor:It coupling with adenylate cyclase, increases cAMP, isdistributed postsynapticallyIt is found mainly in putamen, nucleus accumbens andolfactory tubercle.Peripherally vascular D, receptor is located in renal.mesenteric and coronary beds. The activation of Dreceptor induces vasodilatation and the increase ofmyocardial contractility
Five types of dopamine receptors 1.D1 receptor: It coupling with adenylate cyclase, increases cAMP, is distributed postsynaptically. It is found mainly in putamen, nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Peripherally vascular D1 receptor is located in renal, mesenteric and coronary beds. The activation of D1 receptor induces vasodilatation and the increase of myocardial contractility. Dopamine Receptors
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)19 opioid analgesics and antagonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)05 the autonomic nervous system.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)10 adrenergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)06 cholinergic agonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)07 adrenergic antagonists.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Efferent Sys)12 antidepression.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十八章 抗菌药物概论.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第三十九章 β-内酰胺类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十一章 氨基苷类抗生素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十章 大环内酯类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(抗菌药物)第四十三章 人工合成类.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十四章 肾上腺皮质激素.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十三章 作用于血液及造血器官药物.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十六章 甲状腺激素和抗甲状腺药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(血液与内分泌系统药物)第三十五章 胰岛素及口服降血糖药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十五章 抗心律失常药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十三章 利尿药及脱水药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十九章 抗高血压药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十六章 治疗慢性充血性心力衰竭的药物.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(心血管系统药物)第二十七章 抗心肌缺血药.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)13 anesthesia.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)17 Antiparkin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Central Nervous Sys)12 central nervous system stimulants.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)28 Agents Used in Hyperlipidemia.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)27 treatment for CHF2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)29 treatment for angina pectoris.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)20 anti-inflammation drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)23 diuretic.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Cardiovascular Sys)25 treatment for arrthymia2.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)35 insullin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)34 adrenocortical hormones.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Endocrine Sys)36 thyroid drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43b Sulfonamides and other Synthetic Antimicrobial Drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)43a Quinolones and Urinary Tract Antiseptics.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)41 Aminoglycosides.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)42 Tetracyclines, Chloramphenicol.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)38 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)40 Macrolides, Lincomycin, Clindamycin.ppt
- 《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(Antimicrobial Drugs)39 Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis.ppt
- 《生物药剂学与药物动力学》课程教学大纲 Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics.doc
